| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | 软件工程 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | 结对项目 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 熟悉多人协作 |
成员??:戴子豪3121004649、朱俊荣3121004677
GitHub项目地址?:https://github.com/HaoDavis/FourOperations
效能分析
改进思路
- is_same 改用 hash 对照的方法,不需要遍历表达式列表,而是将表达式列表里的每一个表达式都转换成 hash 值,再用新的表达式与之对比,这样不需要重复遍历表达式列表,也不用重复计算某条表达式的 hash ,效率大幅提高。
- 在 check_result 函数中,用 zip 函数将表达式列表和答案列表打包成一个元组, 再用 map 函数对每一个元组进行判断,提高了效率。
性能分析图
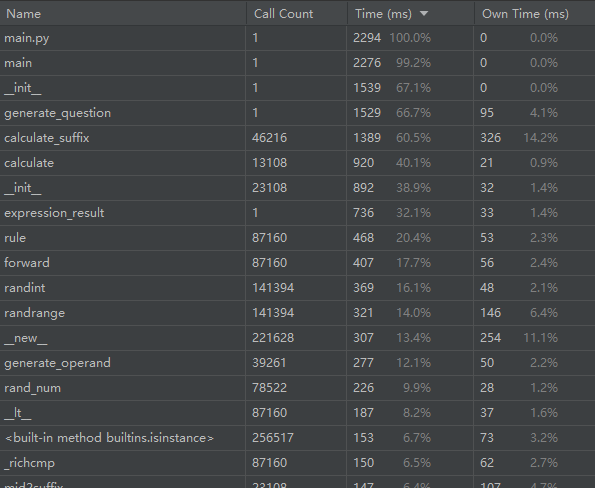
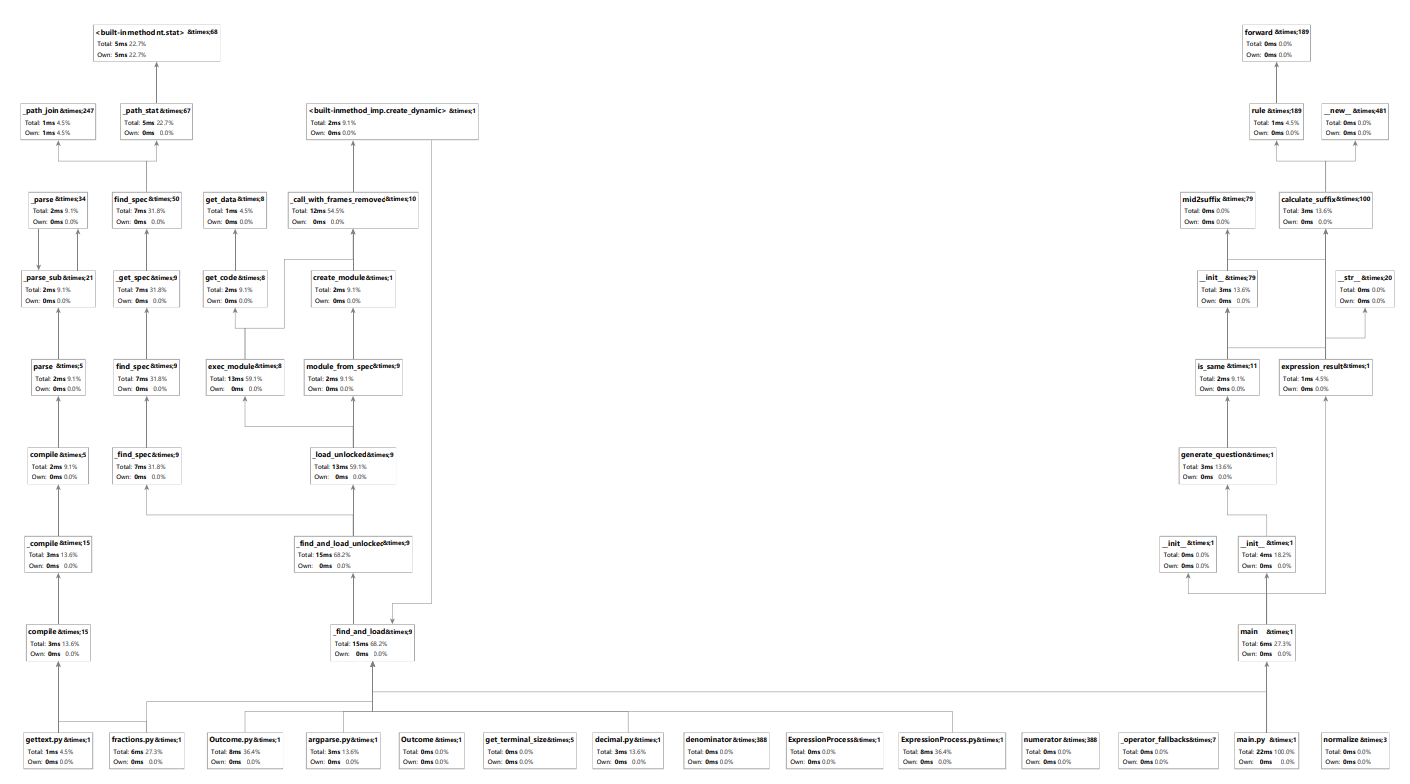
设计实现过程
- Tree 类:由于要判断两个等式本质上是否是一样的,要先将中缀表达式转换为二叉树,用的是 gnerate_tree 函数,然后判断两棵树本质上是否相同,用的是 is_same_tree 函数。
- ExpressionProcess 类:用于处理表达式,包括将中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式,用的是 mid2suffix 函数。以及计算后缀表达式,用的是 calculate_suffix 函数。
- Generate 类:就像类名一样,这个类里包含很多生成所需内容的函数,包括生成运算符、生成运算数 generate_operand 、生成并插入括号 generate_parentheses 以及处理分数的格式等。还有 generate_question 函数它通过调用其他函数,生成题目和答案。 最重要的是 is_same 函数,它用 hash 来判断新生成的表达式是否与之前的表达式相同。
具体实现如下:
def is_same(self, express_set, expression):
# 使用哈希表来存储已生成的表达式的哈希值
hash_set = set()
# 计算新生成表达式的哈希值
suffixExpression = ExpressionProcess(expression)
target_exp_suffix = suffixExpression.re
target_exp_hash = hash("".join(target_exp_suffix))
# 如果哈希值已经存在于哈希集合中,表明表达式重复
if target_exp_hash in hash_set:
return True
# 否则,将哈希值添加到哈希集合中,并继续检查集合中的其他表达式
hash_set.add(target_exp_hash)
for item in express_set:
suffixExpression2 = ExpressionProcess(item)
source_exp_suffix = suffixExpression2.re
source_exp_hash = hash("".join(source_exp_suffix))
if source_exp_hash in hash_set:
return True
return False
- Outcome 类:用写入答案以及实现答案检查。 expression_result 将获取到的答案写入 Answers.txt 文件中,做了改进保证写入的答案是带分数也不是真分数。细节如下:
def expression_result(self, expressions):
with open('Answer.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
for i, exp in enumerate(expressions):
suffix_expression = ExpressionProcess(exp)
exp_value = suffix_expression.calculate_suffix()
flag = float(exp_value)
exp_value = str(exp_value)
if '/' in exp_value and flag > 1:
a,b = exp_value.split('/')
a = int(a)
b = int(b)
# 转化成真分数
c = a//b
d = a%b
e = str(c)+'’'+str(d)+'/'+str(b)
exp_value = e
result = f"Answer{i + 1}: {exp_value}\n"
file.write(result)
使用上下文管理器。这确保了文件在不再需要时会被正确关闭。这有助于避免资源泄漏和文件锁定问题。另外,在 check_result 方法检查答案时,用zip函数将表达式列表和答案列表打包成一个元组,并行迭代对比给定的文本答案与正确答案,简化代码并提高可读性。静态方法可以提高代码的可维护性和可重用性,
@staticmethod
def check_result(exercisefile, answerfile):
correct_list, wrong_list = [], []
exercise_answer = []
try:
with open(exercisefile, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as exercise_file, \
open(answerfile, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as answer_file:
for (exp_line, ans_line) in zip(exercise_file, answer_file):
exp_match = re.match(r'Question\d+: (.*) =\n', exp_line)
ans_match = re.match(r'Answer\d+: (.*)\n', ans_line)
if exp_match and ans_match:
exp = exp_match.group(1)
ans = ans_match.group(1)
p = ExpressionProcess(exp)
exp_value = p.calculate_suffix()
flag = float(exp_value)
exp_value = str(p.calculate_suffix())
if '/' in exp_value and flag > 1:
a, b = exp_value.split('/')
a = int(a)
b = int(b)
# 转化成真分数
c = a // b
d = a % b
e = str(c) + '’' + str(d) + '/' + str(b)
exp_value = e
exercise_answer.append(exp_value)
if ans == exp_value:
correct_list.append(len(correct_list) + 1)
else:
wrong_list.append(len(wrong_list) + 1)
with open('Grade.txt', 'w+', encoding='utf-8') as grade_file:
grade_file.write(f'Correct: {len(correct_list)} {correct_list}\n')
grade_file.write(f'Wrong: {len(wrong_list)} {wrong_list}')
except IOError:
print('请检查文件路径是否正确')
代码说明
- Gnerator 类中的 fraction_to_str 函数,用于将分数转换为字符串,方便写入文件。
def fraction_to_str(self, operArray):
operNum1, operNum2 = operArray
if operNum2 == 1:
return operNum1
if operNum1 > operNum2:
temp = operNum1 // operNum2
operNum1 -= temp * operNum2
return f"{temp}'{operNum1}/{operNum2}"
return f"{operNum1}/{operNum2}"
- ExpressionProcess 类中的 mid2suffix 函数,用于将中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式。算法如下:
- 遇到操作数时直接加入集合
- 遇到操作符,与栈顶操作符比较优先级如果栈为空,或者栈顶元素为(,直接加入栈。如果优先级比栈顶操作数高,直接加入栈。如果优先级比栈顶操作符低或者相等,则弹出栈顶元素入集合,再次进行对比
- 遇到括号时:如果为左括号,直接加入栈。如果为右括号,依次弹出栈顶元素入集合,并且再次对比,直到遇到左括号,弹出栈顶元素不入集合。
- 最后将栈顶元素依次弹出入集合。
def mid2suffix(self):
"""
中缀表达式转为后缀表达式
:param: exp: 表达式字符串
:return: result列表
"""
if not self.exp:
return []
ops_rule = {
'+': 1,
'-': 1,
'×': 2,
'÷': 2,
}
suffix_stack = [] # 后缀表达式结果
ops_stack = [] # 操作符栈
infix = self.exp.split(' ') # 将表达式分割得到单词
# print(infix)
for item in infix:
if item in ['+', '-', '×', '÷']:
while ops_stack and ops_stack[-1] != '(' and ops_rule[item] <= ops_rule.get(ops_stack[-1], 0):
suffix_stack.append(ops_stack.pop())
ops_stack.append(item)
elif item == '(':
ops_stack.append(item)
elif item == ')':
while ops_stack and ops_stack[-1] != '(':
suffix_stack.append(ops_stack.pop())
ops_stack.pop() # 弹出 '('
else:
suffix_stack.append(item)
while len(ops_stack) > 0:
suffix_stack.append(ops_stack.pop())
self.re = suffix_stack
return suffix_stack
- ExpressionProcess 类中的 calculate_suffix 函数,用于计算后缀表达式的值。算法如下:
- 字符为运算数: 直接入栈(先分析出完整的运算数并将其转换为对应的数据类型)
- 字符为操作符: 连续出栈两次,使用出栈的两个数据进行相应计算,并将计算结果入栈 e.g:第一个出栈的运算数为a,第二个出栈的运算数为b,此时的操作符为-,则计算 b-a(a和b顺序不能反),并将结果入栈。
- 重复以上步骤直至遍历完成后缀表达式,最后栈中的数据就是中缀表达式的计算结果。
def calculate_suffix(self):
"""
后缀表达式求值
:return 运算结果
"""
stack_value = []
for item in self.re:
# print("item")
# print(item)
if item in ['+', '-', '×', '÷']:
n2 = stack_value.pop()
n1 = stack_value.pop()
result = self.rule(n1, n2, item)
if result < 0 or result == False:
return False
stack_value.append(result)
else:
if item.find('/') > 0:
attach = 0
right = ""
if item.find("'") > 0:
parts = item.split("'")
attach = int(parts[0])
right = parts[1]
else:
right = item
parts = right.split('/')
result = Fraction(attach * int(parts[1]) + int(parts[0]), int(parts[1]))
stack_value.append(result)
else:
stack_value.append(Fraction(int(item), 1))
return stack_value[0]
测试运行
利用unittest单元测试框架,实现单元测试自动化,以下仅列举部分用例。
- 正确情况下的中缀表达式转后缀表达式:
def test_mid2suffix(self):
# 测试中缀表达式转后缀表达式
exp = "1 + 2 + 3"
exp_process = ExpressionProcess(exp)
self.assertEqual(exp_process.re, ['1', '2', '+', '3', '+'])
- 缺少操作数的中缀表达式转后缀表达式:
def test_mid2suffix2(self):
# 测试中缀表达式转后缀表达式
exp = "1 + 2 +"
with self.assertRaises(IndexError):
exp_process = ExpressionProcess(exp)
- 正确情况下的后缀表达式求值:
def test_calculate_suffix(self):
# 测试后缀表达式求值
exp = "1 2 + 3 +"
exp_process = ExpressionProcess(exp)
self.assertEqual(exp_process.value, 6)
- 缺少操作数的后缀表达式求值:
def test_calculate_suffix2(self):
# 测试后缀表达式求值
exp = "1 + 2 "
with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
exp_process = ExpressionProcess(exp)
- 测试生成题目:
def test_generate_question(self):
# 测试生成题目
gen = Generator(10, 10)
question = gen.generate_question()
self.assertEqual(len(question), 10)
- 测试生成括号:
def test_generate_parentheses(self):
# 测试生成括号
gen = Generator(10, 10)
question = gen.generate_parentheses("1 + 2 + 3", 2)
self.assertEqual("(" in question, True)
- 测试中缀表达式转后缀表达式:
def test_mid2suffix3(self):
# 测试中缀表达式转后缀表达式
exp = "1 + 5 × ( 3 + 2 ) - 4 × 5"
exp_process = ExpressionProcess(exp)
self.assertEqual(exp_process.re, ['1', '5', '3', '2', '+', '×', '+', '4', '5', '×', '-'])
- 测试小数转分数:
def test_to_fraction(self):
# 测试小数转分数
self.assertEqual(Generator.to_fraction(self, 1, 2), [1, 2])
- 测试获取公因子:
def test_get_common_factors(self):
# 测试获取公因子
self.assertEqual(Generator.get_common_factors(self, 6), [2, 3, 6])
- 测试数字转符号:
def test_num2symbol(self):
# 测试数字转符号
self.assertEqual(Generator.num2symbol(self, 1), "+")
- 测试判断重复:
def test_is_same(self):
# 测试判断重复
self.assertEqual(Generator.is_same(self, [], "1 + 2"), False)
项目小结
- 朱俊荣:is_same 函数一开始用暴力法遍历表达式列表,来寻找是否有与新生成出表达式相同的表达式,但效率很低,因为 is_same 底层调用了便利二叉树的函数。后来将表达式列表里的每一个表达式都转换为一个 hash ,然后对于已经产生 hash 的表达式,在后续的判断中就不需要重新遍历他们,这样就将程序运行时间减半。另外答案检查函数中的 zip 手法也提高了效率。另外,这个项目非常综合,考察到了很多方面的内容,有一些规则的判定并没有现成的算法可以参考,需要自己试错。我的伙伴有很好的 Python 语法功底,也很熟练地使用 git 和一些测试工具,让我们的开发效率大大提高。深刻感受到,很多 bug 若是两个人在一起观察讨论就很容易解决,达到一加一远大于二的效果。
- 戴子豪:结对项目和个人项目很不一样,与人合作增加了不少的沟通协调成本,前期沟通、项目的规划占用了不少的时间,但好处是有人帮忙,可以各取所长。从中吸取的经验是,尽量少规划早动手,边动手边讨论边解决,但是也不能毫无规划,前期应明确各人任务,避免杂乱无章。
附录
PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 60 | 60 |
| Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 30 | 20 |
| Development | 开发 | 400 | 400 |
| Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 60 | 60 |
| Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 120 | 60 |
| Design Review | 设计复审 | 60 | 30 |
| Coding Standard | 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 30 | 30 |
| Design | 具体设计 | 60 | 60 |
| Coding | 具体编码 | 300 | 300 |
| Code Review | 代码复审 | 30 | 20 |
| Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 60 | 60 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 60 | 60 |
| Test Repor | 测试报告 | 30 | 20 |
| Size Measurement | 计算工作量 | 20 | 10 |
| Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 60 | 20 |
| Total | 合计 | 1380 | 1210 |