Flash Programming
Flash Programming Algorithms are a piece of software to erase or download applications to Flash devices. A Pack with Device Support usually contains predefined Flash algorithms for programming the devices that are supported by the DFP. A template for creating new algorithms are available in the ARM:CMSIS Pack. The following section describes the process in more detail.
Creating a new Algorithm
Flash programming algorithms are defined with functions to erase and program the Flash device. Special compiler and linker settings are required. Follow these steps to create and configure a new Flash programming algorithm:
- Copy the content from the ARM:CMSIS Pack folder (usually C:\Keil\ARM\Pack\ARM\CMSIS*version*\Device_Template_Flash) to a new folder.
- Rename the project file NewDevice.uvprojx to represent the new Flash ROM device name, for example MyDevice.uvprojx.
- Open the project with uVision. From the toolbar, use the drop-down Select Target to define the processor architecture. Cortex-M fits for all Cortex-M0/M0+, M3, and M4 devices. The configuration assumes a little-endian microcontroller. In case of a big-endian microcontroller, select the correct processor core with Project - Options for Target - Device.
- Open the dialog Project - Options for Target - Output and change the content of the field Name of Executable to represent the device, for example MyDevice.
- Adapt the programming algorithms in the file FlashPrg.
- Adapt the device parameters in the file FlashDev.
- Use Project - Build Target to generate the new Flash programming algorithm. The output file (for example MyDevice.FLM) has to be added to the DFP.
-
Note
Creating a Flash programming algorithm with MDK-Lite is not supported.Flash programming algorithms use Read-Only Position Independent and Read-Write Position Independent program code. These options are set in the dialogs Project - Options for Target - C/C++ and Project - Options for Target - Asm.The dialog Project - Options for Target - Linker defines the linker scatter file Target.lin. The error L6305 is disabled with
–diag_suppressL6305.The Flash Algorithm Functions section contains reference for all the available functions.
FlashPrg.c
The file FlashPrg.c contains the mandatory Flash programming functions Init, UnInit, EraseSector, and ProgramPage. Optionally, depending on the device features (or to speed-up execution), the functions EraseChip, BlankCheck, and Verify can be implemented.
FlashDev.c
The file FlashDev.c contains parameter definitions for:
-
the Flash programming functions.
-
the FlashDevice structure:
struct FlashDevice const FlashDevice = { FLASH_DRV_VERS, // Driver Version, do not modify! "New Device 256kB Flash", // Device Name ONCHIP, // Device Type 0x00000000, // Device Start Address 0x00040000, // Device Size in Bytes (256kB) 1024, // Programming Page Size 0, // Reserved, must be 0 0xFF, // Initial Content of Erased Memory 100, // Program Page Timeout 100 mSec 3000, // Erase Sector Timeout 3000 mSec // Specify Size and Address of Sectors 0x002000, 0x000000, // Sector Size 8kB (8 Sectors) 0x010000, 0x010000, // Sector Size 64kB (2 Sectors) 0x002000, 0x030000, // Sector Size 8kB (8 Sectors) SECTOR_END };
-
Note
The Device Name is usually be shown in tools to identify the Flash algorithm. Make sure that this name reflects the device name.
The Programming Page Size specifies the block size for programming using the function ProgramPage. For devices with small block sizes it might be better to specify a multiple of the physical block size as this reduces the communication overhead to the target. An optimal block size for fast programming is 1024 bytes, however the system itself does not restrict this size value.
Adding an Algorithm to a Pack
The generated *.FLM file needs to be added to the Pack with Device Support, so that it is available to the tool user for programming his device. Usually, a directory Flash is created and the algorithm is saved in this directory.
The algorithm is specified within the the /package/devices/family level:
<family Dfamily="STM32F4" Dvendor="STMicroelectronics:13">
...
<algorithm name="Flash/STM32F2xx_512.flm" start=0x08000000 size=0x10000 default="1"/> <!-- valid for all devices of the family -->
<subFamily DsubFamily="STM32F405">
<algorithm name="Flash/STM32F2xx_1024.flm" start=0x08000000 size=0x20000 default="1"/> <!-- valid for all devices of a subFamily -->
<device Dname="STM32F405OE">
<algorithm name="Flash/STM32F2xx_2048.flm" start=0x08000000 size=0x40000 default="1"/> <!-- finally, this is the default for the device -->
</device>
...
</family>
The argument start specifies the base address for the Flash programming algorithm.
The argument size specifies the size covered by the Flash programming algorithm. End address = start + size - 1.
The argument default specifies whether a Flash programming algorithm is set as the default algorithm in a project (when true). If default is not set or false, the Flash programming algorithm can be configured on a lower level. However, the Flash programming algorithm of a project can be changed manually at any time during development.
Algorithm Functions
Blank Check
The following functions are available for creating new Flash programming algorithms:
| Function Name | Indication | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BlankCheck | optional | Check and compare patterns. |
| EraseChip | optional | Delete entire Flash memory content. |
| EraseSector | mandatory | Delete Flash memory content of a specific sector. |
| Init | mandatory | Initialize and prepare device for Flash programming. |
| ProgramPage | mandatory | Write the application into the Flash memory. |
| UnInit | mandatory | De-initialize the microcontroller after one of the Flash programming steps. |
| Verify | optional | Compare Flash memory content with the program code. |
The following diagrams show how the functions of the Flash Programming Algorithms are executed by a development tool.
The Flash Erase sequence is executed to erase the Flash content.
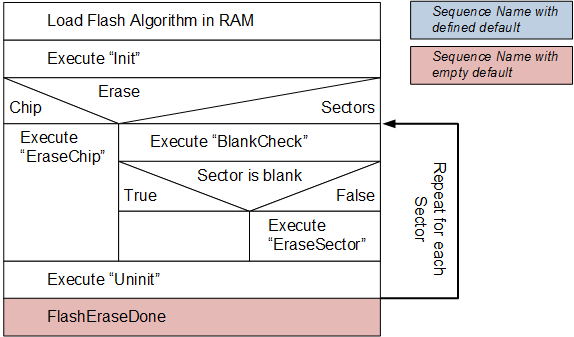
Flash Erase
The Flash Program sequence is executed to program the Flash memory.
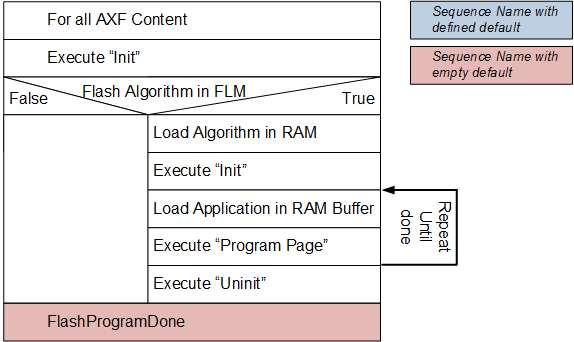
Flash Program
The Flash Verify sequence is executed to verify the content after flash programming.
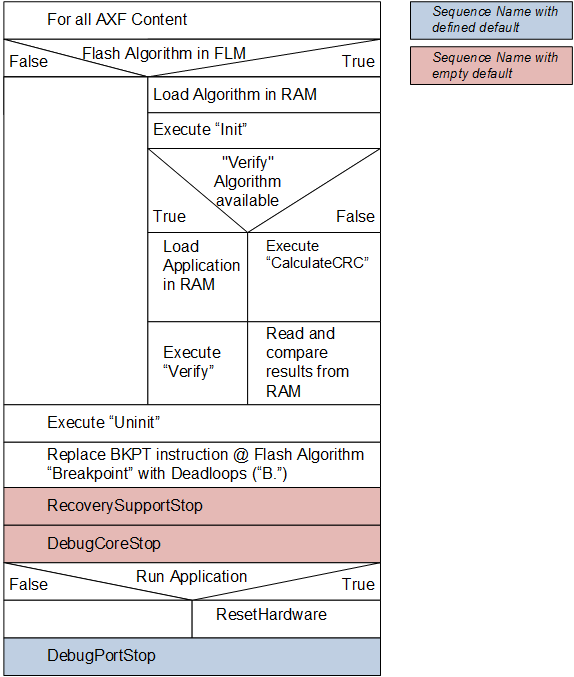
Flash Verify
BlankCheck
int BlankCheck (unsigned long adr, unsigned long sz, unsigned char pat);
-
Parameters
adrBlock start addressszBlock size in bytespatPattern to compare
-
Returns
status information:0 when the block content is equal to the pattern pat.1 when the block content differs from the pattern pat.
The function BlankCheck can be used to check whether the specified block is empty, or whether the content is equal to a specific pattern defined in the argument pat.
The argument adr specifies the start address of the block that is to be verified.
The argument sz specifies the size of the block that is to be verified.
Code Example
int BlankCheck (unsigned long adr, unsigned long sz, unsigned char pat) {
unsigned long i, j, k;
// Recalculate address for External SDRAM addresses
if (adr >= SDRAM_START)
adr = adr - SDRAM_START + USER_OFFSET;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i += 256) {
// Read 256 bytes
ReadPage_HW (adr+i, 256, &rd_buf[0]);
// Determine size to compare
if ((sz-i) >= 256) k = 256;
else k = (sz-i);
// Check up to 256 bytes if equal to pattern "pat"
for (j = 0; j < k; j++)
if (rd_buf[j] != pat) return (1); // Memory is not blank
}
return (0); // Memory is blank
}
EraseChip
int EraseChip (void);
-
Returns
status information:0 on success.1 on failure.
The function EraseChip deletes the content of the entire Flash memory. It is invoked whenever the uVision menu Flash - Erase is used, or whenever an attempt is made to download the program to Flash and the option Erase Full Chip has been set in the Flash Download Setup dialog. If this function is missing in the Flash Programming Algorithm, the EraseSector function is executed until the entire content of the Flash memory area has been deleted.
Code Example
int EraseChip (void) {
FLASH->CR |= FLASH_MER; // Mass Erase Enabled
FLASH->CR |= FLASH_STRT; // Start Erase
while (FLASH->SR & FLASH_BSY) {
IWDG->KR = 0xAAAA; // Reload IWDG
}
FLASH->CR &= ~FLASH_MER; // Mass Erase Disabled
return (0); // Done
}
EraseSector
int EraseSector (unsigned long adr);
-
Parameters
adrSector address
-
Returns
status information:0 on success.1 on failure.
The function EraseSector deletes the content of the sector starting at the address specified by the argument adr. The function is invoked whenever the uVision menu Flash - Erase is used, or whenever an attempt is made to download the program to Flash and the option Erase Sectors has been set in the Flash Download Setup dialog.
Code Example
int EraseSector (unsigned long adr) {
FLASH->CR |= FLASH_PER; // Page Erase Enabled
FLASH->AR = adr; // Page Address
FLASH->CR |= FLASH_STRT; // Start Erase
while (FLASH->SR & FLASH_BSY) {
IWDG->KR = 0xAAAA; // Reload IWDG
}
FLASH->CR &= ~FLASH_PER; // Page Erase Disabled
return (0); // Done
}
Init
int Init (unsigned long adr, unsigned long clk, unsigned long fnc);
-
Parameters
adrDevice base addressclkClock frequency (Hz)fncFunction code
-
Returns
status information:0 on success.1 on failure.
The function Init initializes the microcontroller for Flash programming. It is invoked whenever an attempt is made to download the program to Flash.
The argument adr specifies the base address of the device.
The argument clk specifies the clock frequency for prgramming the device.
The argument fnc is a number:
- 1 stands for Erase.
- 2 stands for Program.
- 3 stands for Verify.
Thus, different initialization sections can be implemented for each individual Flash programming step.
Code Example
int Init (unsigned long adr, unsigned long clk, unsigned long fnc) {
// Zero Wait State
FLASH->ACR = 0x00000000;
// Unlock Flash
FLASH->KEYR = FLASH_KEY1;
FLASH->KEYR = FLASH_KEY2;
// Test if IWDG is running (IWDG in HW mode)
if ((FLASH->OBR & 0x04) == 0x00) {
// Set IWDG time out to ~32.768 second
IWDG->KR = 0x5555; // Enable write access to IWDG_PR and IWDG_RLR
IWDG->PR = 0x06; // Set prescaler to 256
IWDG->RLR = 4095; // Set reload value to 4095
}
return (0);
}
ProgramPage
int ProgramPage (unsigned long adr, unsigned long sz, unsigned char *buf);
-
Parameters
adrPage start addressszPage sizebufData to be written
-
Returns
status information:0 on success.1 on failure.
The function ProgramPage is used to write code into the Flash memory. It is invoked to download a program to Flash. As Flash memory is typically organized in blocks or pages, the parameters to the function ProgramPage must not cross alignment boundaries of these flash pages. The page size is specified in the struct FlashDevice with the value Program Page Size.
The argument adr specifies the start address of the page that is to be programmed. It is aligned by the host programming system to a start address of a flash page.
The argument sz specifies the data size in the data buffer. The host programming system ensures that page boundaries are not crossed.
The argument buf points to the data buffer containing the data to be programmed.
-
Note
The host programming system ensures that the argument adr + sz never crosses any page boundary. The function ProgramPage does therefore not require any provisions for that.
Code Example
int ProgramPage (unsigned long adr, unsigned long sz, unsigned char *buf) {
sz = (sz + 1) & ~1; // Adjust size for Half Words
while (sz) {
FLASH->CR |= FLASH_PG; // Programming Enabled
M16(adr) = *((unsigned short *)buf); // Program Half Word
while (FLASH->SR & FLASH_BSY);
FLASH->CR &= ~FLASH_PG; // Programming Disabled
// Check for Errors
if (FLASH->SR & (FLASH_PGERR | FLASH_WRPRTERR)) {
FLASH->SR |= FLASH_PGERR | FLASH_WRPRTERR;
return (1); // Failed
}
// Go to next Half Word
adr += 2;
buf += 2;
sz -= 2;
}
return (0); // Done
}
UnInit
int UnInit (unsigned long fnc);
-
Parameters
fncFunction code
-
Returns
status information:0 on success.1 on failure.
The function UnInit de-initializes the microcontroller and is invoked at the end of an erasing, programming, or verifying step.
The argument fnc is a number:
- 1 stands for Erase.
- 2 stands for Program.
- 3 stands for Verify.
Thus, different de-initialization sections can be implemented for each individual Flash programming step.
Code Example
int UnInit (unsigned long fnc) {
// Lock Flash
FLASH->CR |= FLASH_LOCK;
return (0);
}
Verify
unsigned long Verify (unsigned long adr, unsigned long sz, unsigned char *buf);
-
Parameters
adrStart addressszSize in bytesbufData to be compared
-
Returns
status information:the sum of (adr+sz) - on success.any other number - on failure, and represents the failing address.
The function Verify compares the content of the Flash memory with the program code **buf*.
The argument adr specifies the start address for the verification.
The argument sz specifies the size of the verification.
The argument buf points to the buffer containing the data to be verified.
Code Example
unsigned long Verify (unsigned long adr, unsigned long sz, unsigned char *buf) {
unsigned long i, adr_dest, in_page_ofs;
if (adr < block_size) { // Verifying 2-nd level bootloader data
adr_dest = adr + page_usr_size; // skip page 0 of block 0
} else { // Verifying program data
FindBlock(adr, 0);
adr_dest = nand_block_offset + (adr & (block_size-1));
}
in_page_ofs = adr_dest & (page_usr_size-1);
if (ReadPage_HW(adr_dest, page_usr_size, data_buf)) return (1);
for (i=0; i<sz; i++)
if (buf[i] != data_buf[i+in_page_ofs])
break;
return (adr+i);
}