rie字典树
也称前缀树prefix tree
什么是Trie字典树
- 也称字典树Digital Tree;前缀树Prefix Tree
- Trie是一个多叉树,通常只用来处理字符串
- 前面几章我们一直在用的都是二叉树
Trie与字典在字符串查找中的性能比较
trie添加和查询字符串只与字符串的长度有关,与有多少个字符串无关
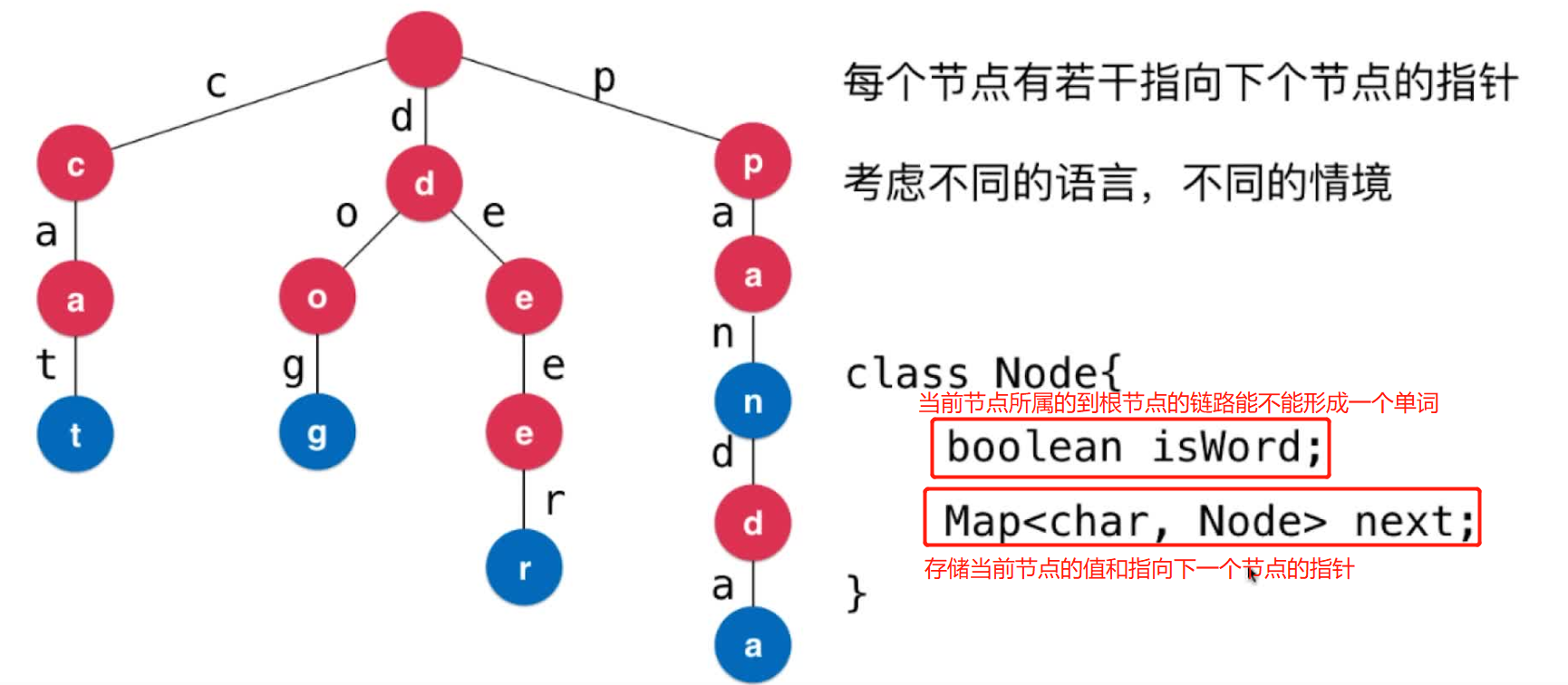
Trie的结构
注意根节点不存储任何字符
Trie的基础结构、添加单词、单词查询、前缀查询
基础结构
基础节点表示和构造方法,
TreeMap<Character, Node> children的某个点的所有子节点,Map是为了快速查询字符与节点的对应关系,好好理解下~~
public class Trie {
class Node {
boolean isWord; // 当前节点所属的到根节点的链路能不能形成一个单词
TreeMap<Character, Node> children; // 当前节点的所有子节点,是一对多的关系,故需要map来存储;此外存Map可以实现快速根据键值选中符合条件的子节点,因此此处必须用Map
Node() {
children = new TreeMap<>();
}
}
private Node root; // 整个Trie树的根节点
private int size; // Trie树种有多少个单词
public Trie() {
root = new Node();
size = 0;
}
/**
* Trie树中有多少个单词
*/
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
}
添加单词:遍历单词的每个字符,刷新Trie树
/**
* 向Trie中添加一个新的单词word
*/
public void add(String word) {
Node cur = root; // 开始从根节点开始
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char c = word.charAt(i);
if (cur.children.get(c) == null) cur.children.put(c, new Node()); // 当在当前节点指向的孩子节点中不存在要插入的字符c的时候。为null表示不存在,把字符串作为新的Trie节点插入
cur = cur.children.get(c); // cur节点往后移动一位,这里用map的作用就体现出来了,可以快速找到当前字符c处在哪个子节点上
}
if (cur.isWord) return; // 先判断这个单词是不是以前就存在
cur.isWord = true; // 插入单词后,把这个单词插入后的末尾节点标记为是单词
size++; // 单词数+1
}
单词查询:查询单词是否在Trie树种存在
/**
* 查询单词word是否在Trie树中
*/
public boolean contains(String word) {
Node cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char c = word.charAt(i);
if (cur.children.get(c) == null) return false; // 当前节点的子节点是否包含字符c,不包含则肯定不包含单词word了,直接返回即可
cur = cur.children.get(c); // 循环到下一个点
}
return cur.isWord; // 到达字符串的最后一个字符,即使有这个单词,但是isWord不为True也表明没有被标记过。不算包含这个单词
}
前缀查询:判断某个字符串是否是Trie树种某个单词的前缀
/**
* 判断某个字符串prefix是否是Trie树种某个单词的前缀(即某个单词以这个字符串开始)
*/
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
Node cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) {
char c = prefix.charAt(i);
if (cur.children.get(c) == null) return false; // 当前节点的子节点是否包含字符c,不包含则肯定不包含前缀prefix了,直接返回即可
cur = cur.children.get(c); // 循环到下一个点
}
return true; // 只要找到这个前缀,就可认为包含这个前缀的单词是存在地,不需要判断前缀到达的位置是否是单词
}
测试代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.add("cat");
trie.add("category");
trie.add("hello");
trie.add("world");
System.out.println(trie.contains("cat")); // true
System.out.println(trie.contains("wor")); // false
System.out.println(trie.startsWith("wor")); // true
}
LeetCode上相关问题:LeetCode208号问题
Trie支持正则表达式
核心逻辑如下:
/**
* 查询单词是否在Trie树中
*
* @param word 要查询的单词,支持正则表达式
* @return 是否包含指定单词
*/
public boolean contains(String word) {
return match(root, word, 0);
}
/**
* 从node开始作为根节点检索word在Trie中是否存在
*
* @param node 本次递归开始检索的节点
* @param word 单词或者正则
* @param index 本次递归检索到了word的第index个字符
* @return 是否在Trie中匹配到word对应的模式
*/
private boolean match(Node node, String word, int index) {
// 1.递归终止条件
if (index == word.length()) {
// word已经检索到最后一个字符,直接返回其在Trie中的状态即可
return node.isWord;
}
// 2.递归逻辑
char c = word.charAt(index);
if (c != '.') {
// 2.1不是正则匹配,用普通的单词匹配即可
if (node.next.get(c) == null) {
// 在当前递归的Trie树中找不到c字符(同时也没有下一个node了,我们的map实际是起到记录当前节点值和下一个节点的指针地作用),则匹配失败(前面层的递归都匹配上了)
return false;
} else {
return match(node.next.get(c), word, index + 1);
}
}else {
// 2.2 c==. 需要遍历node的所有相邻节点,继续向下递归
for (Character cNext : node.next.keySet()) {
if (match(node.next.get(cNext), word, index+1)){
// 任何一个邻接点向下递归找到了匹配就可以返回true
return true;
}
}
// 所有的邻接点往下递归都没找到匹配,才返回false
return false;
}
}
6 带权重的Trie树
每个Node节点加一个weight属性,每次加入节点都要更新权重,每个单词都有自己的权重,多个前缀相同单词的相同前缀要把多个单词的权重加起来
7 更多Trie相关的话题
删除操作
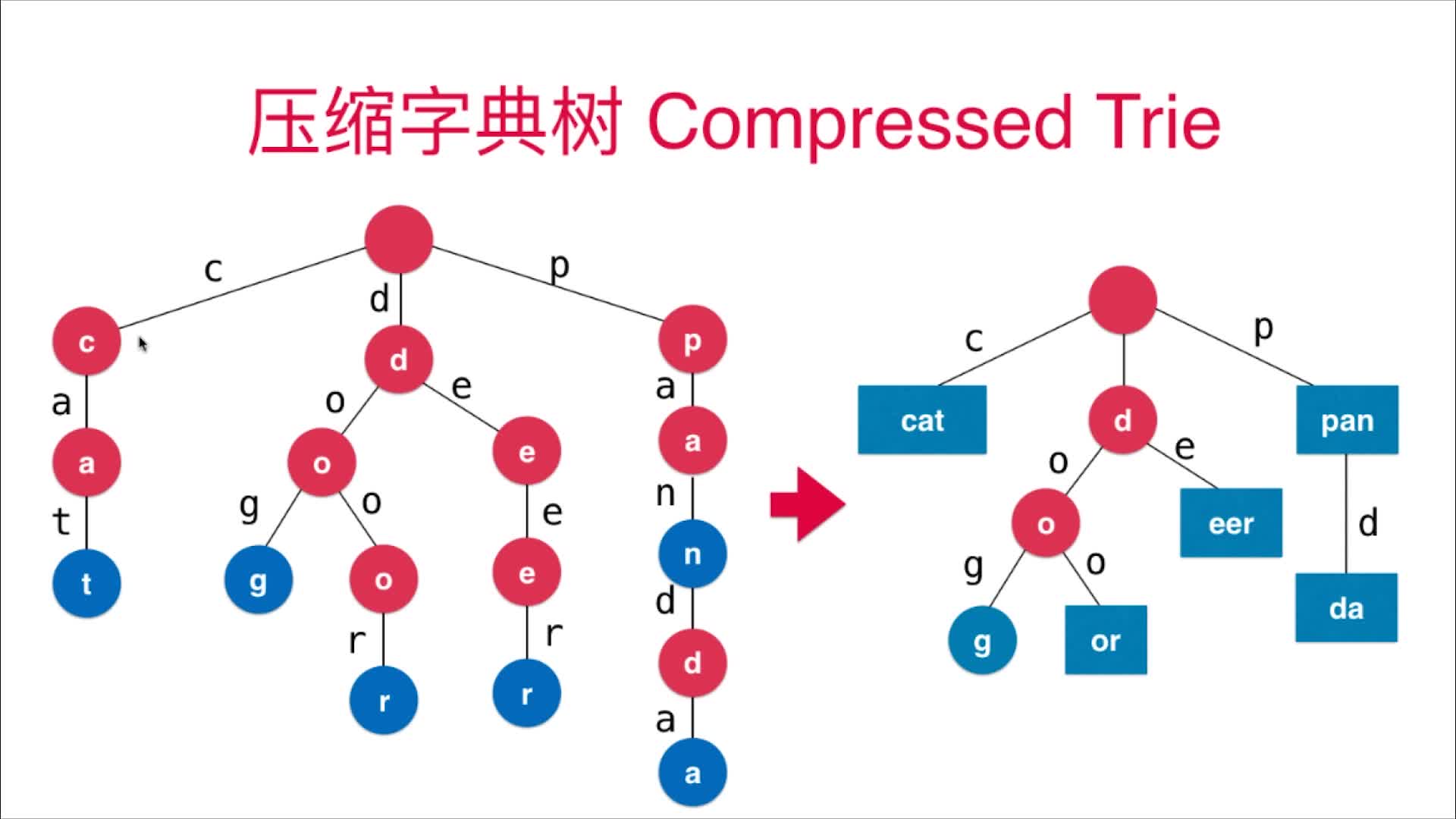
Trie最大的问题:空间
可以用压缩字典树(Compressed Trie)来做
字符串匹配
- KMP
- Boyer-Moore
- Rabin-Karp
文件压缩
- Huffman
模式匹配
编译原理
LeetCode上字典树相关的问题
421.数组中两个数的最大异或值
这个题目很巧妙,暴力法能过,但是效率太低了,还是要用字典树来做。树的子节点因为只有0和1两种,因此可以把children从map改成两个Node属性,代码也好理解
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
// 这里每个节点的邻接子树只有0和1两种情况,实际Map只有两个键
class Node {
int val;
Node left, right; // 左侧为0, 右侧为1
Node(int x) {
val = x;
}
}
private Node root;
public Solution() {
root = new Node(0); // 初始节点
}
public int findMaximumXOR(int[] nums) {
int maxLevel = 0;
for (int num : nums) { // 计算最大的层数
int curLevel = (int) (Math.floor(Math.log(num) / Math.log(2)));
maxLevel = Math.max(maxLevel, curLevel);
}
for (int num : nums) { // 把num的二进制逐位存入到Trie中
Node cur = root; // 从根节点开始
for (int i = maxLevel; i >= 0; i--) {
int ibit = (num >> i) & 1; // num的第位对应的二进制表示
if (ibit == 0) {
if (cur.left == null) cur.left = new Node(ibit);
cur = cur.left;
}
if (ibit == 1) {
if (cur.right == null) cur.right = new Node(ibit);
cur = cur.right;
}
}
}
// DFS求子树的最大值
return dfs(root.left, root.right, maxLevel);
}
// left:左侧取地节点;right:右侧取地节点
private int dfs(Node left, Node right, int level) {
if (root == null && left == null) return 0;
// 走到这里说明左右节点至少一个不为空
int res = 0;
int max = 0;
if (left == null || right == null) {
if (right != null) max = Math.max(max, dfs(right.left, right.right, level - 1));
if (left != null) max = Math.max(max, dfs(left.left, left.right, level - 1));
} else {
// 左右的节点都不为空,则可以累计一次1了,计算下幂指数即可
res = left.val == right.val ? 0 : (int) Math.pow(2, level);
if (left.left != null) {
if (right.right != null) max = Math.max(max, dfs(left.left, right.right, level - 1));
else max = Math.max(max, dfs(left.left, right.left, level - 1));
}
if (left.right != null) {
if (right.left !=null) max = Math.max(max, dfs(left.right, right.left, level - 1));
else max = Math.max(max, dfs(left.right, right.right, level - 1));
}
}
return res + max;
}
}
212.单词搜索II
要对DFS的细节和字典树的细节充分了解,在dfs的过程中,添加了一个trie树的剪枝,然后把符合要求的返回到结果中
结合数据结构和题目的特殊条件进行剪枝,是做DFS和BFS必须学会的技巧
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
class Node {
boolean isWord;
String word;
TreeMap<Character, Node> children;
Node() {
children = new TreeMap<>();
}
}
private Node root;
private Set<String> res;
private int R, C;
private final int[][] dirs = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
public Solution() {
root = new Node();
res = new HashSet<>();
}
private char[][] grid;
private boolean[][] visited;
private boolean inGrid(int r, int c) {
return r >= 0 && r < R && c >= 0 && c < C;
}
public void add(String word) {
Node cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char c = word.charAt(i);
if (cur.children.get(c) == null) cur.children.put(c, new Node());
cur = cur.children.get(c);
}
if (cur.isWord) return;
cur.isWord = true;
cur.word = word; // 在是单词的地方记录下是哪个单词
}
// 把DFS和字典的search结合在一起
public List<String> findWords(char[][] board, String[] words) {
this.grid = board;
this.R = board.length;
this.C = board[0].length;
for (String word : words) add(word); // 添加单词,构建词典树
for (int r = 0; r < R; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < C; c++) {
if (root.children.containsKey(board[r][c])) {
visited = new boolean[R][C];
dfs(r, c, root.children.get(board[r][c])); // 从当前字符开始往下DFS遍历
}
}
}
return new ArrayList<>(res);
}
private void dfs(int r, int c, Node node) {
if (node == null) return;
if (node.isWord) res.add(node.word);
visited[r][c] = true;
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int rNext = r + dir[0];
int cNext = c + dir[1];
if (inGrid(rNext, cNext) && !visited[rNext][cNext] && node.children.containsKey(grid[rNext][cNext])) {
dfs(rNext, cNext, node.children.get(grid[rNext][cNext]));
visited[rNext][cNext] = false; // 回溯时要把标记为改回去
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
char[][] board = {{'o', 'a', 'a', 'n'}, {'e', 't', 'a', 'e'}, {'i', 'h', 'k', 'r'}, {'i', 'f', 'l', 'v'}};
String[] words = {"oath", "pea", "eat", "rain"};
solution.findWords(board, words);
}
}