http请求概述
- 浏览器输入一个地址后,进行DNS解析(通过域名查找对应的IP地址),与server建立TCP连接(进行三次握手),发送http请求
- server接收到http请求,处理,并返回
- 客户端(这里指浏览器)接收到返回数据,处理数据(如渲染页面,执行js)
客户端与服务器的三次握手大致可以理解为:
第一次握手:客户端询问服务器是否可以使用;
第二次握手:服务器告诉服务器自己可以使用;
第三次握手:客户端再次告诉服务器:收到回应,即将访问本服务器
简单创建server
创建文件express-koa-learning => index.js
// 通过require获取nodejs原生提供的http模块
const http = require("http");
// 使用http.createServe() 方法创建Web服务器,返回一个Server 的实例对象。
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.end("hello world");
});
// 监听本地端口
server.listen(8000);
// 然后浏览器访问 http://localhost:8000
在控制台输入命令 node index.js,然后浏览器访问 http://localhost:8000
代码中createServer有2个参数,req就是客户端发送给server的请求信息request,res就是服务器给客户端返回的响应数据response。
处理get请求
- get请求,即客户端要向server端获取数据,如查询博客列表
- 通过querystring来传递数据,如a.html?a=100&b=200
- 浏览器直接访问,就发送get请求
前面提到req是客户端发送给server的请求信息,我们可以从req中获取到客户端请求的url。
我们可以借助querystring将url中的请求参数转为js中的对象,方便我们使用。
// 通过require获取nodejs原生提供的http模块
const http = require("http");
// 通过require获取nodejs原生提供的querystring模块
const querystring = require("querystring");
// 使用http.createServe() 方法创建Web 服务器, 返回一个Server 的实例对象。
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
console.log('method',req.method); // 获取请求的方法 输出:GET
const url = req.url; // 获取请求的完整url
console.log('url',req.url)
req.query = querystring.parse(url.split("?")[1]); // 解析querystring
console.log('query',req.query)
// req就是客户端发送过来的东西,res就是服务器给客户端返回的东西
// res.end("hello world");
res.end(JSON.stringify(req.query)); // 将querystring返回
});
// 监听本地端口
server.listen(8000);
// 然后浏览器访问 http://localhost:8000
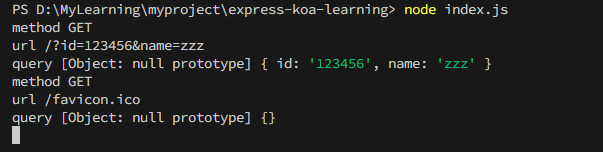
PS:每次修改代码后都需要重新执行命令:node index.js,在浏览器输入http://localhost:8000/?id=123456&name=zzz
可以看到控制台结果以及浏览器的页面显示了server返回的数据{"id":"123456","name":"zzz"}
处理post请求
- post请求,即客户端要像服务端传递数据,如新建博客
- 通过post data传递数据
- 浏览器无法直接模拟,需要手写js,或者使用postman
const http = require("http");
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
if (req.method == "POST") {
// 数据格式
console.log("content-type", req.headers["content-type"]);
// 接收数据
let postData = "";
req.on("data", (chunk) => {
postData += chunk.toString();
});
req.on("end", () => {
console.log(postData);
res.end("hello world"); // 在这里返回,因为是异步
});
}
});
server.listen(8000);
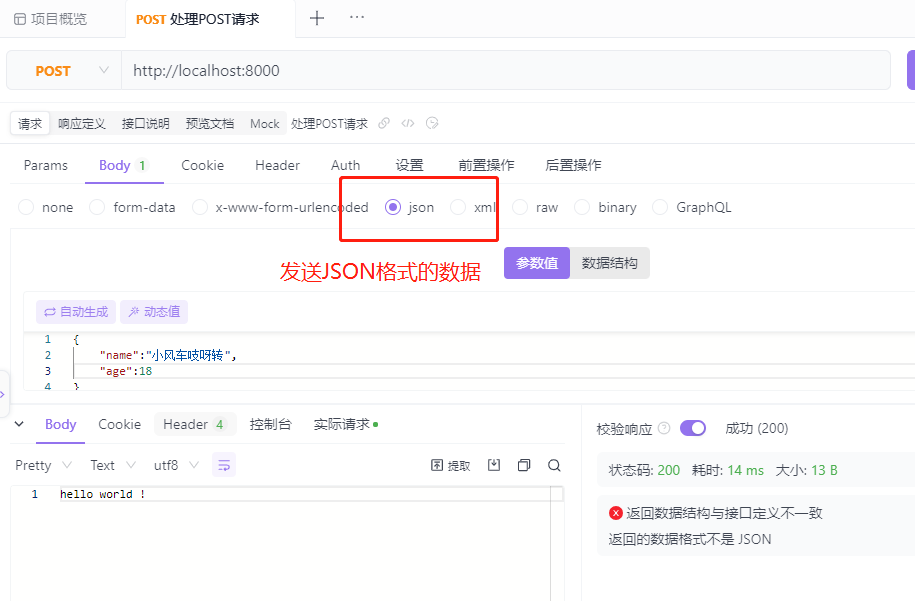
运行服务端,打开Postman或者Apifox进行POST请求。
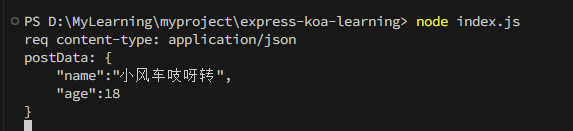
处理http请求的综合实例
const http = require("http");
const querystring = require("querystring");
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
const method = req.method; //获取请求方法
const url = req.url; //获取请求路由
const path = url.split("?")[0];
const query = querystring.parse(url.split("?")[1]);//解析路由
// 设置返回数据的格式为 JSON
res.setHeader("Content-type", "application/json");
// 返回的数据
const resData = {
method,
url,
path,
query,
};
// 返回
if (method === "GET") {
res.end(JSON.stringify(resData)); // res.end只能返回二进制或者字符串
}
if (method === "POST") {
let postData = "";
req.on("data", (chunk) => {
postData += chunk.toString();
});
req.on("end", () => {
resData.postData = postData;
res.end(JSON.stringify(resData)); // res.end只能返回二进制或者字符串
});
}
});
// 监听本地端口
server.listen(8000);
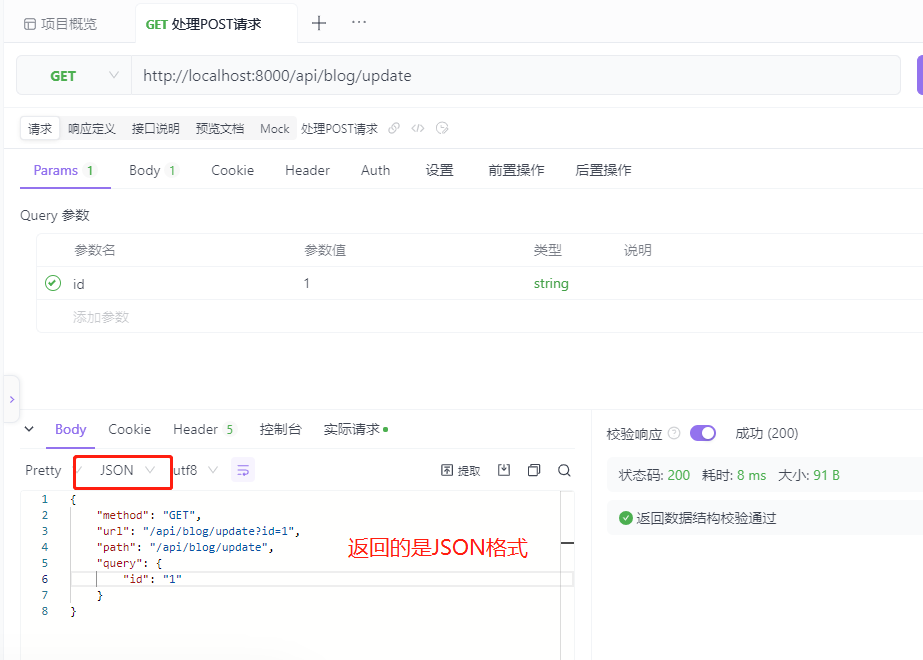
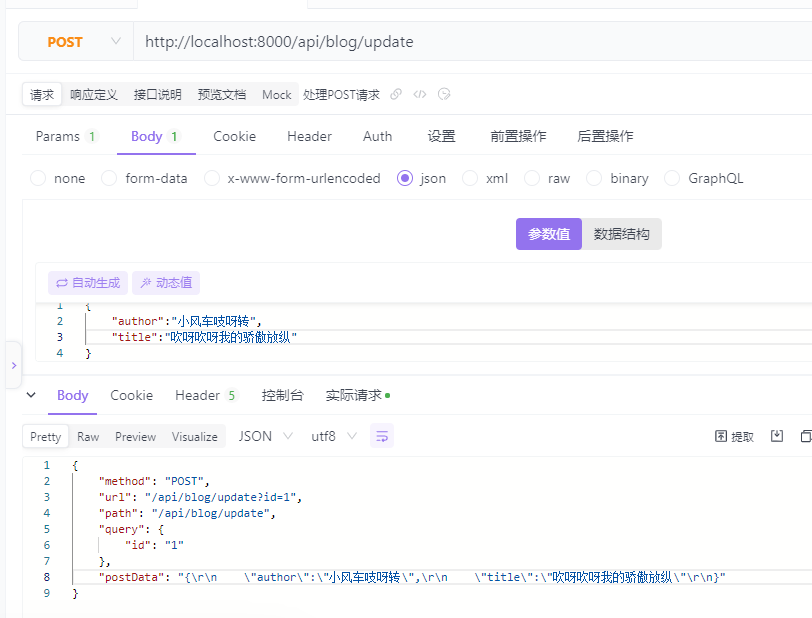
运行服务端,打开Postman或者Apifox进行HTTP请求,返回客户端向服务器发送的请求数据,例如请求方法、请求路由等。
请求GET接口:http://localhost:8000/api/blog/update?id=1