1. 队列概念及结构
队列一种先进先出的数据结构, 先入队列的数据先出队列
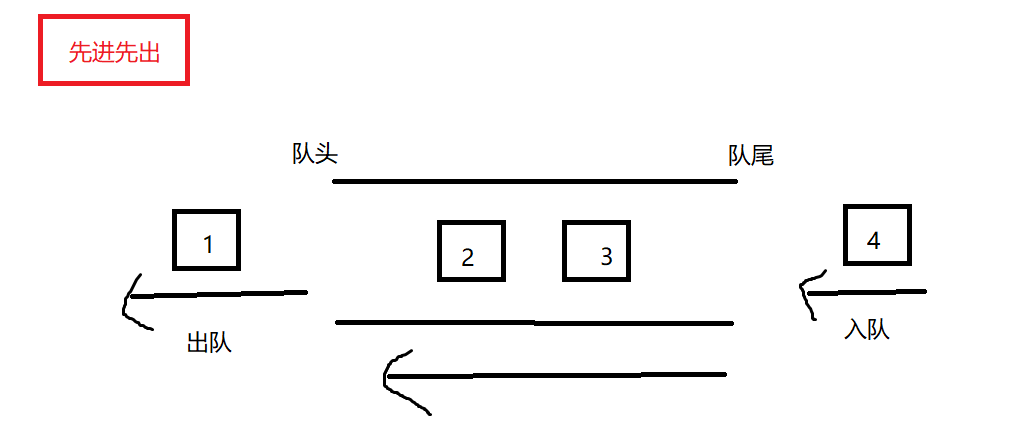
单链表能实现队列 ?
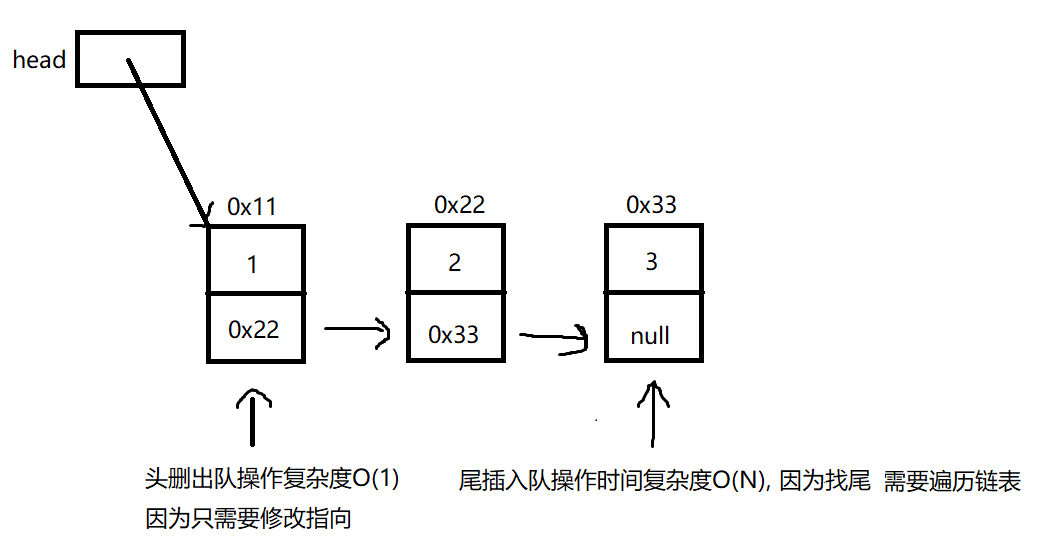
所以以原来的单链表无法用来实现队列, 如何修改 ?
只需再加个last引用指向尾,这样尾插入队操作复杂度就能达到O(1)
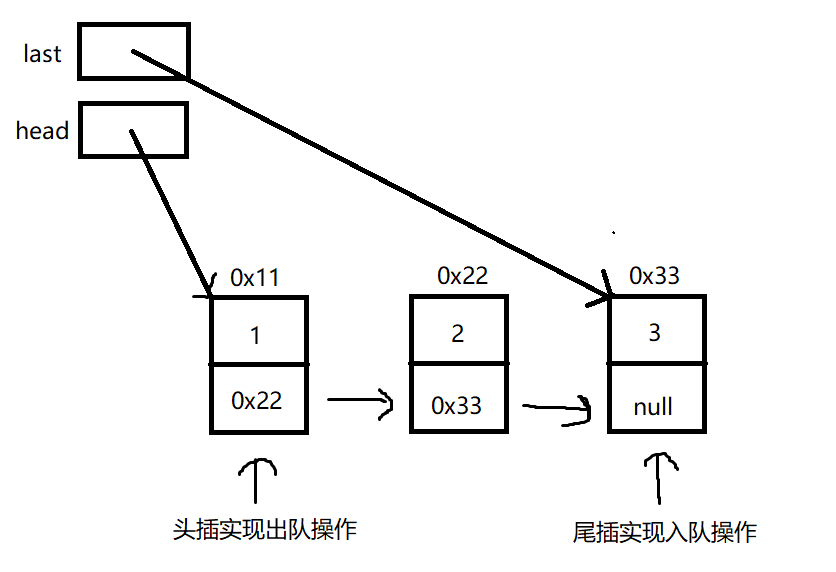
但是需要注意:
这种结构的单链表只能头插实现出队 尾插实现入队, 不能头插实现入队 尾插实现出队
因为单链表的尾删需要找到删除节点的前一个,需要遍历链表复杂度O(N)

双向链表能实现队列 ?
无论是头删出队 尾插入队,头插入队尾删出队都可以实现队列
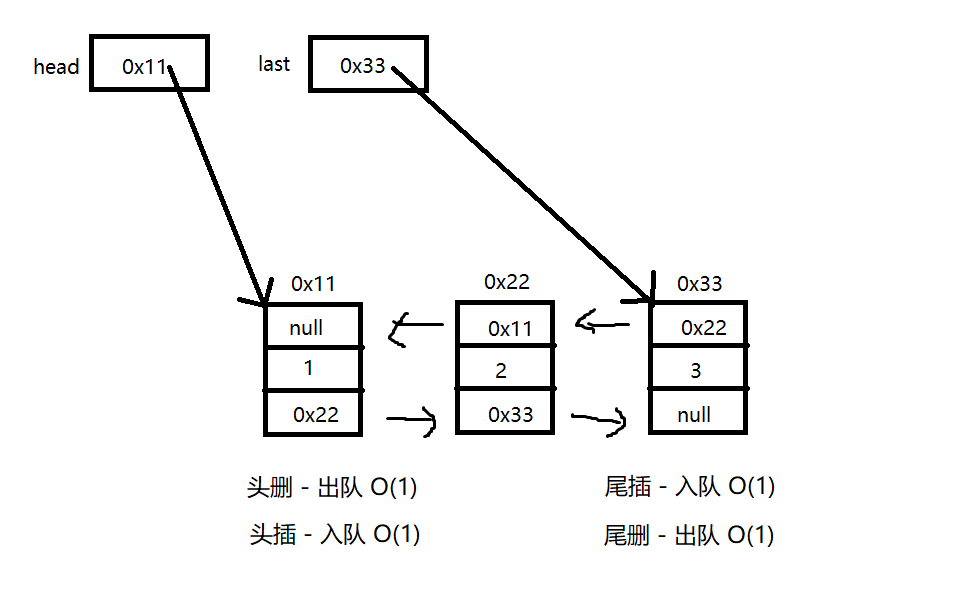
双向链表实现队列:
https://github.com/znxcmakhsd/DS/tree/main/12-20/MyQueue
2. 设计循环队列
数组是否可以用来实现队列 ?
答: 数组不仅可以用来实现普通队列还可以用来实现循环队列
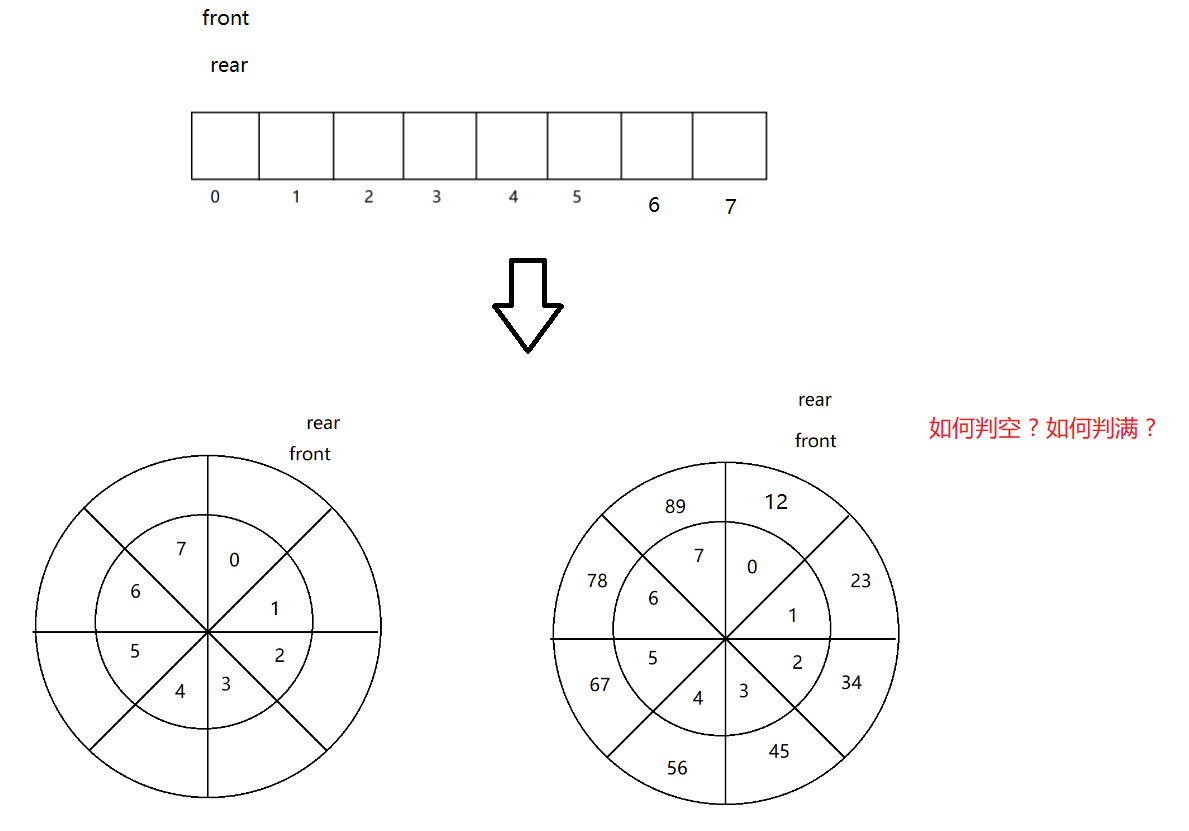

以上是解这道题的重点,关于入队出队操作可以参考下面代码
class MyCircularQueue {
private int[] elem;
private int front; // 指向队头
private int rear; // 指向队尾
// k = 有效数据 不考虑用来判空满的空间
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
this.elem = new int[k+1];
this.front = 0;
this.rear = 0;
}
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
// 满了不能入队
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
this.elem[rear] = value;
rear = (rear + 1) % elem.length;
return true;
}
public boolean deQueue() {
// 空了不能出队
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
this.front = (front + 1) % elem.length;
return true;
}
public int Front() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return this.elem[front];
}
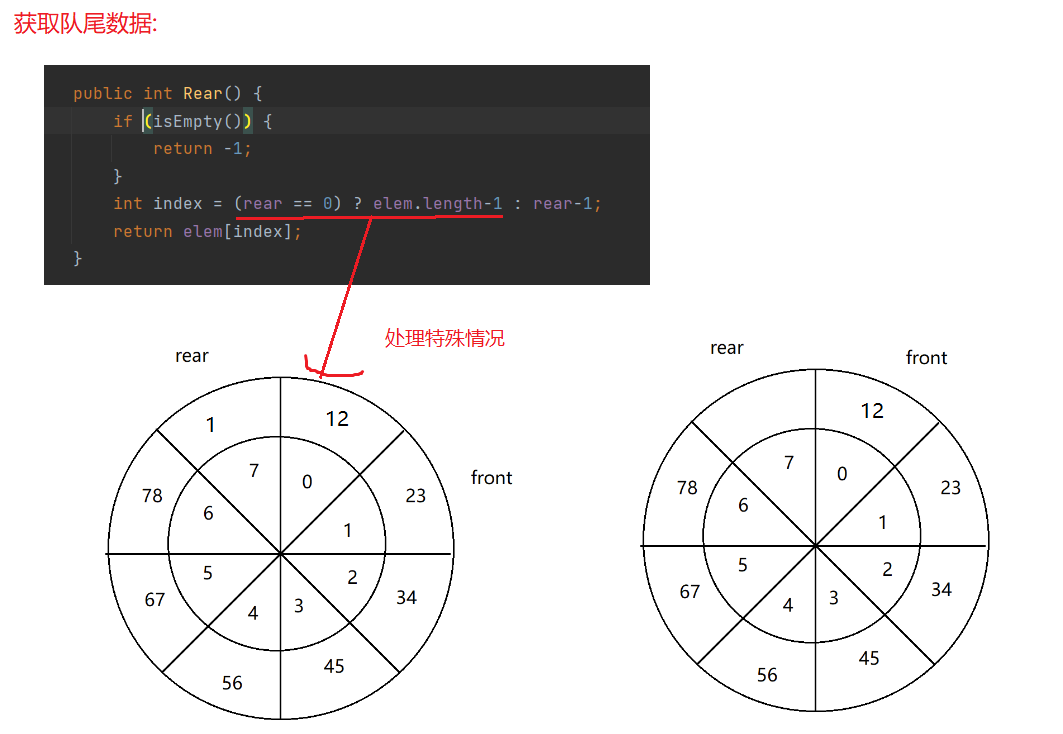
public int Rear() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
int index = (rear == 0) ? elem.length-1 : rear-1;
return elem[index];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear + 1) % elem.length == front;
}
}
/**
* Your MyCircularQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyCircularQueue obj = new MyCircularQueue(k);
* boolean param_1 = obj.enQueue(value);
* boolean param_2 = obj.deQueue();
* int param_3 = obj.Front();
* int param_4 = obj.Rear();
* boolean param_5 = obj.isEmpty();
* boolean param_6 = obj.isFull();
*/3. 用队列实现栈

// 队列实现栈
class MyStack {
public Queue<Integer> queueA;
public Queue<Integer> queueB;
public MyStack() {
queueA = new LinkedList<>();
queueB = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
// 如果两个队列都为空入QueueA
if (empty()) {
queueA.offer(x);
return;
}
// 入不为空的队列
if (!queueA.isEmpty()) {
queueA.offer(x);
}else {
queueB.offer(x);
}
}
public int pop() {
int tmp = -1;
if (!queueA.isEmpty()) {
int n = queueA.size();
for (int i = 0;i < n - 1;i++) {
queueB.offer(queueA.poll());
}
tmp = queueA.poll();
}else {
int n = queueB.size();
for (int i = 0;i < n - 1;i++) {
queueA.offer(queueB.poll());
}
tmp = queueB.poll();
}
return tmp;
}
public int top() {
int tmp = -1;
if (!queueA.isEmpty()) {
int n = queueA.size();
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++) {
tmp = queueA.poll();
queueB.offer(tmp);
}
}else {
int n = queueB.size();
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++) {
tmp = queueB.poll();
queueA.offer(tmp);
}
}
return tmp;
}
public boolean empty() {
return queueA.isEmpty() && queueB.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack obj = new MyStack();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/4. 用栈实现队列
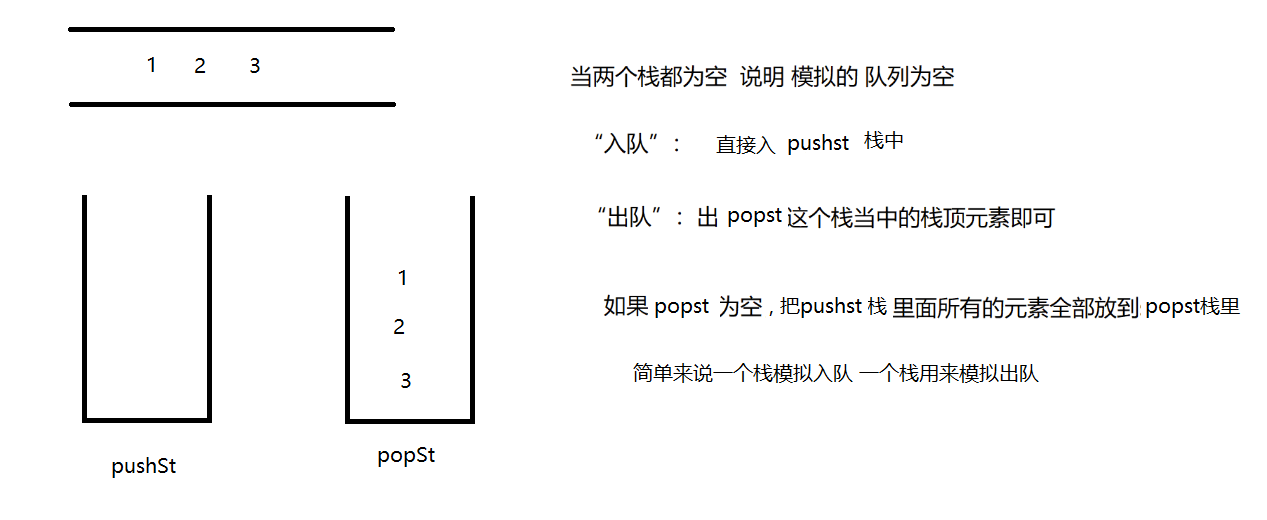
class MyQueue {
private Stack<Integer> pushst;
private Stack<Integer> popst;
public MyQueue() {
pushst = new Stack<>();
popst = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
pushst.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if (empty()) {
return -1;
}
if (popst.isEmpty()) {
while (!pushst.isEmpty()) {
popst.push(pushst.pop());
}
}
return popst.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if (empty()) {
return -1;
}
if (popst.isEmpty()) {
while (!pushst.isEmpty()) {
popst.push(pushst.pop());
}
}
return popst.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return pushst.isEmpty() && popst.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/