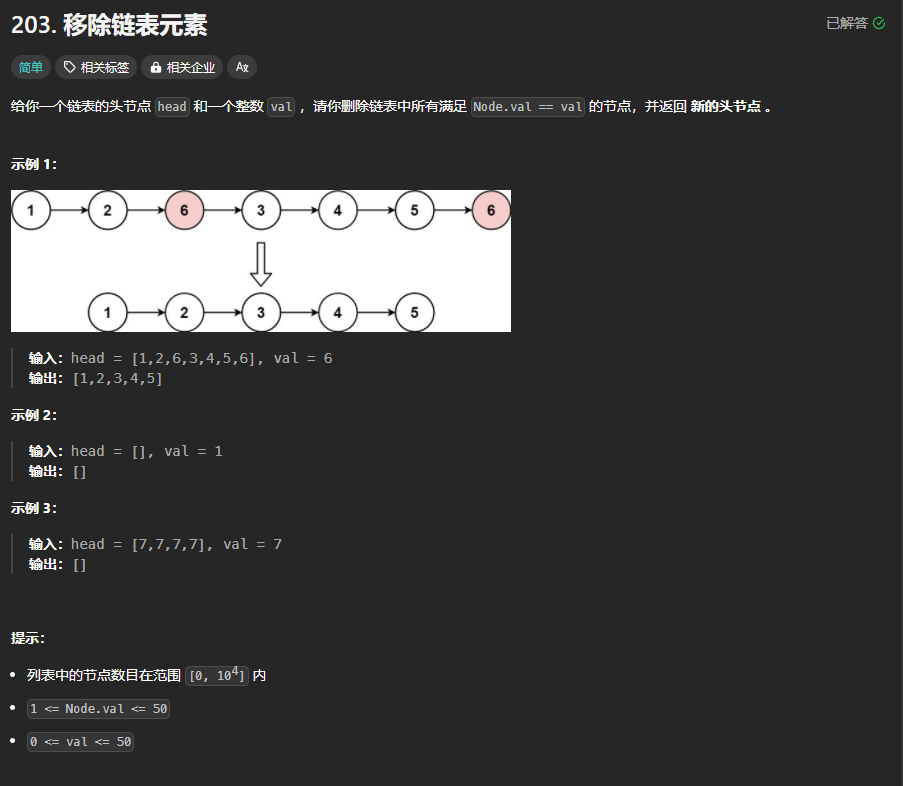
203.移除链表元素
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
//先删头节点
while(head != nullptr && head->val == val)
head = head->next;
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur != nullptr && cur->next != nullptr)
{
if(cur->next->val == val)
cur->next = cur->next->next;
else //这里else是为了保证,比如1 2 2 1,删完第一个2,如果直接后移cur,就不会判断第二个2了
cur = cur->next;
}
return head;
}
};
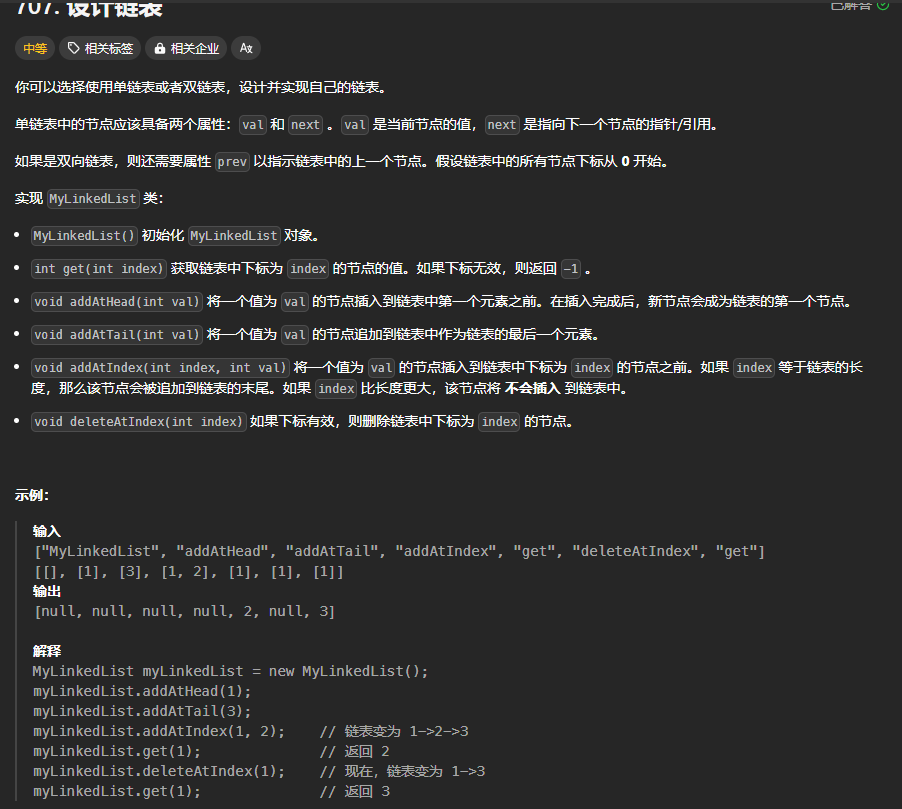
707. 设计链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/design-linked-list/
class MyLinkedList {
public:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *next;
Node() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
Node(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
Node(int x, Node *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
Node *dummyhead;
int size; //size表示链表一共有几个元素,所以最大索引是size-1
MyLinkedList() {
dummyhead = new Node();
size = 0;
}
int get(int index) {
if(index < 0 || index >= size) //保证一定可以获取到正确的索引位置的val
return -1;
Node* cur = dummyhead->next; //cur从头节点开始,遍历index次
while(index--)
cur = cur->next;
return cur->val;
}
void addAtHead(int val) {
Node* node = new Node(val);
node->next = dummyhead->next;
dummyhead->next = node;
size++;
}
void addAtTail(int val) {
Node* node = new Node(val);
Node* cur = dummyhead;
while(cur->next != nullptr) //跑到尾,现在的cur就是最后一个节点
cur = cur->next;
cur->next = node;
size++;
}
void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if(index > size) //为什么没等号,比如一共三节点,在索引3前加就是尾插的意思,至于负数统统看成头插
return;
Node* node = new Node(val);
Node* cur = dummyhead; //需要锁定index索引的前一个,因为要求插入第index个的前一个
while(index--)
cur = cur->next;
node->next = cur->next;
cur->next = node;
size++;
}
void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if(index < 0 || index >= size) //保证一定可以找到正确的索引位置的val
return;
Node* cur = dummyhead; //保证找到index-1索引处的值
while(index--)
cur = cur->next;
Node* del = cur->next;
cur->next = del->next;
delete del;
size--;
}
};
/**
* Your MyLinkedList object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyLinkedList* obj = new MyLinkedList();
* int param_1 = obj->get(index);
* obj->addAtHead(val);
* obj->addAtTail(val);
* obj->addAtIndex(index,val);
* obj->deleteAtIndex(index);
*/
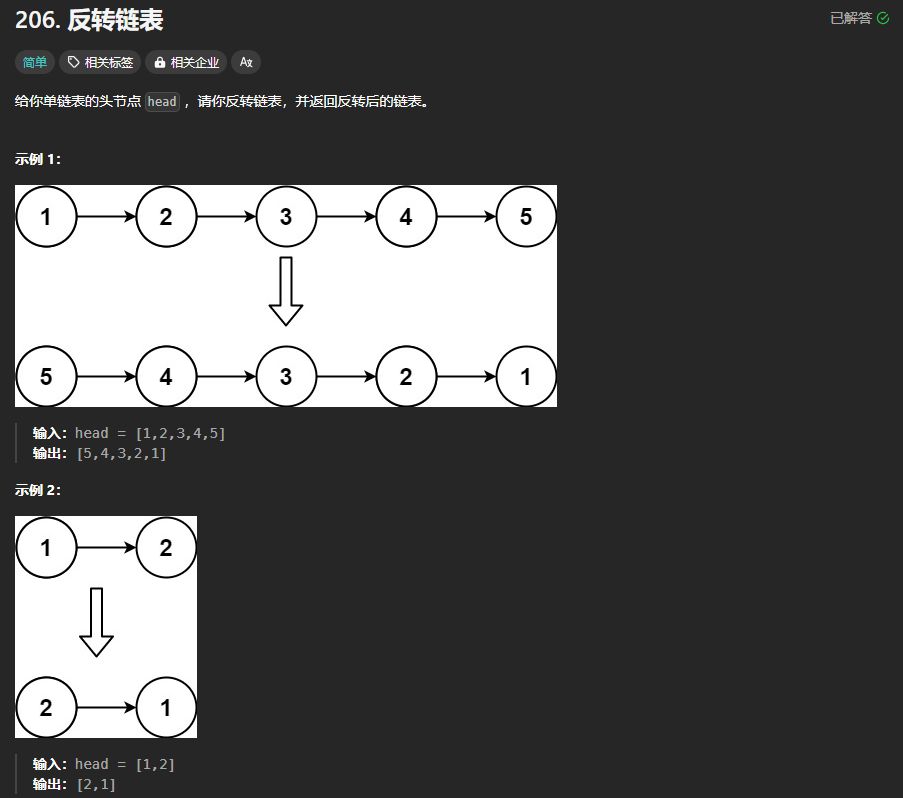
206.翻转链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return head;
//思路 用temp记录当前的后面所有节点,即temp->next = remain,现在temp和cur都指向了remain,
//就可以断掉cur->next,让cur指向它前面的那个,也就是cur->next = pre; 接下来,temp cur pre都后移一个,继续操作。
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
ListNode* cur = head;
//ListNode* temp = cur;
ListNode* temp = cur->next;
while(cur != nullptr)
{
// cur->next = pre; //这一步实际上改变了原链表的结构,所以temp->next也找不到了!!!!
// pre = cur;
// cur = temp->next;
// temp = cur;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
if(temp != nullptr)
temp = cur->next;
}
return pre;
}
};
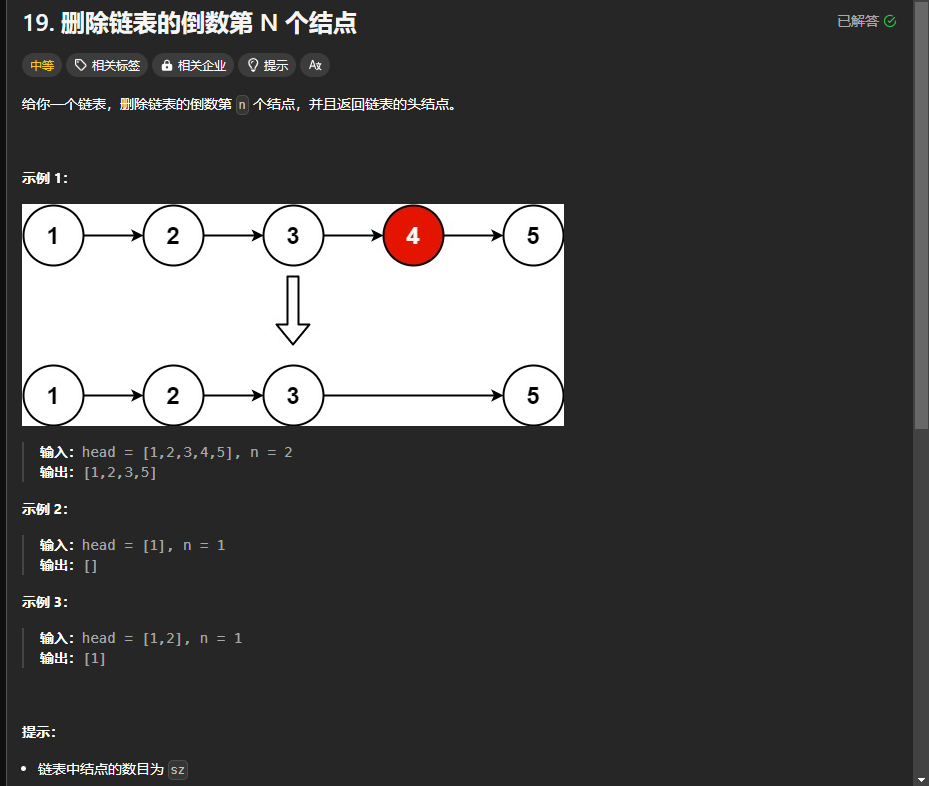
19.删除链表的倒数第N个节点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
//好妙的双指针,移动快指针直至快慢差n,一起移动,快指针到结尾了,说明该删除慢指针了
//这里需要推算一下,当fast是倒一了,比如要删除倒3,实际上他们之间只隔了1!但是为了方便删除,需要找到倒4操作!!!
ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode();
dummyhead->next = head;
ListNode* slow = dummyhead;
ListNode* fast = dummyhead;
//令fast等于第n-1索引的位置
//题目已经说了n的范围合法!!不用判断!!
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
fast = fast->next;
//现在slow和fast隔了n-1个,只要fast移到最后,slow的位置就是要删除的前一个,让这个的next跳过下一个即可
while(fast->next!=nullptr)
{
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
ListNode* del = slow->next;
slow->next = slow->next->next;
delete del;
return dummyhead->next;
}
};
24.两两交换链表中的节点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/description/
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return head;
ListNode* cur = new ListNode();
cur->next = head;
ListNode* res = cur;
while(cur->next!=nullptr && cur->next->next!=nullptr)
{
ListNode* tmp1 = cur->next;
ListNode* tmp2 = cur->next->next;
// cur->next = tmp2;
// tmp2->next = tmp1;
//这样写会导致死循环。第一行表示剔除tmp1,第二行表示tmp2指向tmp1,而tmp1又指向tmp2,它应该指向tmp2下一个
cur->next = tmp2;
tmp1->next = tmp2->next;
tmp2->next = tmp1;
cur = cur->next->next; //实际上就是tmp2->next,也是tmp1->next
}
return res->next;
}
};
链表相交
https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci/description/

class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
//k神的解法,A全部+B公共以前 = B全部+A公共以前
ListNode* A = headA;
ListNode* B = headB;
while(A!=B)
{
//相当于if(A!=nullptr) A = A->next; else A = headB
A = A != nullptr? A->next : headB;
B = B != nullptr? B->next : headA;
}
return A;
}
};
142.环形链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
//fast一次走两步,slow一次走一步,他们在环内相遇,如果到末尾还没相遇就是没有环,
// fast - slow = nb, fast = 2*slow ==> slow = nb, fast = 2nb!!!
// 一步一步地走,必然可以停留在入口处,slow = nb 想办法让他再走a步,就可以找到入口!
// 相遇后,fast回到起点,一次走一步走a步,slow跟着走a步,二者再次相恰好是环入口
/*重点:① 二者第一次相遇 slow = nb
② 不管一次几步,只要走了a + mb步一定停在入口处,只是一次两步可能永远找不到m!(b = 4 a = 3 a+mb必然是奇数)
*/
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
//while(fast != slow) //不要这样写,,因为初始的时候俩都是head,根本不会进入循环。。。。
while(true)
{
if(fast == nullptr || fast->next == nullptr) //这里顺序也有讲究的。。如果输入一个空链表,访问fast->next是错误的
return nullptr;
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if(fast == slow)
break;
}
fast = head;
while(slow != fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return fast;
}
};