作业①
实验要求
指定一个网站,爬取这个网站中的所有的所有图片,例如:中国气象网(http://www.weather.com.cn)。使用scrapy框架分别实现单线程和多线程的方式爬取。
–务必控制总页数(学号尾数2位)、总下载的图片数量(尾数后3位)等限制爬取的措施。
输出信息:
将下载的Url信息在控制台输出,并将下载的图片存储在images子文件中,并给出截图。
码云连接:https://gitee.com/EI-Shaddoll-Midrash/2023-data-collection/tree/master/作业3/作业3_1
代码展示:
单线程:
MySpider部分:
import scrapy
import urllib.request
from caiji.shiyan3.demo.demo.items import DemoItem
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from bs4 import UnicodeDammit
class MySpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = "mySpider"
def start_requests(self):
url = "http://www.weather.com.cn/"
yield scrapy.Request(url=url, callback=self.parse)
def parse(self, response):
global item
count = 1
try:
dammit = UnicodeDammit(response.body, ["utf-8", "gbk"])
data = dammit.unicode_markup
soup = BeautifulSoup(data, "html.parser")
images = soup.select("img") # 获取图像标签
for image in images:
src = image["src"]
#print(image)
try:
if (src[len(src) - 4] == "."):
ext = src[len(src) - 4:]
else:
ext = ""
req = urllib.request.Request(src)
data = urllib.request.urlopen(req, timeout=100)
data = data.read()
fobj = open("D:/pythonProject/caiji/shiyan3/images/" + str(count) + ext, "wb")
fobj.write(data)
fobj.close()
count +=1
except Exception as err:
print(err)
item = DemoItem()
item["name"] = src.strip() if src else ""
yield item
except Exception as err:
print(err)
items部分:
# Define here the models for your scraped items
#
# See documentation in:
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html
import scrapy
class DemoItem(scrapy.Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
# name = scrapy.Field()
name = scrapy.Field()
pass
pipelines部分
# Define your item pipelines here
#
# Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting
# See: https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
# useful for handling different item types with a single interface
from itemadapter import ItemAdapter
class DemoPipeline:
def process_item(self, item, spider):
try:
print(item["name"])
except Exception as err:
print(err)
return item
settings部分
BOT_NAME = "demo"
SPIDER_MODULES = ["demo.spiders"]
NEWSPIDER_MODULE = "demo.spiders"
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'demo.pipelines.DemoPipeline': 300,
}
# Crawl responsibly by identifying yourself (and your website) on the user-agent
#USER_AGENT = "demo (+http://www.yourdomain.com)"
# Obey robots.txt rules
ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = True
多线程
MySpider部分
import threading
import scrapy
import urllib.request
from caiji.shiyan3.demo1.demo1.items import Demo1Item
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from bs4 import UnicodeDammit
class MySpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = "mySpider1"
def start_requests(self):
url = "http://www.weather.com.cn/"
yield scrapy.Request(url=url, callback=self.parse)
def download(self,url,count):
# 下载图片
try:
if (url[len(url) - 4] == "."):
ext = url[len(url) - 4:]
else:
ext = ""
req = urllib.request.Request(url)
data = urllib.request.urlopen(req, timeout=100)
data = data.read()
fobj = open("D:/pythonProject/caiji/shiyan3/images/" + str(count) + ext, "wb")
fobj.write(data)
fobj.close()
count += 1
except Exception as err:
print(err)
def parse(self, response):
global item
count = 0
threads = []
srcs=[]
try:
dammit = UnicodeDammit(response.body, ["utf-8", "gbk"])
data = dammit.unicode_markup
soup = BeautifulSoup(data, "html.parser")
images = soup.select("img") # 获取图像标签
for image in images:
src = image["src"]
#item中的name
item = Demo1Item()
item["name"] = src.strip() if src else ""
if src not in srcs:
# print(url)
count = count + 1
T = threading.Thread(target=self.download, args=(src, count))
T.daemon = False
T.start()
threads.append(T)
yield item
for t in threads:
t.join()
except Exception as err:
print(err)
items部分
import scrapy
class Demo1Item(scrapy.Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
# name = scrapy.Field()
name = scrapy.Field()
pass
pipelines部分
# Define your item pipelines here
#
# Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting
# See: https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
# useful for handling different item types with a single interface
from itemadapter import ItemAdapter
class DemoPipeline:
def process_item(self, item, spider):
try:
print(item["name"])
except Exception as err:
print(err)
return item
settings部分
BOT_NAME = "demo1"
SPIDER_MODULES = ["demo1.spiders"]
NEWSPIDER_MODULE = "demo1.spiders"
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'demo1.pipelines.DemoPipeline': 300,
}
# Crawl responsibly by identifying yourself (and your website) on the user-agent
#USER_AGENT = "demo1 (+http://www.yourdomain.com)"
# Obey robots.txt rules
ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = True
运行结果
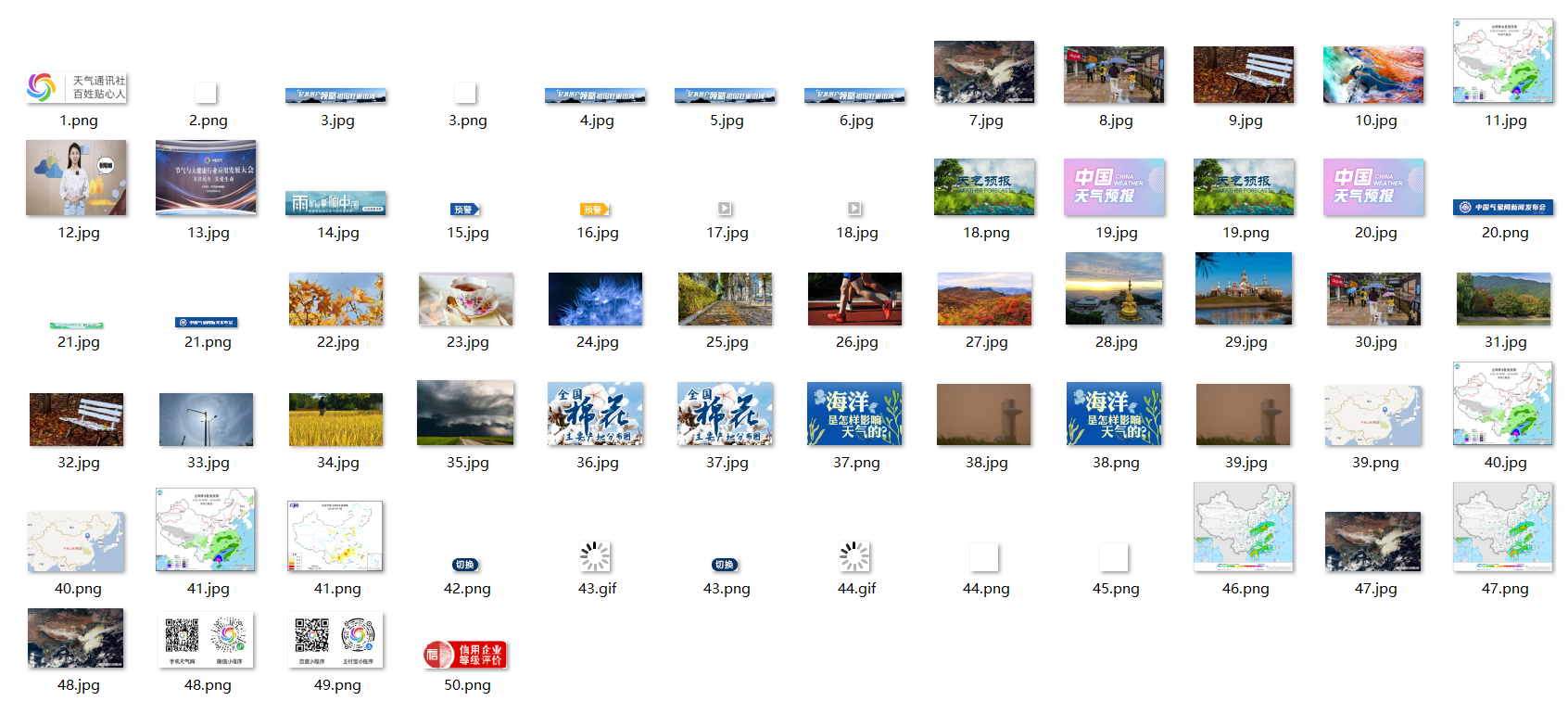
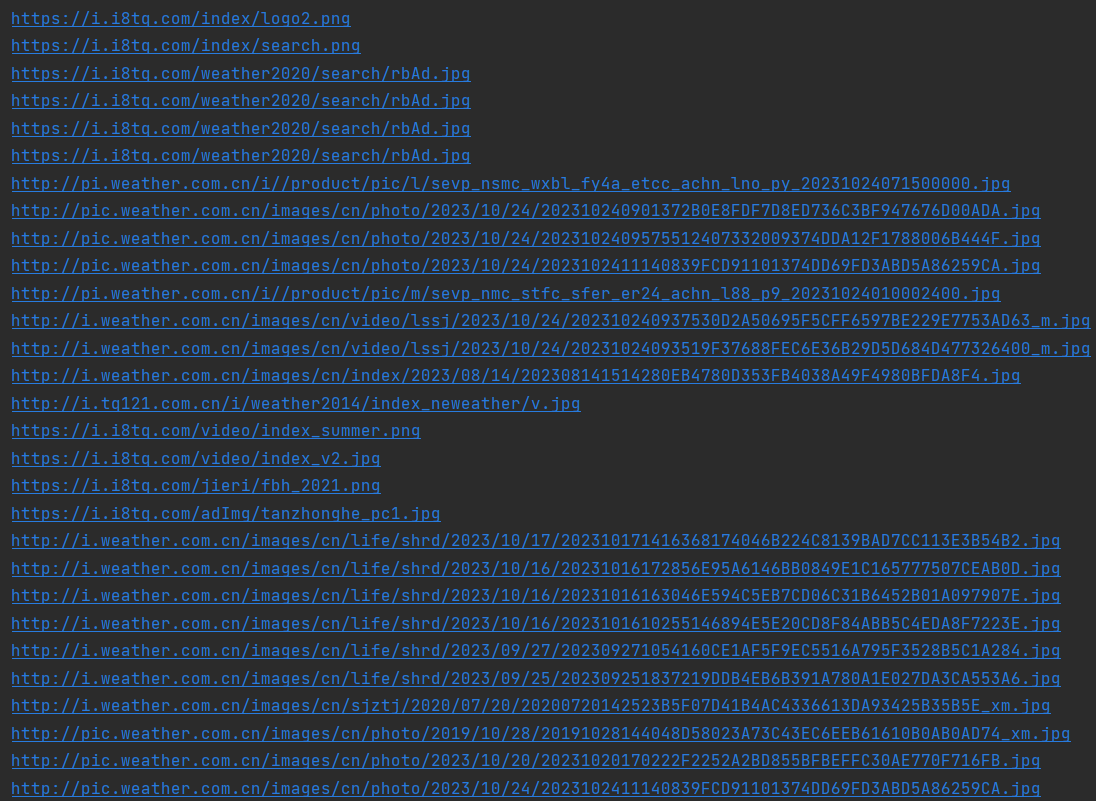
心得体会
这个实验融合了之前做过的多线程和单线程下载图片,还是比较简单的
作业②
实验要求
熟练掌握 scrapy 中 Item、Pipeline 数据的序列化输出方法;使用scrapy框架+Xpath+MySQL数据库存储技术路线爬取股票相关信息。
候选网站:东方财富网:https://www.eastmoney.com/
输出信息:
码云连接:https://gitee.com/EI-Shaddoll-Midrash/2023-data-collection/tree/master/作业3/作业3_2
代码展示
MySpider部分
import scrapy
from lxml import etree
from caiji.shiyan3.demo2.demo2.items import Demo2Item
import time
from selenium import webdriver
class MySpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = "mySpider2"
edge_options = webdriver.EdgeOptions()
edge_options.add_argument('--headless')
edge_options.add_argument('--disable-gpu')
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=edge_options)
# 定义start_requests方法,生成对特定URL的请求并返回该请求
def start_requests(self):
url = 'https://quote.eastmoney.com/center/gridlist.html#hs_a_board' # 要爬取的网页URL
self.driver.get(url)
time.sleep(1) # 等待页面加载完毕
html = etree.HTML(self.driver.page_source) # 获取网页HTML内容
yield scrapy.Request(url, self.parse, meta={'html': html})
# 定义parse方法,用于处理服务器返回的响应
def parse(self, response):
# 定义一个全局变量item,这样在处理响应之外的地方也可以引用到这个变量
global item
html = response.meta['html']
# 获取元素
lis = html.xpath('//*[@id="table_wrapper-table"]/tbody/tr')
for link in lis:
stock_id = link.xpath('./td[2]/a/text()')[0]
stock_name = link.xpath('./td[3]/a/text()')[0]
newest_price = link.xpath('./td[5]/span/text()')[0]
up_down_extent = link.xpath('./td[6]/span/text()')[0]
up_down_value = link.xpath('./td[7]/span/text()')[0]
deal_value = link.xpath('./td[8]/text()')[0]
freq = link.xpath('./td[10]/text()')[0]
highest = link.xpath('./td[11]/span/text()')[0]
lowest = link.xpath('./td[12]/span/text()')[0]
opening = link.xpath('./td[13]/span/text()')[0]
zt = link.xpath('./td[14]/text()')[0]
item = Demo2Item()
item['stock_id'] = stock_id
item['stock_name'] = stock_name
item['newest_price'] = newest_price
item['up_down_extent'] = up_down_extent
item['up_down_value'] = up_down_value
item['deal_value'] = deal_value
item['freq'] = freq
item['highest'] = highest
item['lowest'] = lowest
item['opening'] = opening
item['zt'] = zt
yield item
items部分
# Define here the models for your scraped items
#
# See documentation in:
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html
import scrapy
class Demo2Item(scrapy.Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
# name = scrapy.Field()
stock_id = scrapy.Field()
stock_name = scrapy.Field()
newest_price = scrapy.Field()
up_down_extent = scrapy.Field()
up_down_value = scrapy.Field()
deal_volume = scrapy.Field()
deal_value = scrapy.Field()
freq = scrapy.Field()
highest = scrapy.Field()
lowest = scrapy.Field()
opening = scrapy.Field()
zt = scrapy.Field()
pass
pipelines部分
# Define your item pipelines here
#
# Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting
# See: https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
# useful for handling different item types with a single interface
import pymysql
class DemoPipeline:
def process_item(self, item, spider):
# print(
# item['stock_id'], item['stock_name'], item['newest_price'], item['up_down_extent'], item['up_down_value'],
# item['deal_value'], item['freq'], item['highest'],
# item['lowest'], item['opening'], item['zt'])
# 使用数据库录入数据
try:
mydb = pymysql.connect(host="127.0.0.1", port=3306, user="root", passwd="123456", db="mydb",charset="utf8")
mycursor = mydb.cursor()
sql = "INSERT INTO demo2 (stock_id, stock_name, newest_price, up_down_extent, up_down_value,deal_value, " \
"freq, highest, lowest, opening, zt) VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s)"
val = (item['stock_id'], item['stock_name'], item['newest_price'], item['up_down_extent'], item['up_down_value'],item['deal_value'], item['freq'], item['highest'],item['lowest'], item['opening'], item['zt'])
mycursor.execute(sql, val)
mydb.commit()
except Exception as err:
print(err)
return item
settings部分
BOT_NAME = "demo2"
SPIDER_MODULES = ["demo2.spiders"]
NEWSPIDER_MODULE = "demo2.spiders"
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'demo2.pipelines.DemoPipeline': 300,
}
# Crawl responsibly by identifying yourself (and your website) on the user-agent
#USER_AGENT = "demo2 (+http://www.yourdomain.com)"
# Obey robots.txt rules
ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = True
运行结果
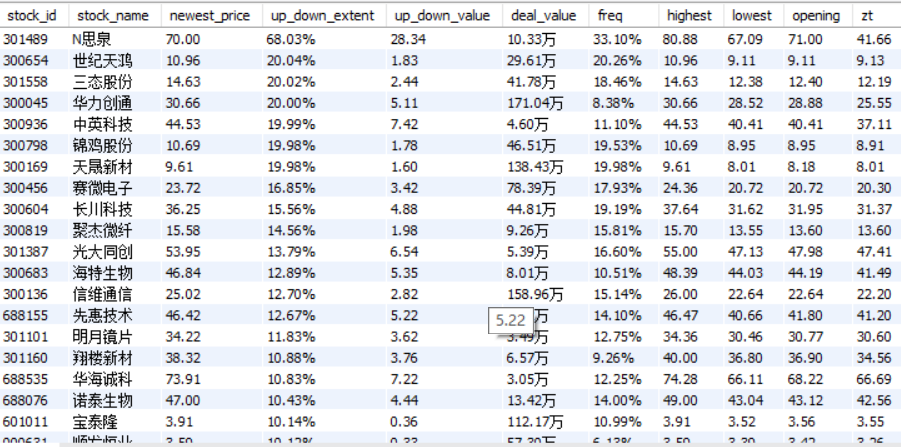
心得体会
这个实验比实验一难了许多,需要使用pymysql库连接数据库。然后对数据库进行操作。刚开始发现pipelines能输出股票数据但数据库中没有股票数据,发现原因是在数据库操作系统中没有建立相应的数据库和相对应的表,完成后成功实现。
作业③
实验要求
熟练掌握 scrapy 中 Item、Pipeline 数据的序列化输出方法;使用scrapy框架+Xpath+MySQL数据库存储技术路线爬取股票相关信息。
候选网站:东方财富网:https://www.eastmoney.com/
输出信息:
码云链接:https://gitee.com/EI-Shaddoll-Midrash/2023-data-collection/tree/master/作业3/作业3_3
代码展示
MySpider部分
import time
import scrapy
from lxml import etree
from caiji.shiyan3.demo3.demo3.items import Demo3Item
from selenium import webdriver
class MySpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = "mySpider3"
edge_options = webdriver.EdgeOptions()
edge_options.add_argument('--headless')
edge_options.add_argument('--disable-gpu')
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=edge_options)
# 定义start_requests方法,生成对特定URL的请求并返回该请求
def start_requests(self):
url = 'https://www.boc.cn/sourcedb/whpj/' # 要爬取的网页URL
self.driver.get(url)
time.sleep(1) # 等待页面加载完毕
html = etree.HTML(self.driver.page_source) # 获取网页HTML内容
yield scrapy.Request(url, self.parse, meta={'html': html})
# 定义parse方法,用于处理服务器返回的响应
def parse(self, response):
# 定义一个全局变量item,这样在处理响应之外的地方也可以引用到这个变量
global item
html = response.meta['html']
lis = html.xpath('/html/body/div/div[5]/div[1]/div[2]/table/tbody/tr')
i = 1
#获取元素
for link in lis:
if i != 1:
texts = link.xpath('./td[1]/text()')
if texts:
name = texts[0]
else:
name = ''
texts = link.xpath('./td[2]/text()')
if texts:
TBP = texts[0]
else:
TBP = ''
texts = link.xpath('./td[3]/text()')
if texts:
CBP = texts[0]
else:
CBP = ''
texts = link.xpath('./td[4]/text()')
if texts:
TSP = texts[0]
else:
TSP = ''
texts = link.xpath('./td[5]/text()')
if texts:
CSP = texts[0]
else:
CSP = ''
texts = link.xpath('./td[8]/text()')
if texts:
TIME = texts[0]
else:
TIME = ''
item = Demo3Item()
item["currency"] = name
item["TBP"] = TBP
item["CBP"] = CBP
item["TSP"] = TSP
item["CSP"] = CSP
item["time"] = TIME
yield item
if i == 1:
i = i + 1
items部分
# Define here the models for your scraped items
#
# See documentation in:
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html
import scrapy
class Demo3Item(scrapy.Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
# name = scrapy.Field()
currency = scrapy.Field()
TSP = scrapy.Field()
CSP = scrapy.Field()
TBP = scrapy.Field()
CBP = scrapy.Field()
time = scrapy.Field()
pass
pipelines部分
# Define your item pipelines here
#
# Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting
# See: https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
# useful for handling different item types with a single interface
from itemadapter import ItemAdapter
import pymysql
class DemoPipeline:
def process_item(self, item, spider):
try:
print(item["currency"])
print(item["TSP"])
print(item["CSP"])
print(item["TBP"])
print(item["CBP"])
print(item["time"])
print()
# 将数据插入数据库的表中
mydb = pymysql.connect(host="127.0.0.1", port=3306, user="root", passwd="123456", db="mydb", charset="utf8")
mycursor = mydb.cursor()
sql="insert into currency (currency,TSP,CSP,TBP,CBP,time) values (%s,%s,%s,%s,%s,%s)"
val=(item["currency"], item["TSP"], item["CSP"], item["TBP"], item["CBP"], item["time"])
mycursor.execute(sql, val)
mydb.commit()
except Exception as err:
print(err)
return item
settings部分
BOT_NAME = "demo3"
SPIDER_MODULES = ["demo3.spiders"]
NEWSPIDER_MODULE = "demo3.spiders"
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'demo3.pipelines.DemoPipeline': 300,
}
# Crawl responsibly by identifying yourself (and your website) on the user-agent
#USER_AGENT = "demo3 (+http://www.yourdomain.com)"
# Obey robots.txt rules
ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = True
输出结果
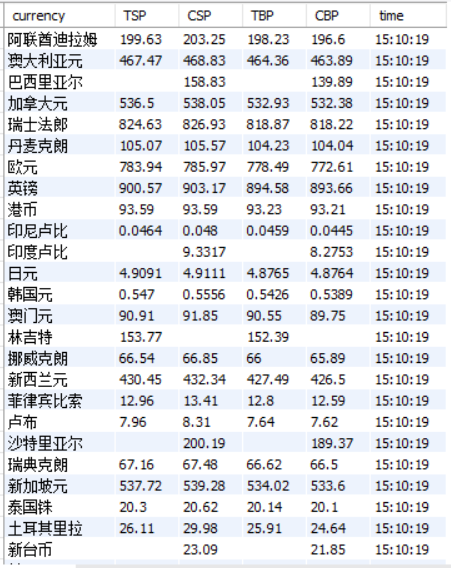
心得体会
这个实验和实验2类似,但元素获取需要甄别。