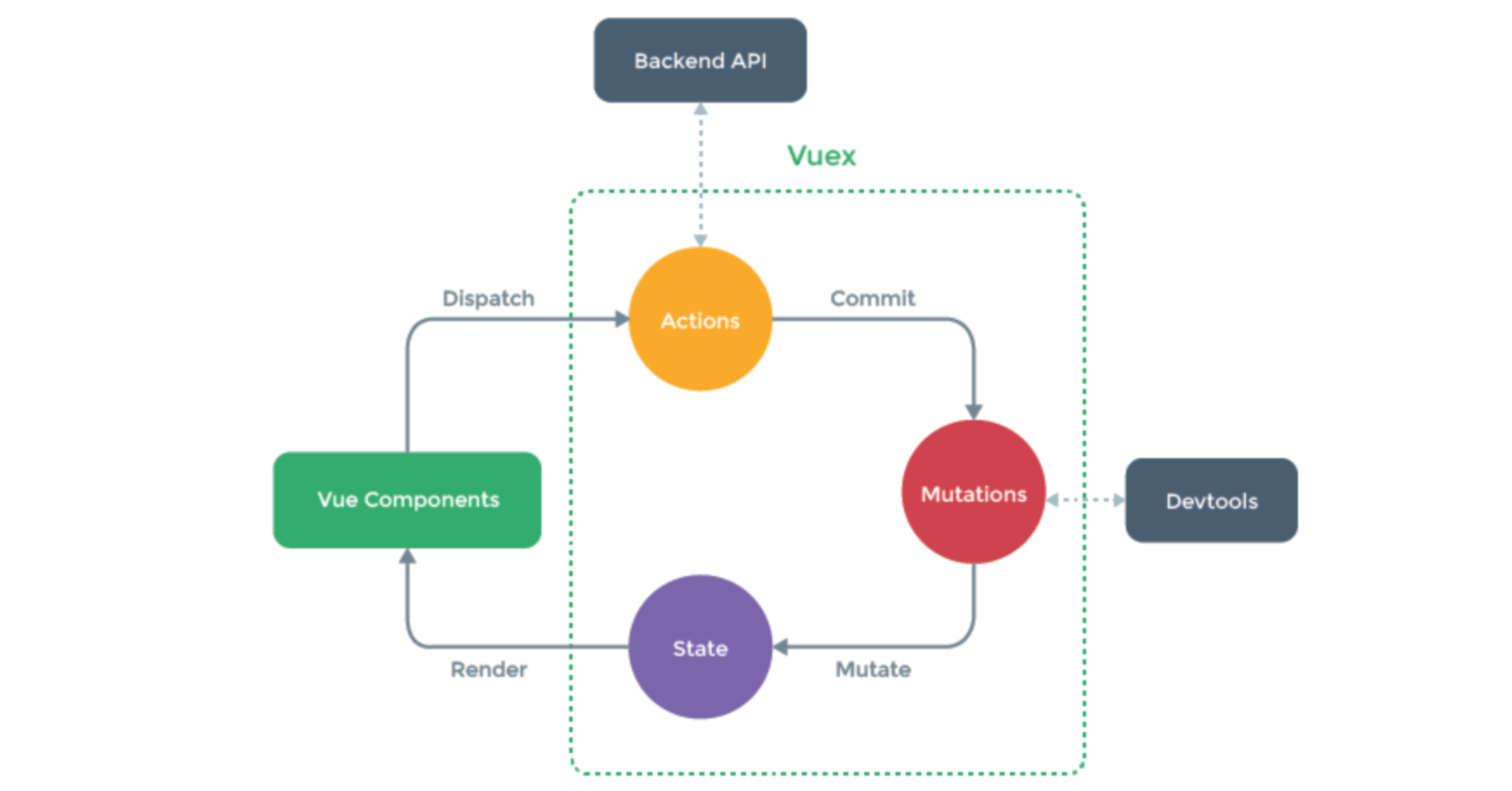
vuex
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
说人话:将组件中需要共享的数据交给vuex来帮我们进行管理,例如:用户登录状态、加入购物车。

1. 案例:登录
vue create vxdemo
npm install vue-router@3
npm install vuex@3
-
main.js
import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App.vue' import router from "./router" import store from "./store" Vue.config.productionTip = false new Vue({ router: router, store: store, render: h => h(App), }).$mount('#app') -
App.vue
<template> <div id="app"> <div class="menu"> <div class="container"> <router-link to="/home">首页</router-link> <router-link to="/course">课程</router-link> <div style="float: right"> <a v-if="this.$store.state.isLogin"> {{this.$store.state.userInfo.username}} </a> <router-link v-else to="/login">登录</router-link> </div> </div> </div> <div class="container"> <router-view></router-view> </div> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'App', data() { return {} }, components: {}, } </script> <style> body { margin: 0; } .container { width: 1100px; margin: 0 auto; } .menu { height: 48px; background-color: #499ef3; line-height: 48px; } .menu a { color: white; text-decoration: none; padding: 0 10px; } </style> -
store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex) export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { isLogin: false, //是否登录 userInfo: null //用户信息 }, mutations: { login: function (state, info) { state.userInfo = info; state.isLogin = true; }, }, actions: {} }) -
router/index.js
// router/index.js import Vue from 'vue' import VueRouter from 'vue-router' import Home from '../components/Home' import Course from '../components/Course' import Login from '../components/Login' Vue.use(VueRouter) const router = new VueRouter({ routes: [ { path: '/home', name: "Home", component: Home }, { path: '/course', name: "Course", component: Course }, { path: '/login', name: "Login", component: Login }, ] }) export default router -
components/Login.vue
<template> <div> <input type="text" v-model="info.username" placeholder="用户名"> <input type="password" v-model="info.password" placeholder="密码"> <input type="button" value="登录" @click="doLogin"/> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "Login", data() { return { info: { username: "", password: "" } } }, methods: { doLogin: function () { // 1.用户登录 this.$store.commit('login', this.info); // 2.登录成功修改状态 this.$router.push({name: 'Home'}); } } } </script> <style scoped> </style>
2. 关于computed属性
在vue的组件中有一个computed属性(计算属性),监听关联的数据,如果发生变化则重新计算并显示。
<template>
<div>
<h1>主页 {{v1}} {{ v2}}</h1>
<div>总数:{{totalData}}</div>
<input type="button" value="点我" @click="addData"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Home",
data() {
return {
v1: 123,
v2: 456
}
},
computed: {
totalData: {
get() { // 只读
let data = this.v1 + this.v2;
return data + 1000;
},
set(value) { // 设置值
this.v1 = value;
}
}
},
methods: {
addData() {
this.totalData = 999;
// this.v2 = 1000;
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
所以,上述案例也可以用computed属性来实现,例如:App.vue改成:
<template>
<div id="app">
<div class="menu">
<div class="container">
<router-link to="/home">首页</router-link>
<router-link to="/course">课程</router-link>
<div style="float: right">
<a v-if="userState">
{{userName}}
</a>
<router-link v-else to="/login">登录</router-link>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="container">
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data() {
return {}
},
computed: {
userState: {
get() {
return this.$store.state.isLogin;
}
},
// 也可以这样简写
userName() {
return this.$store.state.userInfo.username;
},
},
components: {},
}
</script>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
}
.container {
width: 1100px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.menu {
height: 48px;
background-color: #499ef3;
line-height: 48px;
}
.menu a {
color: white;
text-decoration: none;
padding: 0 10px;
}
</style>
6.3 案例:添加购物车
基于刚才的案例额外添加购物车功能

- Car.vue组件
<template>
<span>购物车的数量: {{counter}}</span>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// eslint-disable-next-line vue/multi-word-component-names
name: "Car",
computed: {
counter(){ // 绑定着store的变量
return this.$store.state.Car;
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
- Course.Vue组件
<template>
<div>
<h2>课程</h2>
<input type="button" value="添加购物车" @click="Buy">
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// eslint-disable-next-line vue/multi-word-component-names
name: "Course",
methods: {
Buy: function (){
this.$store.commit("buy")
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
- Store/index.js
import vue from 'vue'
import vuex from 'vuex'
vue.use(vuex)
export default new vuex.Store({ // 处理共享的数据, 中间商交互
state: {
isLogin: false,
UserInfo: null,
Car: 0, // 购物车数量
},
mutations: { // 调用 this.$store.commit('login', this.info) -> (函数名, info)
login: function (state, info) {
// 将用户信息保存
state.UserInfo = info;
// 修改登录状态
state.isLogin = true;
},
buy: function (state){
// 购物车数量+1
state.Car += 1;
}
},
actions: { // 如果存在一步请求要先到action提交commit -> 保持数据在异步过程中不会发生变化
}
})
6.4 关于Action
Action 类似于 mutation,不同在于:
- Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态。
- Action 可以包含任意异步操作。
代码示例:
const store = createStore({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment (state) {
state.count+=1;
}
},
actions: {
increment (context) {
// 触发mutations
context.commit('increment')
}
}
})
在组件中如果要触发,则应该执行:
this.$store.dispatch('increment')
这就有点像脱裤子放屁,意义何在呢? 当有异步操作时,应该使用action、而不是mutation,例如:
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
isLogin: false, //是否登录
userInfo: null, //用户信息
carNumber: 0,
xxxxx: 10
},
mutations: {
login: function (state, info) {
state.userInfo = info;
state.isLogin = true;
},
addCar: function (state) {
state.carNumber += 1;
},
fetchAsync: function (state) {
// ajax
setTimeout(function () {
state.xxxxx += 1;
}, 1000);
}
},
actions: {}
})
this.$store.commit("fetchAsync");
从效果上看是没有问题的,但是通过开发者工具就会发现,监测到的state的数据不准确。
所以,这种情况可以选择用Action。
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
isLogin: false, //是否登录
userInfo: null, //用户信息
carNumber: 0,
xxxxx: 10
},
mutations: {
login: function (state, info) {
state.userInfo = info;
state.isLogin = true;
},
addCar: function (state) {
state.carNumber += 1;
},
fetchAsync: function (state,data) {
state.xxxxx += 1;
console.log(data);
}
},
actions: {
fetchAsync: function (context,data) {
setTimeout(function () {
context.commit("fetchAsync",data);
}, 1000);
}
}
})
再触发时,调用:
this.$store.dispatch('fetchAsync',{ amount: 10})