2023-04-14 算法面试中常见的查找表问题
1 Set的使用
给定两个数组,编写一个函数来计算它们的交集。
示例 1:
输入: nums1 = [1,2,2,1], nums2 = [2,2]
输出: [2]
示例 2:
输入: nums1 = [4,9,5], nums2 = [9,4,9,8,4]
输出: [9,4]
说明:
输出结果中的每个元素一定是唯一的。
我们可以不考虑输出结果的顺序。
package Chapter04SetAndMap.IntersectionofTwoArrays;
import java.util.*;
/***********************************************************
* @note :
* @author : l00379880 梁山广
* @version : V1.0 at 2019/8/20 15:46
***********************************************************/
class Solution {
/**
* 用retainAll方法实现求交集
*/
public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
Set<Integer> numSet = new HashSet<>();
for (int i : nums1) {
numSet.add(i);
}
Set<Integer> num2Set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i : nums2) {
num2Set.add(i);
}
// 求交集
numSet.retainAll(num2Set);
int[] result = new int[numSet.size()];
int i = 0;
for (Integer num : numSet) {
result[i] = num;
i++;
}
return result;
}
/**
* 用自己的方法实现交集,核心是contains方法
*/
public int[] intersection2(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
TreeSet<Integer> record = new TreeSet<>();
for (int num : nums1) {
record.add(num);
}
TreeSet<Integer> resultSet = new TreeSet<>();
for (int num : nums2) {
if (record.contains(num)) {
resultSet.add(num);
}
}
int[] res = new int[resultSet.size()];
int index = 0;
for (Integer num : resultSet) {
res[index++] = num;
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums1 = {4, 9, 5};
int[] nums2 = {9, 4, 9, 8, 4};
int[] result = new Solution().intersection2(nums1, nums2);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result));
}
}
2 Map的使用
给定两个数组,编写一个函数来计算它们的交集。
示例 1:
输入: nums1 = [1,2,2,1], nums2 = [2,2]
输出: [2,2]
示例 2:
输入: nums1 = [4,9,5], nums2 = [9,4,9,8,4]
输出: [4,9]
说明:
输出结果中每个元素出现的次数,应与元素在两个数组中出现的次数一致。
我们可以不考虑输出结果的顺序。
进阶:
package Chapter04SetAndMap.IntersectionofTwoArrays2;
import java.util.*;
/***********************************************************
* @note :
* @author : l00379880 梁山广
* @version : V1.0 at 2019/8/20 16:36
***********************************************************/
class Solution {
public int[] intersect(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
Map<Integer, Integer> num1Map = new HashMap<>();
Set<Integer> num1Set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i : nums1) {
num1Map.merge(i, 1, Integer::sum);
num1Set.add(i);
}
Map<Integer, Integer> num2Map = new HashMap<>();
Set<Integer> num2Set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i : nums2) {
num2Map.merge(i, 1, Integer::sum);
num2Set.add(i);
}
// 求交集
num1Set.retainAll(num2Set);
// num1Set就是交集的元素了
List<Integer> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Integer num : num1Set) {
int count = Math.min(num1Map.get(num), num2Map.get(num));
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
resultList.add(num);
}
}
int[] result = new int[resultList.size()];
int i = 0;
for (Integer num : resultList) {
result[i] = num;
i++;
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums1 = {1, 2, 2, 1};
int[] nums2 = {2};
int[] result = new Solution().intersect(nums1, nums2);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result));
}
}
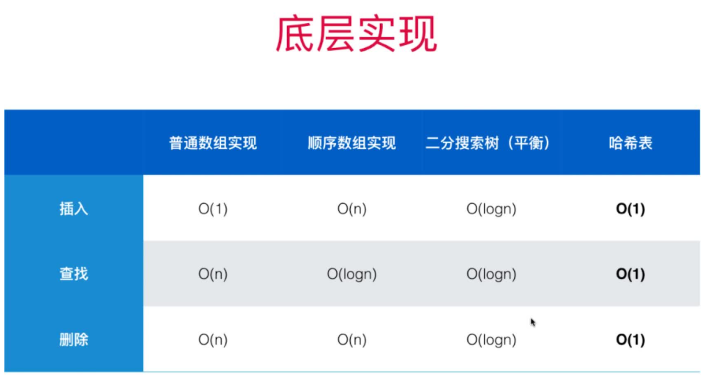
3 Set和Map不同底层实现的区别
参考Part2Basic全课程,每部分实现地数组、链表和树可以用来作为Map的底层,不同的实现比较如下:
哈希表虽然性能高,劣势是空间占用大,而且元素不能保持顺序~~
LeetCode上更多相似问题:242、202、290、205、451
242.有效的字母异位词
基于频率表的实现
class Solution {
// 字母异位词:字母相同但是顺序不同的单词,,类似问题是438号问题
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
if("".equals(s) && "".equals(t)){
return true;
}
if("".equals(s) || "".equals(t) || s.length() != t.length()){
return false;
}
int[] freq = new int[256];
int len = s.length();
for(int i = 0; i< len; i++){
freq[s.charAt(i)] = freq[s.charAt(i)] + 1;
freq[t.charAt(i)] = freq[t.charAt(i)] - 1;
}
for(int i = 0; i< len; i++){
if(freq[s.charAt(i)] != 0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
进一步优化,缩小数组范围,性能最高:
class Solution {
// 字母异位词:字母相同但是顺序不同的单词,,类似问题是438号问题
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
if("".equals(s) && "".equals(t)){
return true;
}
if("".equals(s) || "".equals(t) || s.length() != t.length()){
return false;
}
int[] freq = new int[26];
int len = s.length();
for(int i = 0; i< len; i++){
int sInt = s.charAt(i) - 'a';
int tInt = t.charAt(i) - 'a';
freq[sInt] = freq[sInt] + 1;
freq[tInt] = freq[tInt] - 1;
}
for(int i = 0; i< len; i++){
if(freq[s.charAt(i) - 'a'] != 0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
基于HashMap的实现
class Solution {
/**
* 字母异位词:字母相同但是顺序不同的单词,,类似问题是438号问题
*/
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
if ("".equals(s) && "".equals(t)) {
return true;
}
if ("".equals(s) || "".equals(t) || s.length() != t.length()) {
return false;
}
int len = s.length();
// 哈希表,类似用来存频率
Map<Character, Integer> cMap = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char sC = s.charAt(i);
char tC = t.charAt(i);
if (cMap.get(sC) == null) {
cMap.put(sC, 1);
} else {
cMap.put(sC, cMap.get(sC) + 1);
}
if (cMap.get(tC) == null) {
cMap.put(tC, -1);
} else {
cMap.put(tC, cMap.get(tC) - 1);
}
}
for (Character c : cMap.keySet()) {
if (cMap.get(c) != 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
202.快乐数
关键是观察规律
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
class Solution {
int getSquareSum(int n) {
int sum = 0;
while (n != 0) {
sum += (n % 10) * (n % 10);
n = n / 10;
}
return sum;
}
/**
* 若一个数是快乐数,最终变换会回到1,因此确定循环终结条件;
* 若不是快乐数,会进入死循环,如何终至死循环,将每次变换过后的值存入HashSet中,判断是否出现过重复值,出现则return false;
*/
public boolean isHappy(int n) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
while (true) {
n = getSquareSum(n);
if (n == 1) {
return true;
}
if (set.contains(n)) {
// 出现重复值了,直接退出
return false;
} else {
set.add(n);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 19->82->100->1
int n = 19;
System.out.println(new Solution().isHappy(n));
}
}
290.单词规律
class Solution {
public boolean wordPattern(String pattern, String str) {
if("".equals(pattern) || "".equals(str)){
return false;
}
String[] words = str.split(" ");
int len = pattern.length();
if(len != words.length){
return false;
}
Set<Character> setPattern = new HashSet<>();
Set<String> setWord = new HashSet<>();
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
setPattern.add(pattern.charAt(i));
setWord.add(words[i]);
}
if(setPattern.size() != setWord.size()){
return false;
}
Map<Character, String> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
Character c = pattern.charAt(i);
String word = map.get(c);
if(word == null){
map.put(c, words[i]);
}else {
// 映射在之前就存在了,但是之前对应的关系和现在不符,直接返回false
if(!word.equals(words[i])){
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
205.同构字符串
和290几乎完全相同,单词边字符而已
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
class Solution {
public boolean isIsomorphic(String s, String t) {
if ("".equals(s) && "".equals(t)) {
return true;
}
if ("".equals(s) || "".equals(t)) {
return false;
}
int len = s.length();
if (len != t.length()) {
return false;
}
Set<Character> setS = new HashSet<>();
Set<Character> setT = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
setS.add(s.charAt(i));
setT.add(t.charAt(i));
}
if (setS.size() != setT.size()) {
return false;
}
Map<Character, Character> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
Character cS = s.charAt(i);
Character cSMap = map.get(cS);
Character cT = t.charAt(i);
if (cSMap == null) {
map.put(cS, cT);
} else {
// 映射在之前就存在了,但是之前对应的关系和现在不符,直接返回false
if (!cT.equals(cSMap)) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "egg";
String t = "add";
System.out.println(new Solution().isIsomorphic(s, t));
}
}
451.根据字符出现频率排序
class Solution {
public String frequencySort(String s) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int[] freq = new int[256];
int len = s.length();
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
char c = s.charAt(i);
freq[c] += 1;
}
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
// max记录频率值最大的索引(字符的ASCII值,即在freq中的下标)
int max = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < 256; j++) {
if(freq[j] > freq[max]){
max = j;
}
}
// 插入频率个字符
for(int m = 0; m < freq[max]; m++){
sb.append((char)max);
}
// 一定记得清零
freq[max] = 0;
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "cccaaa";
System.out.println(new Solution().frequencySort(s));
}
}
4 Two Sum的问题
定一个整数数组 nums 和一个目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出和为目标值的那 两个 整数,并返回他们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,你不能重复利用这个数组中同样的元素。
示例:
给定 nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9
因为 nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9
所以返回 [0, 1]
第一种解法:把整个数组当做查找表
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
// 值和索引组成Map
Map<Integer, Integer> mapValIndex = new HashMap<>();
int len = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// 重复的元素不要二次加入
mapValIndex.putIfAbsent(nums[i], i);
}
int[] result = new int[2];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
Integer index = mapValIndex.get(target - nums[i]);
if (index != null && index != i) {
// 注意顺序问题, 当nums=[3,3],target=6时会体现Math函数的作用
result[0] = Math.min(i, index);
result[1] = Math.max(i, index);
// 找到就退出,因为用例保证了答案是唯一地了
break;
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {7, 3, 3};
int target = 6;
int[] result = new Solution().twoSum(nums, target);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result));
}
}
第2种解法:把遍历过程前面的元素作为查找表,顺便还能保证顺序
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
// 值和索引组成Map
Map<Integer, Integer> mapValIndex = new HashMap<>();
int len = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
Integer index = mapValIndex.get(target - nums[i]);
if (index != null) {
// 找到就退出,因为用例保证了答案是唯一地了
return new int[]{index, i};
}
// 加入当前节点
mapValIndex.put(nums[i], i);
}
return new int[0];
}
}
相关的题目:
- 15. 三数之和
a+b = -c,转化为Two Sum的问题,但是注意这里的TwoSum可能不止有唯一解给定一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?找出所有满足条件且不重复的三元组。 注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。 例如, 给定数组 nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4], 满足要求的三元组集合为: [ [-1, 0, 1], [-1, -1, 2] ]/*********************************************************** * @Description : LeetCode第15号问题:三数之和 * https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/3sum/ * @author : 梁山广(Liang Shan Guang) * @date : 2020/1/16 22:31 * @email : liangshanguang2@gmail.com ***********************************************************/ package Chapter03.ThreeSum; import java.util.*; class Solution { /** * 这里的Two Sum和LeetCode第一题不同,这里一个target可能对应多个结果 * * @param nums 要检索的数组 * @param target 要求的目标值 * @return 符合条件的下标对 */ public List<int[]> twoSum(int[] nums, int target) { List<int[]> resultList = new ArrayList<>(); // 值和索引组成Map Map<Integer, Integer> mapValIndex = new HashMap<>(); int len = nums.length; for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { Integer index = mapValIndex.get(target - nums[i]); if (index != null) { // 找到了一个满足条件地 resultList.add(new int[]{index, i}); } // 加入当前节点 mapValIndex.put(nums[i], i); } return resultList; } /** * 三个数字之和 * * @param nums 数组 * @return 所有满足三个数之和的元素对 */ public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) { // 这个排序很重要!!可能省掉下面大量的Collections.sort() Arrays.sort(nums); Set<List<Integer>> result = new HashSet<>(); if (nums.length < 3) { return new ArrayList<>(); } int len = nums.length; for (int i = 2; i < len; i++) { // 时间优化 if (nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && nums[i] == nums[i - 2]) { if (nums[i] == 0) { // 把三个0加进去 result.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(0, 0, 0))); } // 三个连续相等地,第3个开始就不用看了 continue; } // 注意twoSum返回地是nums的索引下标 List<int[]> twoSumResultList = twoSum(Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, 0, i), -nums[i]); for (int[] twoSumResult : twoSumResultList) { // 找到的两个索引不能和当前索引相等 if (twoSumResult.length == 2) { // 这个是set,会自动去重 result.add(Arrays.asList(nums[twoSumResult[0]], nums[twoSumResult[1]], nums[i])); } } } return new ArrayList<>(result); } /** * 输出顺序不重要,结果对就行~~ * nums = {-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4} ===> [ [-1, 0, 1], [-1, -1, 2]] * {-4, -2, -2, -2, 0, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 6, 6} ==> [[-4,-2,6],[-4,0,4],[-4,1,3],[-4,2,2],[-2,-2,4],[-2,0,2]] */ public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums = {-4, -2, -2, -2, 0, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 6, 6}; List<List<Integer>> lists = new Solution().threeSum(nums); System.out.println(lists); } } - 18. 四数之和
给定一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums 和一个目标值 target,判断 nums 中是否存在四个元素 a,b,c 和 d ,使得 a + b + c + d 的值与 target 相等?找出所有满足条件且不重复的四元组。 注意: 答案中不可以包含重复的四元组。 示例: 给定数组 nums = [1, 0, -1, 0, -2, 2],和 target = 0。 满足要求的四元组集合为: [ [-1, 0, 0, 1], [-2, -1, 1, 2], [-2, 0, 0, 2] ]/*********************************************************** * @Description : LeetCode第18号问题:四数之和 * https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/4sum/ * @author : 梁山广(Liang Shan Guang) * @date : 2020/1/16 23:46 * @email : liangshanguang2@gmail.com ***********************************************************/ package Chapter03.FourSum; import java.util.*; class Solution { /** * 这里的Two Sum和LeetCode第一题不同,这里一个target可能对应多个结果 * * @param nums 要检索的数组 * @param target 要求的目标值 * @return 符合条件的元素列表 */ public List<List<Integer>> twoSum(int[] nums, int target) { List<List<Integer>> resultList = new ArrayList<>(); // 值和索引组成Map Map<Integer, Integer> mapValIndex = new HashMap<>(); int len = nums.length; for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { Integer index = mapValIndex.get(target - nums[i]); if (index != null) { // 找到了一个满足条件地 resultList.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(nums[index], nums[i]))); } // 加入当前节点 mapValIndex.put(nums[i], i); } return resultList; } /** * 三个数字之和 * * @param nums 数组 * @return 所有满足三个数之和的元素对 */ public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums, int target) { // 这个排序很重要!!可能省掉下面大量的Collections.sort() Arrays.sort(nums); Set<List<Integer>> result = new HashSet<>(); if (nums.length < 3) { return new ArrayList<>(); } int len = nums.length; for (int i = 2; i < len; i++) { // 时间优化 if (nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && nums[i] == nums[i - 2]) { if (nums[i] + nums[i - 1] + nums[i - 2] == target) { // 把三个加进去 result.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[i - 1], nums[i - 2]))); } // 三个连续相等地,第3个开始就不用看了 continue; } // 注意twoSum返回地是nums的索引下标 List<List<Integer>> twoSumResultList = twoSum(Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, 0, i), target - nums[i]); for (List<Integer> twoSumResult : twoSumResultList) { // 找到的两个索引不能和当前索引相等 if (twoSumResult.size() == 2) { // 这个是set,会自动去重 result.add(Arrays.asList(twoSumResult.get(0), twoSumResult.get(1), nums[i])); } } } return new ArrayList<>(result); } public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) { // 这个排序很重要!!可能省掉下面大量的Collections.sort() Arrays.sort(nums); Set<List<Integer>> result = new HashSet<>(); if (nums.length < 4) { return new ArrayList<>(); } int len = nums.length; for (int i = 3; i < len; i++) { // 时间优化 if (nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && nums[i] == nums[i - 2] && nums[i] == nums[i - 3]) { if (nums[i] + nums[i - 1] + nums[i - 2] + nums[i - 3] == target) { // 把三个加进去 result.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[i - 1], nums[i - 2], nums[i - 3]))); } // 四个连续相等地,第4个开始就不用看了 continue; } // 注意twoSum返回地是nums的索引下标 List<List<Integer>> threeSumResultList = threeSum(Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, 0, i), target - nums[i]); for (List<Integer> threeSumResult : threeSumResultList) { // 找到的两个索引不能和当前索引相等 if (threeSumResult.size() == 3) { // 这个是set,会自动去重 result.add(Arrays.asList(threeSumResult.get(0), threeSumResult.get(1), threeSumResult.get(2), nums[i])); } } } return new ArrayList<>(result); } /** * 输出顺序不重要,结果对就行~~ * nums = {-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4} ===> [ [-1, 0, 1], [-1, -1, 2]] * {-4, -2, -2, -2, 0, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 6, 6} ==> [[-4,-2,6],[-4,0,4],[-4,1,3],[-4,2,2],[-2,-2,4],[-2,0,2]] */ public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums = {0, 0, 0, 0}; int target=1; List<List<Integer>> lists = new Solution().fourSum(nums, target); System.out.println(lists); } } - 16.最接近的三数之和
给定一个包括 n 个整数的数组 nums 和 一个目标值 target。找出 nums 中的三个整数,使得它们的和与 target 最接近。返回这三个数的和。假定每组输入只存在唯一答案。 例如,给定数组 nums = [-1,2,1,-4], 和 target = 1. 与 target 最接近的三个数的和为 2. (-1 + 2 + 1 = 2)./*********************************************************** * @Description : LeetCode第16号问题:最接近的三数之和 * https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/3sum-closest/ * @author : 梁山广(Liang Shan Guang) * @date : 2020/1/17 00:19 * @email : liangshanguang2@gmail.com ***********************************************************/ package Chapter03.ThreeSumClosest; import java.util.*; class Solution { /** * 这里的Two Sum和LeetCode第一题不同,这里一个target可能对应多个结果 * * @param nums 要检索的数组 * @param target 要求的目标值 * @return 符合条件的元素列表 */ public List<List<Integer>> twoSum(int[] nums, int target) { List<List<Integer>> resultList = new ArrayList<>(); // 值和索引组成Map Map<Integer, Integer> mapValIndex = new HashMap<>(); int len = nums.length; for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { Integer index = mapValIndex.get(target - nums[i]); if (index != null) { // 找到了一个满足条件地 resultList.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(nums[index], nums[i]))); } // 加入当前节点 mapValIndex.put(nums[i], i); } return resultList; } /** * 三个数字之和 * * @param nums 数组 * @return 所有满足三个数之和的元素对 */ public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums, int target) { // 这个排序很重要!!可能省掉下面大量的Collections.sort() Arrays.sort(nums); Set<List<Integer>> result = new HashSet<>(); if (nums.length < 3) { return new ArrayList<>(); } int len = nums.length; for (int i = 2; i < len; i++) { // 时间优化 if (nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && nums[i] == nums[i - 2]) { if (nums[i] + nums[i - 1] + nums[i - 2] == target) { // 把三个加进去 result.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[i - 1], nums[i - 2]))); } // 三个连续相等地,第3个开始就不用看了 continue; } // 注意twoSum返回地是nums的索引下标 List<List<Integer>> twoSumResultList = twoSum(Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, 0, i), target - nums[i]); for (List<Integer> twoSumResult : twoSumResultList) { // 找到的两个索引不能和当前索引相等 if (twoSumResult.size() == 2) { // 这个是set,会自动去重 result.add(Arrays.asList(twoSumResult.get(0), twoSumResult.get(1), nums[i])); } } } return new ArrayList<>(result); } public int threeSumClosest(int[] nums, int target) { int len = nums.length; if (len < 3) { return -1; } if (len == 3) { return nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2]; } Arrays.sort(nums); int minTarget = nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2]; int maxTarget = nums[len - 3] + nums[len - 2] + nums[len - 1]; if (target >= maxTarget) { return maxTarget; } if (target <= minTarget) { return minTarget; } // 临时的targetTmp和target的距离,从最小开始找,只要找到一个就退出,即是最小的distance int distance = 0; int maxDistance = Math.max(maxTarget - target, target - minTarget); // target一定在minTarget和maxTarget之间了 while (distance < maxDistance) { if (target + distance <= maxTarget && threeSum(nums, target + distance).size() != 0) { return target + distance; } if (target - distance >= minTarget && threeSum(nums, target - distance).size() != 0) { return target - distance; } distance++; } return -1; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums = {-1, 2, 1, -4}; int target = 1; System.out.println(new Solution().threeSumClosest(nums, target)); } }
5 灵活选择键值 454号问题 4Sum
解题思路:把C+D的组合放入查找表中,通过查找A+B是否等于-(C+D)
给定四个包含整数的数组列表 A , B , C , D ,计算有多少个元组 (i, j, k, l) ,使得 A[i] + B[j] + C[k] + D[l] = 0。
为了使问题简单化,所有的 A, B, C, D 具有相同的长度 N,且 0 ≤ N ≤ 500 。所有整数的范围在 -2^28 到 2^28 - 1 之间,最终结果不会超过 2^31 - 1 。
例如:
输入:
A = [ 1, 2]
B = [-2,-1]
C = [-1, 2]
D = [ 0, 2]
输出:
2
解释:
两个元组如下:
1. (0, 0, 0, 1) -> A[0] + B[0] + C[0] + D[1] = 1 + (-2) + (-1) + 2 = 0
2. (1, 1, 0, 0) -> A[1] + B[1] + C[0] + D[0] = 2 + (-1) + (-1) + 0 = 0
/***********************************************************
* @Description : 给定四个包含整数的数组列表 A , B , C , D ,计算有多少个元组 (i, j, k, l) ,使得 A[i] + B[j] + C[k] + D[l] = 0
* 解题思路:把C+D的组合放入查找表中,通过查找A+B是否等于-(C+D)
* @author : 梁山广(Liang Shan Guang)
* @date : 2019/8/20 23:52
* @email : liangshanguang2@gmail.com
***********************************************************/
package Chapter04.TwoSum2;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/*
*时间复杂度是:O(n^2)
*空间复杂度是:O(n^2)
*/
class Solution {
public int fourSumCount(int[] A, int[] B, int[] C, int[] D) {
Map<Integer, Integer> record = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < C.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < D.length; j++) {
if (record.get(C[i] + D[j]) == null) {
record.put(C[i] + D[j], 1);
} else {
record.put(C[i] + D[j], record.get(C[i] + D[j]) + 1);
}
}
}
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < A.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < B.length; j++) {
if (record.containsKey(-A[i] - B[j])) {
result += record.get(-A[i] - B[j]);
}
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] A = {1, 2};
int[] B = {-2, -1};
int[] C = {-1, 2};
int[] D = {0, 2};
int result = new Solution().fourSumCount(A, B, C, D);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
类似问题:49. 字母异位词分组
下面的实现行用时 :13 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了66.68%的用户;内存消耗 :40.9 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了96.06%的用户
核心优化:数组或者字符串长度不要单独赋值
// 教训:len不要单独赋值
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>();
Map<String, List<String>> anagramsMap = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < strs.length; i++) {
char[] chs = strs[i].toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(chs);
String strSorted = new String(chs);
if (anagramsMap.get(strSorted)==null){
List<String> anagrams = new ArrayList<>();
anagrams.add(strs[i]);
anagramsMap.put(strSorted, anagrams);
}else {
List<String> anagrams = anagramsMap.get(strSorted);
anagrams.add(strs[i]);
anagramsMap.put(strSorted,anagrams);
}
}
for (String key : anagramsMap.keySet()) {
result.add(anagramsMap.get(key));
}
return result;
}
}
4.6 灵活选择键值:LeetCode447号问题-回旋镖的数量
选择距离作为键
class Solution {
/**
* 获取距离,暂时不开方,只要能表示距离的唯一值即可
*/
int getDistance(int[] p1, int[] p2) {
return (p2[0] - p1[0]) * (p2[0] - p1[0]) + (p2[1] - p1[1]) * (p2[1] - p1[1]);
}
public int numberOfBoomerangs(int[][] points) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < points.length; i++) {
// 到i的距离和相等距离点的个数组成的映射
Map<Integer, Integer> mapDistancePoints = new HashMap<>();
for (int j = 0; j < points.length; j++) {
int distance = getDistance(points[i], points[j]);
if (mapDistancePoints.get(distance) == null) {
mapDistancePoints.put(distance, 1);
} else {
mapDistancePoints.put(distance, mapDistancePoints.get(distance) + 1);
}
}
// 统计到points[i]距离相等的点数
for (Integer distance : mapDistancePoints.keySet()) {
int cnt = mapDistancePoints.get(distance);
// 指定的举例值至少有一个元素地,所以这里不需要判空
if (cnt > 1) {
// 因为考虑顺序,所以求组合而不是排列A-N-2 = N * (N - 1)
count += cnt * (cnt - 1);
}
}
}
return count;
}
}
坑非常多,同时锻炼价值也很大,用例考察地角度非常多。执行用时 :14 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了81.61%的用户;内存消耗 :36 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了60.83%的用户
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
class Solution {
public int maxPoints(int[][] points) {
int max = 0;
if (points.length < 3) {
return points.length;
}
for (int i = 0; i < points.length; i++) {
// 到i的斜率和斜率相等的点的个数组成的映射
Map<Double, Integer> mapKPoints = new HashMap<>();
// 和points[i]的横纵坐标都相同的点,初始至少有自己
int sameCount = 1;
for (int j = i + 1; j < points.length; j++) {
// 斜率可能是浮点数
double k = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (points[i][1] != points[j][1]) {
k = (points[i][0] - points[j][0]) * 1.0 / (points[i][1] - points[j][1]);
} else {
if (points[i][0] == points[j][0]) {
// 横纵坐标都相等,那么这样的点可以加到任何一条和i相连的直线上
sameCount++;
continue;
}
}
// 下面这一行是为了解决用例[[4,0],[4,-1],[4,5]] ,Java中0.0和-0.0是不同的,https://blog.csdn.net/ouy5933/article/details/72461239
k += 0.0;
if (mapKPoints.get(k) == null) {
mapKPoints.put(k, 1);
} else {
mapKPoints.put(k, mapKPoints.get(k) + 1);
}
}
// 统计到points[i]距离相等的点数
for (Double k : mapKPoints.keySet()) {
int cnt = mapKPoints.get(k);
// 要算上当前点points[i],所以要cnt+1
max = Math.max(cnt + sameCount, max);
}
// 全部都是一个点的用例:[[1,1],[1,1],[1,1]]
max = Math.max(sameCount, max);
}
return max;
}
/***
* 典型用例:
*
* {{1, 1}, {2, 2}, {3, 3}} ==>3
* {{0, 0}} ==> 1
* {{0, 0},{0, 0}} ==> 2
* {{0, 0},{1, 1},{0, 0}} ==> 3
* [[1,1],[1,1],[2,2],[2,2]] ==> 4
* {{-4, 1}, {-7, 7}, {-1, 5}, {9, -25}} ==》 3 这里例子终点考察斜率是浮点类型
* [[4,0],[4,-1],[4,5]] ==> 3 考察 Java中0.0和-0.0是不同的
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] points = {{4, 0}, {4, -1}, {4, 5}};
System.out.println(new Solution().maxPoints(points));
}
}
4.7 查找表+滑动数组:219号问题,Contains Duplicate II
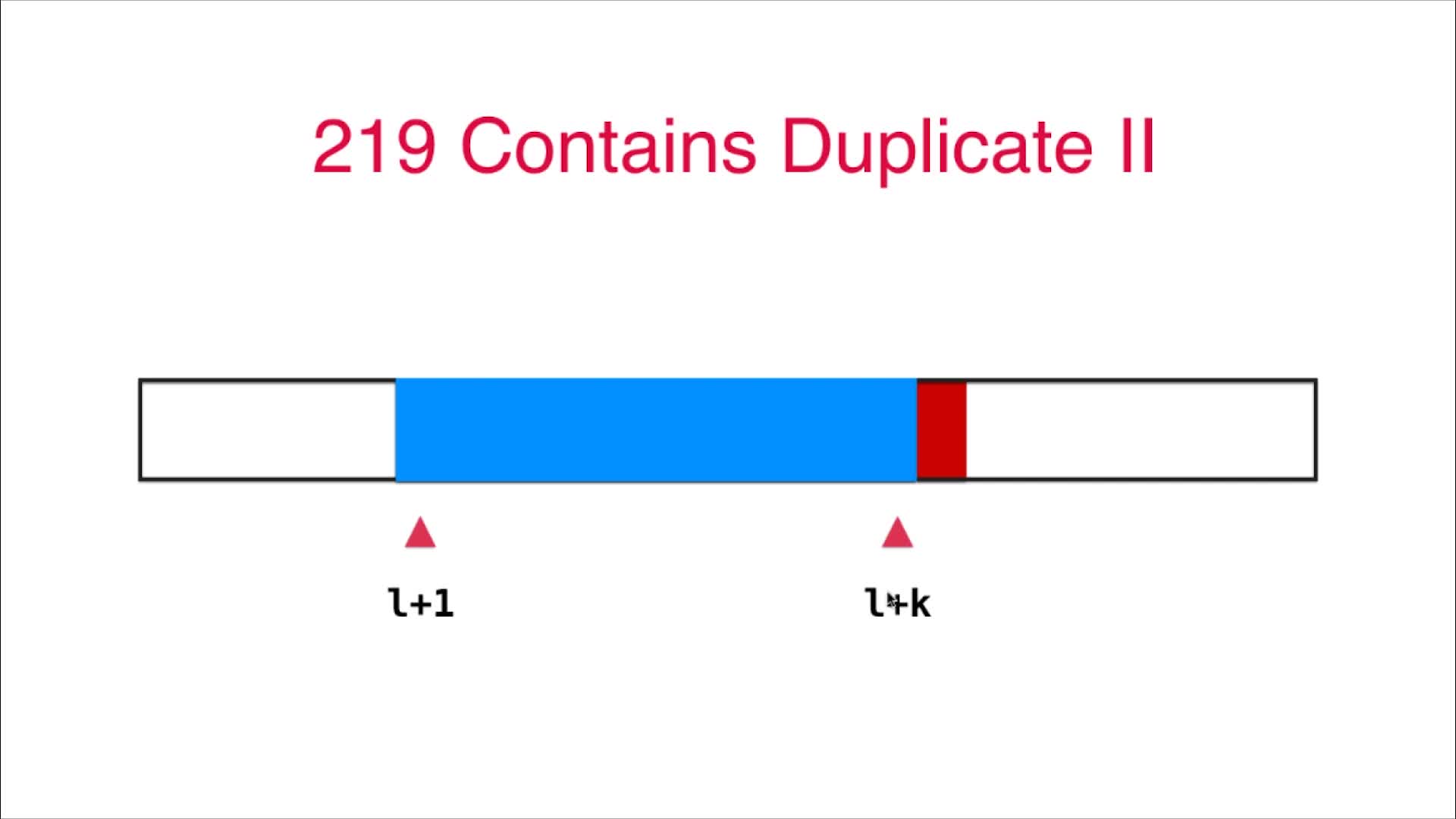
给定一个整数数组和一个整数 k,判断数组中是否存在两个不同的索引 i 和 j,使得 nums [i] = nums [j],并且 i 和 j 的差的绝对值最大为 k。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [1,2,3,1], k = 3
输出: true
示例 2:
输入: nums = [1,0,1,1], k = 1
输出: true
示例 3:
输入: nums = [1,2,3,1,2,3], k = 2
输出: false
/***********************************************************
* @Description : 给定一个整数数组和一个整数 k,判断数组中是否存在两个不同的索引 i 和 j,使得 nums [i] = nums [j],并且 i 和 j 的差的绝对值最大为 k
* 思路:控制一个宽度为不大于k的窗口(record)不断滑动,检测到有相等的两个不同下标的就返回true
* @author : 梁山广(Liang Shan Guang)
* @date : 2019/8/21 08:16
* @email : liangshanguang2@gmail.com
***********************************************************/
package Chapter04.ContainDuplicate;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* 时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(k)
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean containsNearbyDuplicate(int[] nums, int k) {
Set<Integer> record = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (record.contains(nums[i])) {
// 前面加入的元素nums[j]包含已经包含nums[i]了,
return true;
}
record.add(nums[i]);
// 保持record中不超过k个元素,即i和j的索引最大差值不大于k,超过k时抹掉最左边的元素即可
if (record.size() == k + 1) {
record.remove(nums[i - k]);
}
}
// 遍历到最后还找不到就返回false
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1, 2, 3, 1};
int k = 3;
boolean contain = new Solution().containsNearbyDuplicate(nums, k);
System.out.println(contain);
}
}
相似的问题:217.存在重复元素,相似的思路,只是不用维护窗口了
class Solution {
public boolean containsDuplicate(int[] nums) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet();
for(int num : nums){
if(set.contains(num)){
return true;
}
set.add(num);
}
return false;
}
}
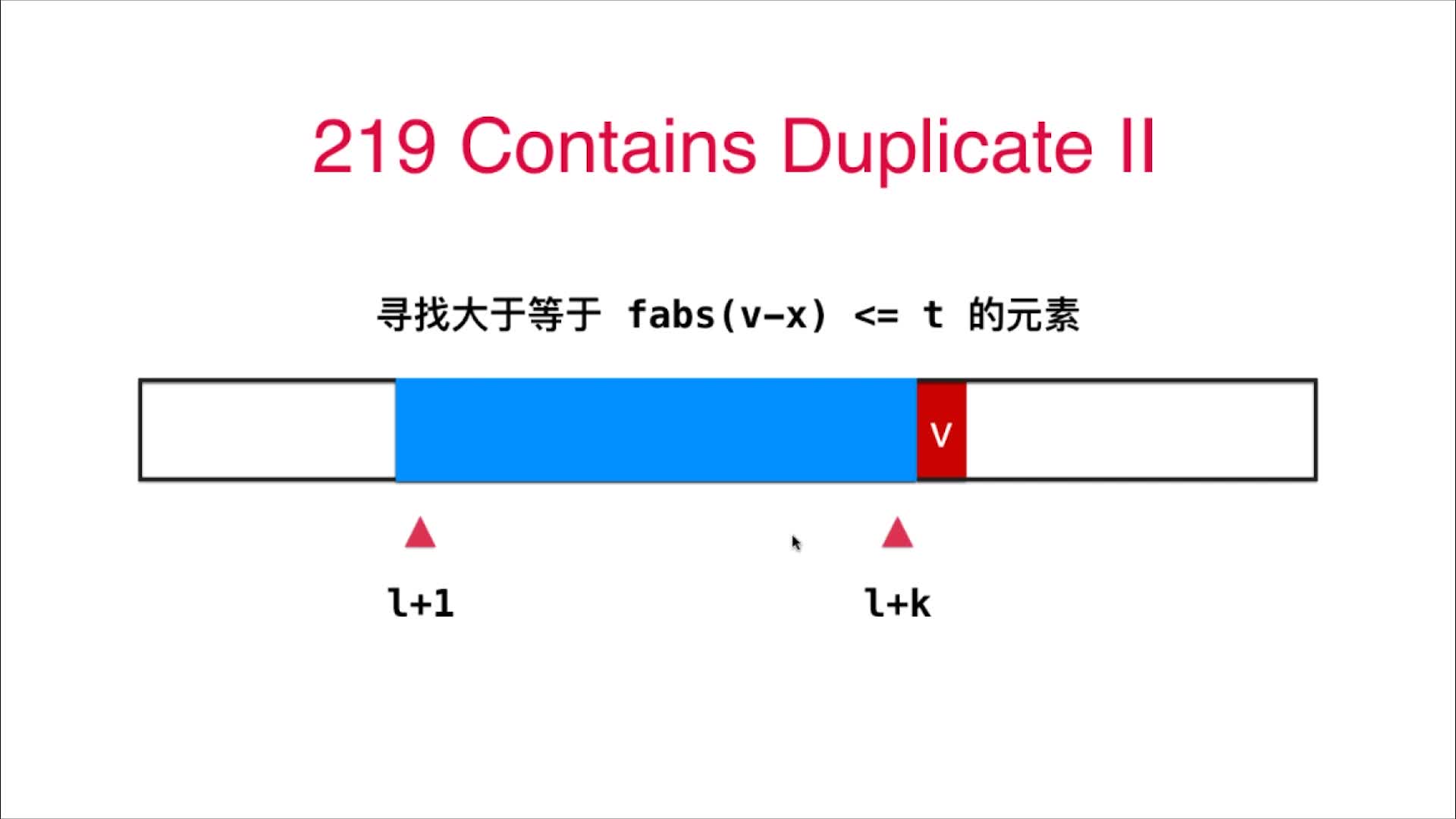
4.8 二分搜索树底层实现的顺序性 220号问题 Contain Duplicate III
给定一个整数数组,判断数组中是否有两个不同的索引 i 和 j,使得 nums [i] 和 nums [j] 的差的绝对值最大为 t,并且 i 和 j 之间的差的绝对值最大为 ķ。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [1,2,3,1], k = 3, t = 0
输出: true
示例 2:
输入: nums = [1,0,1,1], k = 1, t = 2
输出: true
示例 3:
输入: nums = [1,5,9,1,5,9], k = 2, t = 3
输出: false
在上一节的基础上加一个判断即可:在大小为k的窗口中找值差不大于t的即可
/***********************************************************
* @Description : 给定一个整数数组,判断数组中是否有两个不同的索引 i 和 j,使得 nums [i] 和 nums [j] 的差的绝对值最大为 t,并且 i 和 j 之间的差的绝对值最大为 ķ。
* @author : 梁山广(Liang Shan Guang)
* @date : 2019/8/21 08:16
* @email : liangshanguang2@gmail.com
***********************************************************/
package Chapter04.ContainDuplicate;
import java.util.TreeSet;
/**
* 时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(k)
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean containsNearbyAlmostDuplicate(int[] nums, int k, int t) {
TreeSet<Integer> record = new TreeSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
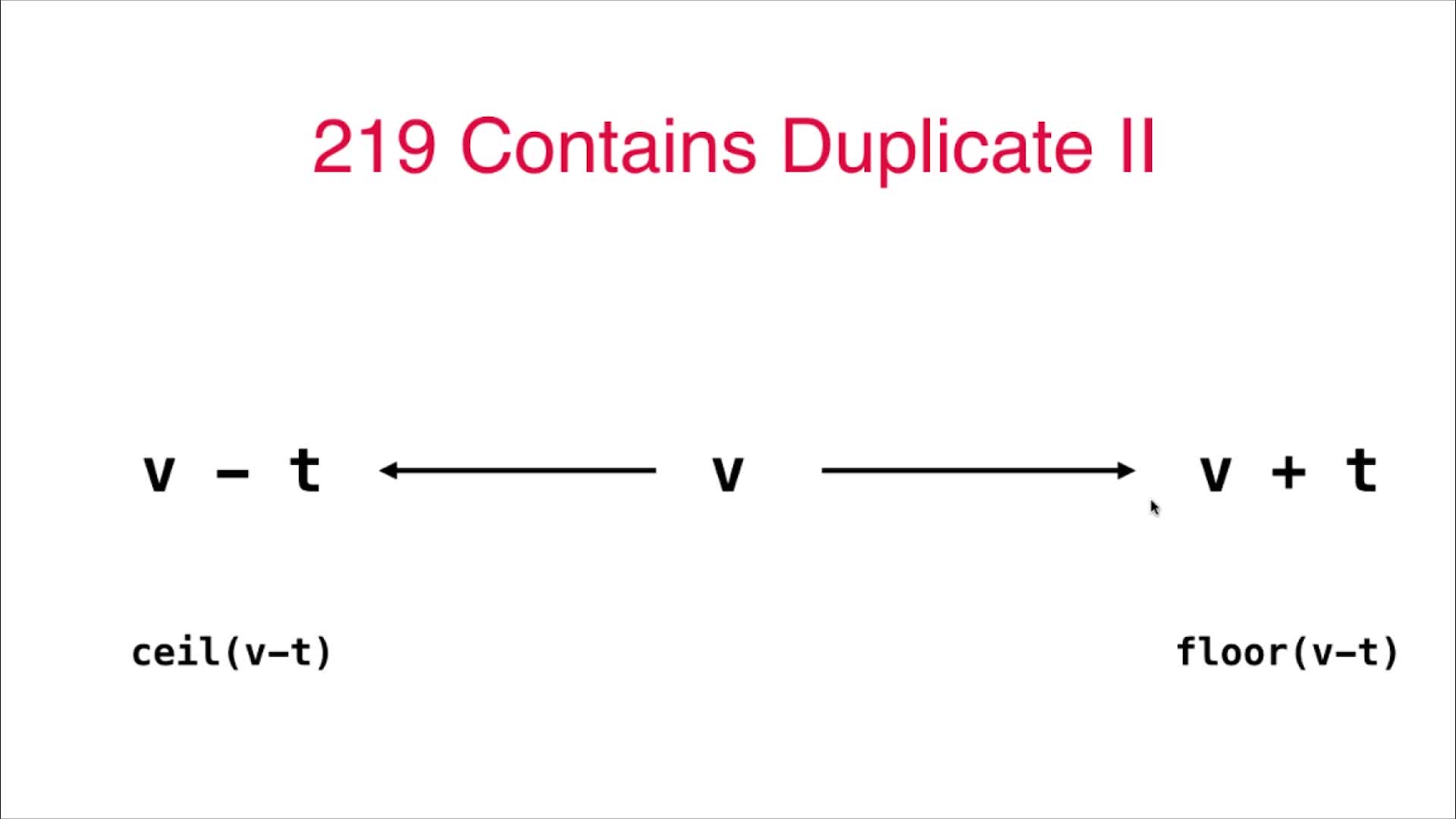
// 在长度为k的窗口内存在一个下标为j的元素nums[j],使得abs(nums[i] - nums[j]) < t,推导出 nums[i]-t <= nums[j] <= nums[i] + t
// 这里的nums[j]就取最接近窗口内大于"nums[i]-t"的最小值,如果这个值也小于"nums[i]+t",说明j满足题干条件,返回true即可
if (record.ceiling(nums[i] - t) != null && record.ceiling(nums[i] - t) <= nums[i] + t){
// 前面加入的元素包含nums[k了]
return true;
}
record.add(nums[i]);
// 保持record中不超过k个元素,即i和j的索引最大差值不大于k,超过k时抹掉最左边的元素即可
if (record.size() == k + 1) {
record.remove(nums[i - k]);
}
}
// 遍历到最后还找不到就返回false
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1, 2, 3, 1};
int k = 3;
int t = 0;
boolean contain = new Solution().containsNearbyAlmostDuplicate(nums, k, t);
System.out.println(contain);
}
}