Problem: Climate Warming
Overview: According to data from the National Climate Center, China's annual average temperature has shown a significant upward trend since 1951, with a warming rate of 0.26 ℃/10 years, which is higher than the global average level (0.15 ℃/10 years) during the same period. It is a sensitive area for global climate change.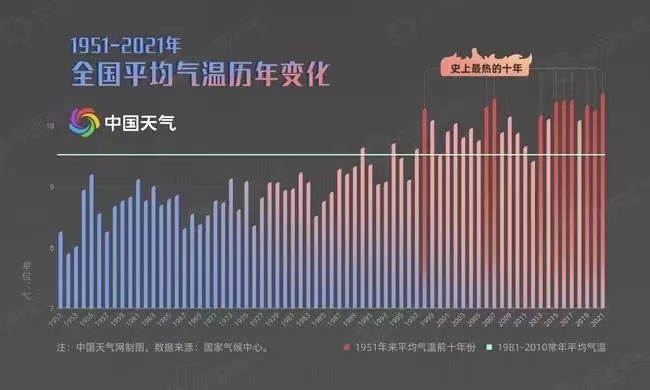
2012-2021 was the warmest decade in history in the past 70 years. Among the top ten years with the highest average temperature in the country, 7 occurred in the 10 years since 2012, with 2021 being the hottest year on meteorological records.

Reasons:
1. Greenhouse gas emissions: With the continuous increase of industrial and transportation activities, China's greenhouse gas emissions continue to increase, leading to a continuous increase in the concentration of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane in the atmosphere, thereby increasing the temperature of the Earth.
2. Population growth and urbanization: The increase in China's population and the acceleration of urbanization have led to increased energy consumption, reduced water resources, and land consumption, further exacerbating the impact of climate change.
3. Natural factors: Climate change in China is also related to natural factors, such as changes in the global climate system caused by global warming, changes in the Asian monsoon and the Qinghai Tibet Plateau.
4. Air pollution: China's air pollution problem will also have an impact on climate change. For example, particulate matter and other pollutants can absorb solar radiation and alter the temperature distribution on the Earth's surface, while pollutants can also mix with water vapor such as clouds and mist to form more cloud droplets, thereby affecting the reflection of solar radiation.
Consequences: With the intensification of climate warming, the average temperature in China will continue to rise in the future, extreme heat waves will become more frequent, heavy precipitation and induced floods will increase, sea levels will further rise, and more floods will occur in coastal areas; The reduction of cold waves and frost events does not mean that they will not occur; Reduced snow cover and river/lake ice, retreat of glaciers in the western region, and continued degradation of permafrost in the western region. The intensity of extreme weather and climate events in the future will become stronger, and the probability of composite and concurrent extreme events will also increase, especially the concurrent events of heat waves and droughts, as well as the composite flood events caused by the combination of extreme sea level events and heavy precipitation, mainly characterized by storm surges, ocean giant waves, and tidal floods, will be more common. Based on future climate change trends and differences in vulnerability and exposure in different regions, it can be seen that eastern China is a high-risk area for extreme rainfall from Northeast to South China. This area is also a gathering area for population and economy, and developed areas in the eastern region will bear higher climate risks; The central region from North China to South China, as well as the northwest, is a high-risk area for high-temperature heatwaves; North China, the Loess Plateau, the eastern, northwestern, and southwestern regions of the Qinghai Tibet Plateau are high-risk areas for drought; Southwest, South China, the agricultural and pastoral ecotone of the Loess Plateau, and the Songnen Plain are areas where natural ecosystems bear high risks; The southwest of South China, the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, and the northwest oases are areas where grain production bears high risks.