| 软件工程 | 计科一班 陈倚星-3119000414 , 甫尔达吾斯.吐拉江-3119000416 |
|---|---|
| 作业要求 | 与班上同学组队完成项目 |
| 作业目的 | 提高合作与团队意识 |
| GitHub链接 | https://github.com/xingch123456789/my_app |
- PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 30 | 60 |
| Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 440 | 1000 |
| Development | 开发 | 150 | 600 |
| Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 400 | 800 |
| Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 75 | 120 |
| Design Review | 设计复审 | 80 | 100 |
| Coding Standard | 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 65 | 80 |
| Design | 具体设计 | 500 | 600 |
| Coding | 具体编码 | 420 | 500 |
| Code Review | 代码复审 | 200 | 240 |
| Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 800 | 850 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 600 | 700 |
| Test Repor | 测试报告 | 500 | 600 |
| Size Measurement | 计算工作量 | 80 | 60 |
| Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 60 | 80 |
| 合计 | 3天 | 4天 |
-
效能分析
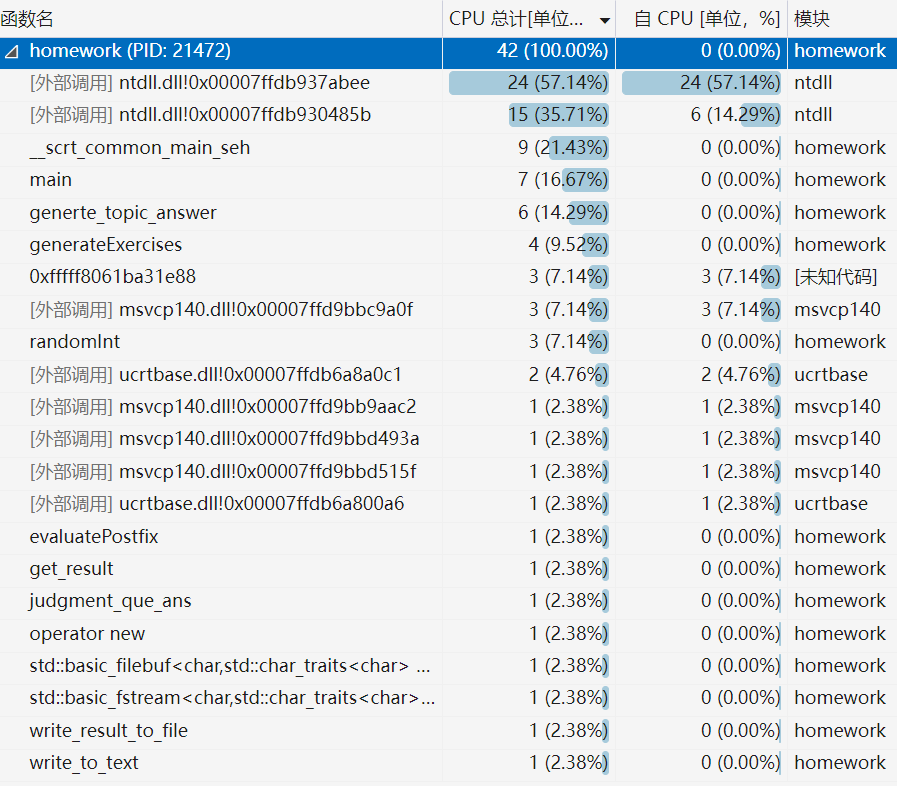
由图可知,CPU的使用大多为系统文件的外部调用所致,源文件的main和generte_topic_answer函数的CPU使用率较高,其他的函数CPU使用率都不高 -
设计实现过程
因为对C++类的使用不太熟悉,所以本次项目主要由函数实现,下面是项目的函数声明
点击查看代码
//输出min到max范围的一个整数
int randomInt(int min, int max);
//生成随机题目
std::vector<std::string> generateExercises(int num, int range);
//判断是否为运算符
bool isOperator(char c);
//获得符号的优先级
int getPrecedence(char op);
//中缀表达式转化为后缀表达式
std::string infixToPostfix(const std::string& infixExpression);
//将数组中的题目由中缀表达式转化为后缀表达式
std::vector<std::string> transform(const std::vector<std::string>& vec);
//根据不同符号计算结果
double performOperation(double operand1, double operand2, char op);
//计算后缀表达式
double evaluatePostfix(const std::string& postfixExpression);
//计算结果
std::vector<double> get_result(const std::vector<std::string>& vec);
//将题目写入文件,把文件名当参数传入
void write_to_text(const std::vector<std::string>& vec, std::string file_name);
//把结果写入文件,把文件名当参数传入
void write_result_to_file(const std::vector<double>& vec, std::string file_name);
//读取文件中的内容,并存入字符串数组中
std::vector<std::string> get_file_to_string(const std::string str);
//把string转化为double
std::vector<double>string_to_double(std::vector<std::string>v);
//通过判断两个数组是否相等,把相等下标存到correct数组中,其余的存到wrong数组中
void compareArrays(const std::vector<double>& array1, const std::vector<double>& array2, std::vector<int>& correct, std::vector<int>& wrong);
//把correct和wrong的内容存到Grade.txt中
void writeResultToFile(const std::vector<int>& correct, const std::vector<int>& wrong, std::string file_name);
//封装函数,随机生成题目,并把题目和答案分别输出到Exercises.txt,Answers.txt文件中
//参数num代表生成题目数量,range代表范围,即多大数字以内的运算,字符串exercises,answer分别代表两个文件名
void generte_topic_answer(int num, int range, const std::string exercises, const std::string answer);
//封装函数,输入question.txt,answer.txt就直接判断答案是否正确,并把内容输出到Grade.txt中
void judgment_que_ans(const std::string question, const std::string answer);
其中最为重要的是随机生成题目的函数和计算生成题目的函数实现,下面是两个函数的流程图
1.随机生成题目函数流程图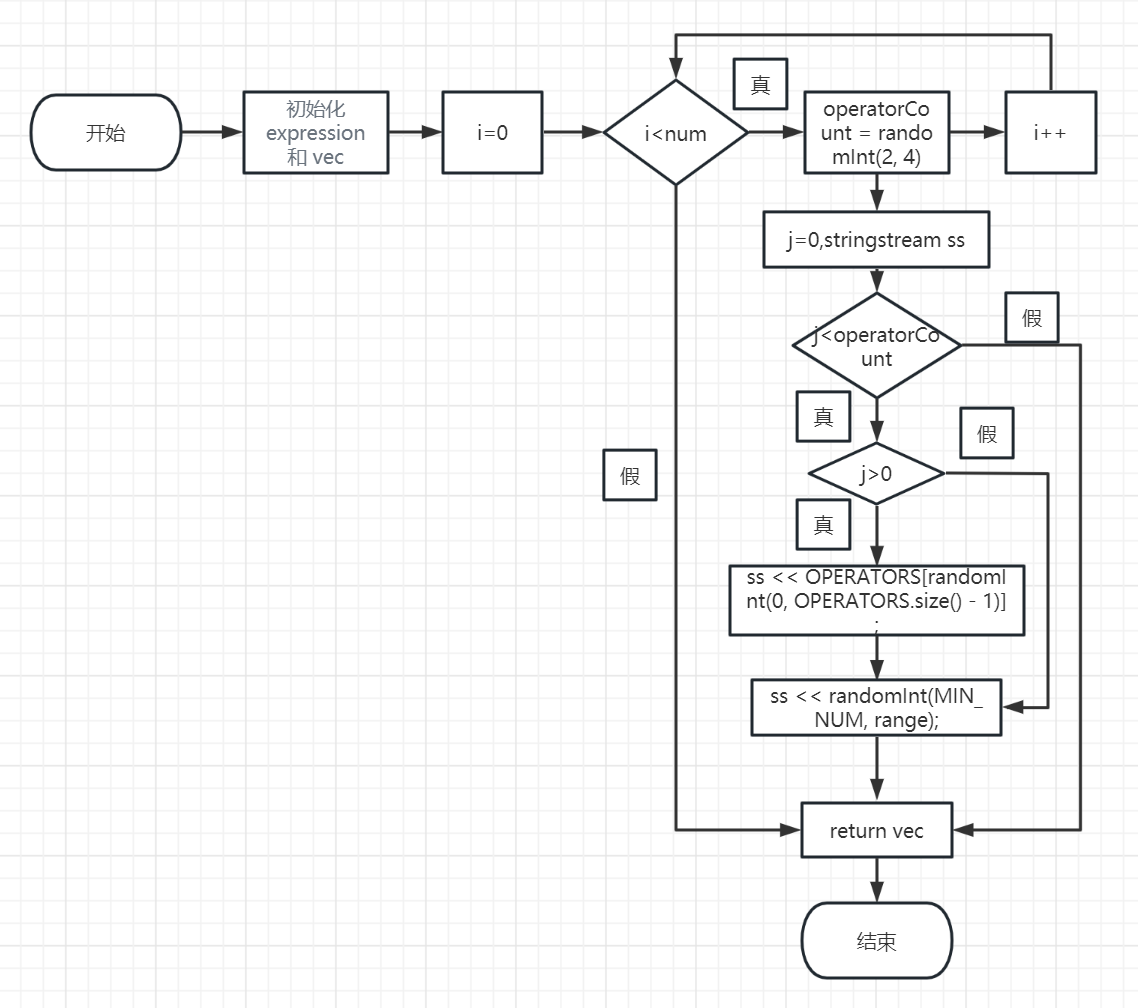
2.计算生成题目函数流程图
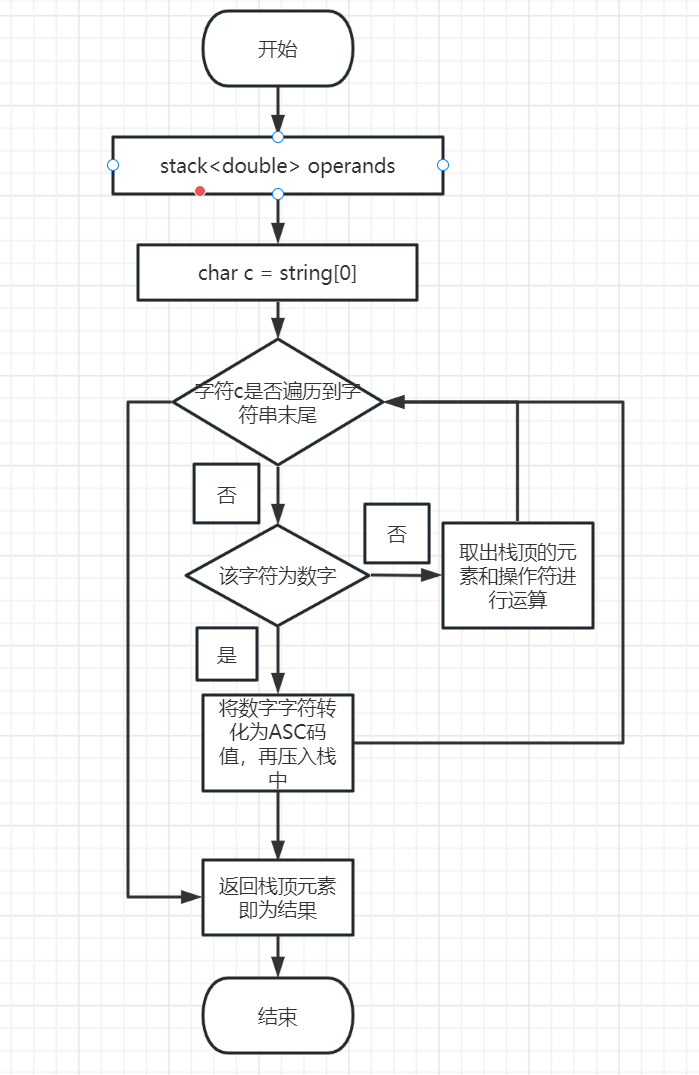
- 代码说明
1.输出min到max范围的一个整数
点击查看代码
int randomInt(int min, int max) {
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 gen(rd());
std::uniform_int_distribution<> dis(min, max);
return dis(gen);
}
2.生成随机题目
点击查看代码
std::vector<std::string> generateExercises(int num, int range) {//num控制生成题目的数量,range控制数字的大小
std::string expression;
std::vector<std::string>vec;
//vec.reserve(num);
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
// 随机生成算术表达式
std::stringstream ss;
int operatorCount = randomInt(2, 4);//控制运算符的数量不超过3个
for (int j = 0; j < operatorCount; j++) {
if (j > 0) {//保证第一个字符不是操作符
ss << OPERATORS[randomInt(0, OPERATORS.size() - 1)];
}
ss << randomInt(MIN_NUM, range);
}
expression = ss.str();
vec.push_back(expression);
// std::cout << expression << std::endl;
}
//std::cout << expression << std::endl;
return vec;
}
3.中缀表达式转化为后缀表达式
点击查看代码
std::string infixToPostfix(const std::string& infixExpression) {
std::stack<char> operators;//暂存string中的操作符,用于优先级的判断
std::string postfixExpression;//存放转化后的结果
for (char c : infixExpression) {
if (c == ' ') {
continue;
}
if (isdigit(c)) {//如果是数字就直接加入string中
postfixExpression += c;
}
else if (isOperator(c)) {
//符号优先级高的先操作
while (!operators.empty() && operators.top() != '(' && getPrecedence(operators.top()) >= getPrecedence(c)) {
postfixExpression += operators.top();
operators.pop();
}
operators.push(c);
}
}
//如果string已经遍历完了,存放操作符的栈还有元素,就直接加到string中
while (!operators.empty()) {
postfixExpression += operators.top();
operators.pop();
}
return postfixExpression;
}
4.计算后缀表达式
点击查看代码
double evaluatePostfix(const std::string& postfixExpression) {
std::stack<double> operands;
for (char c : postfixExpression) {
if (isdigit(c)) {
operands.push(c - '0');//将字符转化为数字
}
else if (isOperator(c)) {
double operand2 = operands.top();
operands.pop();
double operand1 = operands.top();
operands.pop();
double result = performOperation(operand1, operand2, c);
operands.push(result);
}
}
return operands.top();
}
5.封装函数,随机生成题目,并把题目和答案分别输出到Exercises.txt,Answers.txt文件中
参数num代表生成题目数量,range代表范围,即多大数字以内的运算,字符串exercises,answer分别代表两个文件名
点击查看代码
void generte_topic_answer(int num, int range, const std::string exercises, const std::string answer)
{
std::vector<std::string> v;
v = generateExercises(num, range);//生成num多个题目
std::vector<std::string>v1 = transform(v);//由中缀转化为后缀
std::vector<double>v2 = get_result(v1);//得到算出的结果
write_to_text(v, exercises);//写入文件Exercises.txt
write_result_to_file(v2, answer);//写入文件Answers.txt
}
6.封装函数,输入question.txt,answer.txt就直接判断答案是否正确,并把内容输出到Grade.txt中
点击查看代码
void judgment_que_ans(const std::string question, const std::string answer)
{
//首先将两个文件里的内容读取到字符串数组中
std::vector<std::string>v = get_file_to_string(question);
std::vector<std::string>v3 = get_file_to_string(answer);
std::vector<std::string>v1 = transform(v);//由中缀转化为后缀
std::vector<double>v2 = get_result(v1);//得到算出的结果
std::vector<double>v4 = string_to_double(v3);//answer.txt的内容,转化为double
std::vector<int> correct;
std::vector<int> wrong;
compareArrays(v2, v4, correct, wrong);
writeResultToFile(correct, wrong, "Grade.txt");//结果输出到Grade.txt
}
- 测试运行
测试是我手动编写的,一共5个,代码如下,结果看注释
点击查看代码
#include"my_app.h"
//question.txt的内容为3+5+1, 5 * 3 - 1,9 / 9 + 1,5 * 4,3 + 2
void test1()
{
judgment_que_ans("question.txt", "answer.txt");//answer.txt的内容为9,14,2,20,1
}
void test2()
{
judgment_que_ans("question.txt", "answer.txt");//answer.txt的内容为9,10,2,20,1
}
void test3()
{
judgment_que_ans("question.txt", "answer.txt");//answer.txt的内容为9,14,20,2,1
}
void test4()
{
judgment_que_ans("question.txt", "answer.txt");//answer.txt的内容为5,14,2,20,2
}
void test5()
{
judgment_que_ans("question.txt", "answer.txt");//answer.txt的内容为5,14,20,20,1
}
int main()
{
test1();//此时Grade.txt的内容为Correct: 5 (0, 1, 2, 3, 4),Wrong: 0 ()
test2();//此时Grade.txt的内容为Correct: 5 (0, 2, 3, 4),Wrong: 0 (1)
test3();//此时Grade.txt的内容为Correct: 5 (0, 1, 4),Wrong: 0 (2, 3)
test4();//此时Grade.txt的内容为Correct: 5 (1, 2, 3),Wrong: 0 (0, 4)
test5();//此时Grade.txt的内容为Correct: 5 (1, 3, 4),Wrong: 0 (0, 2)
return 0;
}
- 项目小结
难点:再做项目的过程中,我们也遇到了许多困难,首先是对于真分数的处理,我们做出了随机生成真分数的代码如下
点击查看代码
//输出随机真分数
std::string randomFraction(int min, int max) {
int numerator = randomInt(min, max);
int denominator = randomInt(min, max);
int integer = numerator / denominator;
//std::cout << numerator << " " << denominator << std::endl;
//numerator %= denominator;
std::stringstream ss;
if (integer > 0) {
numerator %= denominator;
if (numerator == 0)ss << integer;//分子分母相等
else ss << integer << "'"<< numerator << "/" << denominator;
}
else ss << numerator << "/" << denominator;
return ss.str();
}
好的建议:在计算题目是,我一开始想得是从头到尾按顺序计算的,然后发现这样做有很大的问题,然后他建议对符号进行优先级判定,优先级高的先算。在数据结构的选择上,我们尝试了vector,queue,stack,set,map,最后发现还是stack最好。
最后总结一下,做这个项目我们遇到了很多困难,但我们没有被困难阻拦,在克服后收获了满满的满足感,也丰富了我们的编程经历,提高了我们的团队合作能力,是一次美好的作业体验