链表面试题解析
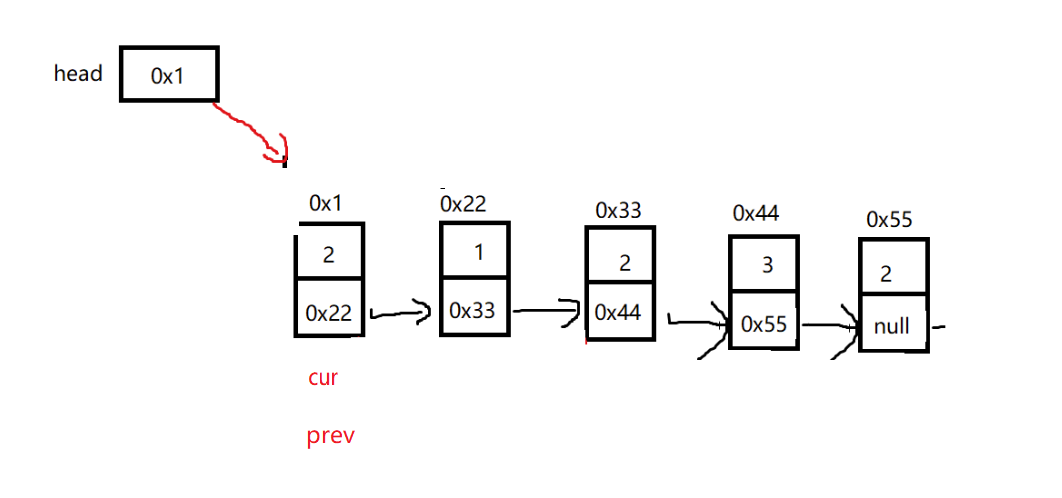
1. 删除链表中=val的所有节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode prev = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == val) {
// 处理头删
if (cur == head) {
head = head.next;
}else {
prev.next = cur.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}else {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
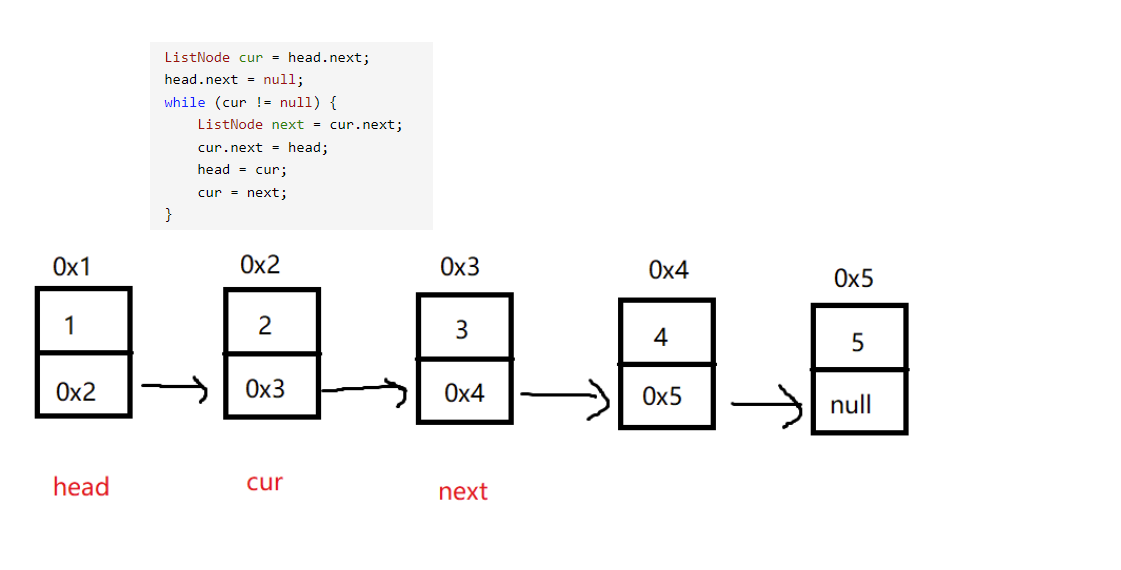
2. 反转一个单链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 处理链表为空
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
// 处理链表一个节点
if (head.next == null) {
return head;
}
// 节点 >=2 正常情况反转链表
ListNode cur = head.next;
head.next = null;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = head;
head = cur;
cur = next;
}
return head;
}
}
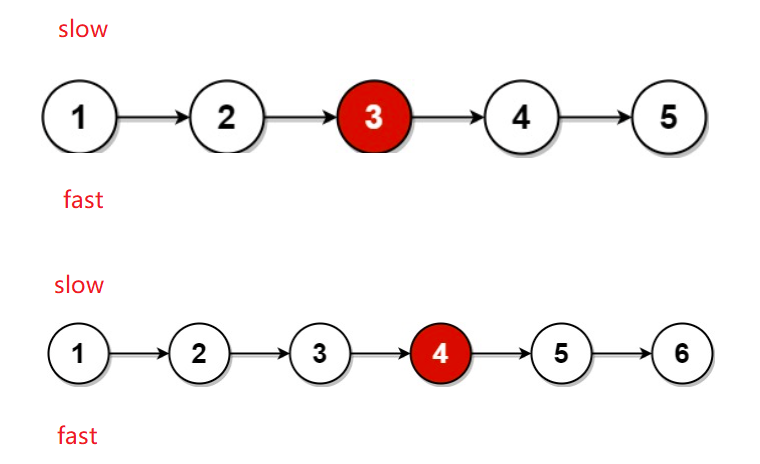
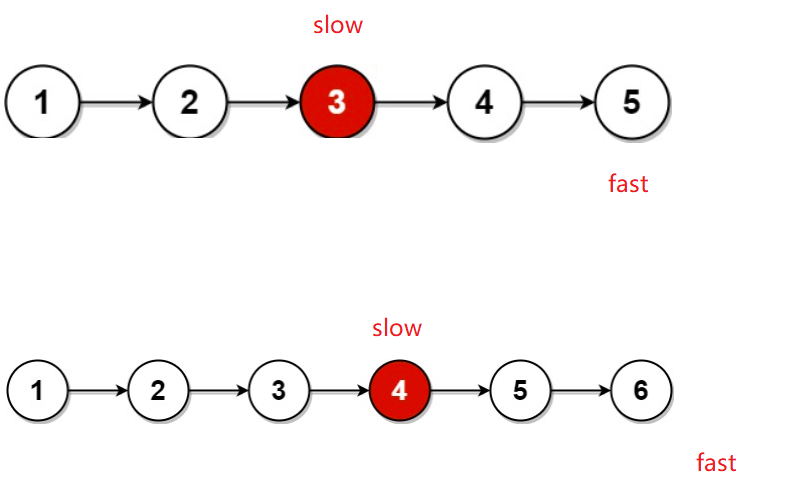
3. 判断链表的中间结点
思路:
慢指针每次走一步 快指针每次走两步,当快指针走完 慢指针所在位置就是链表的中心节点
注意:判断条件一定得这样写 (fast != null && fast.next != null) ,因为如果是偶数个节点 fast走到最后是null, fast.next写在前面会访问空指针异常
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
4. 返回倒数第 k 个节点
思路:
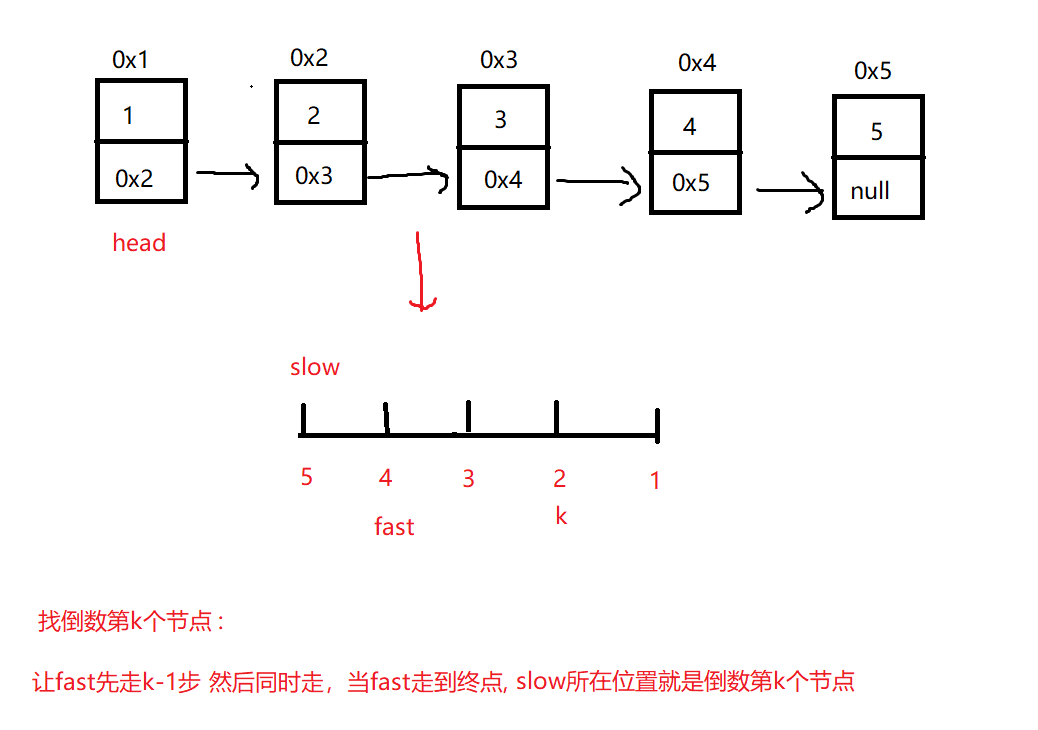
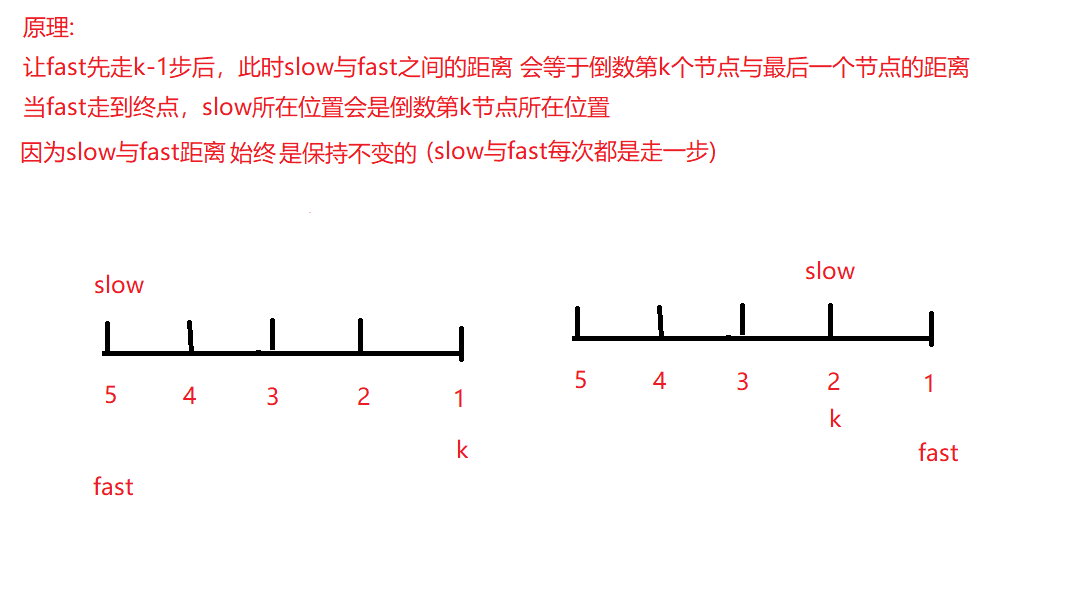
import java.util.*;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
if (k < 0) {
return null;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = fast;
// 让fast先走k-1步
int count = 0;
while (count != k-1) {
// 当fast.next == null, fast还没有走完k-1步
// 说明k超过节点大小 不能拿到倒数第k个节点,返回null
if (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
count++;
}else {
return null;
}
}
// 然后同时走
while (fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
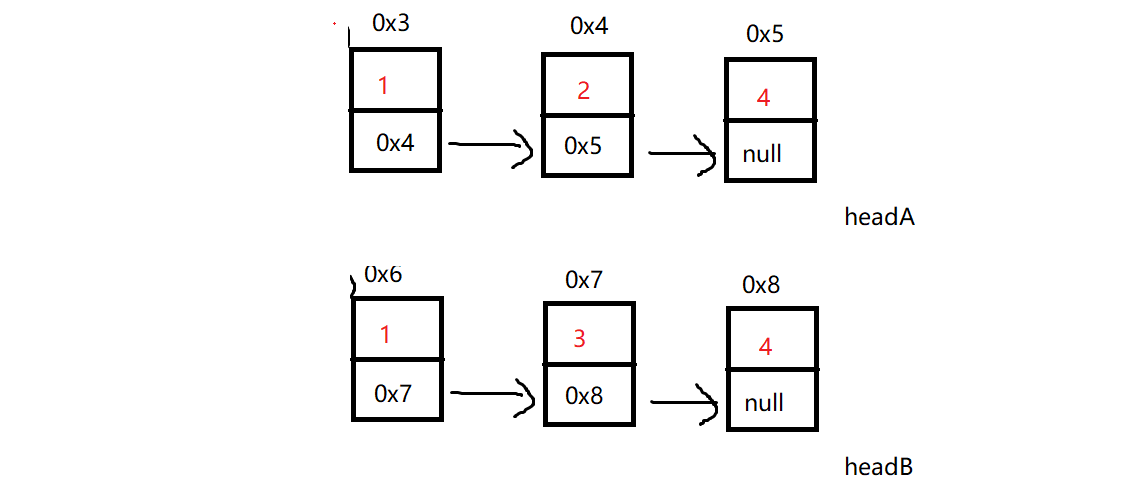
}5. 合并两个有序链表
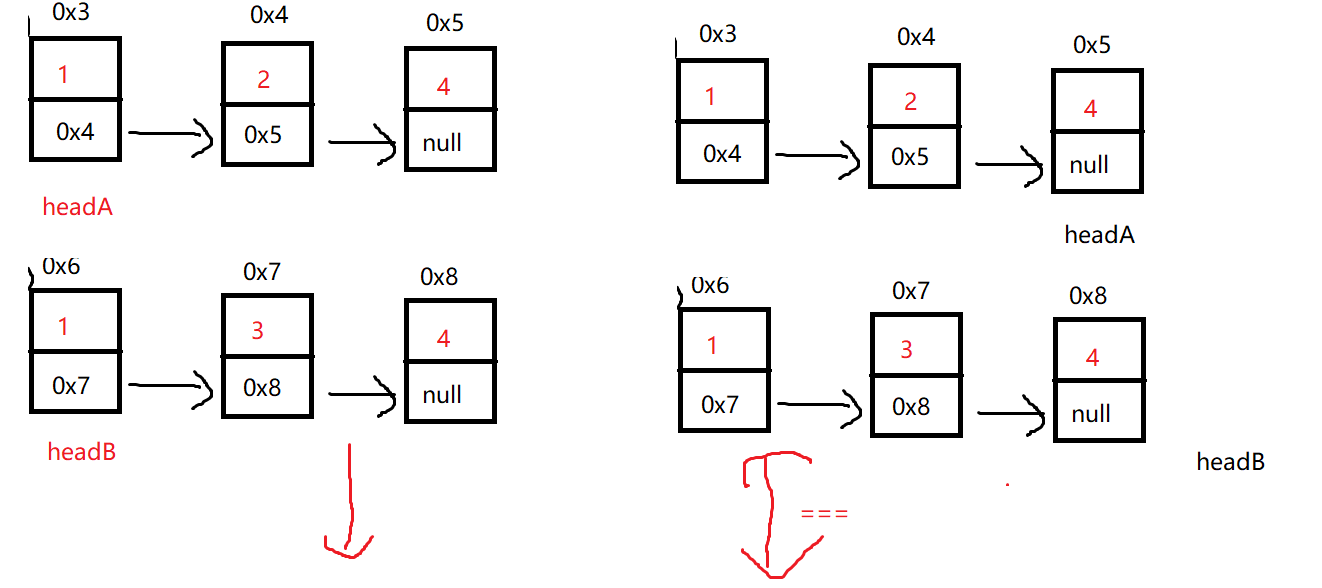
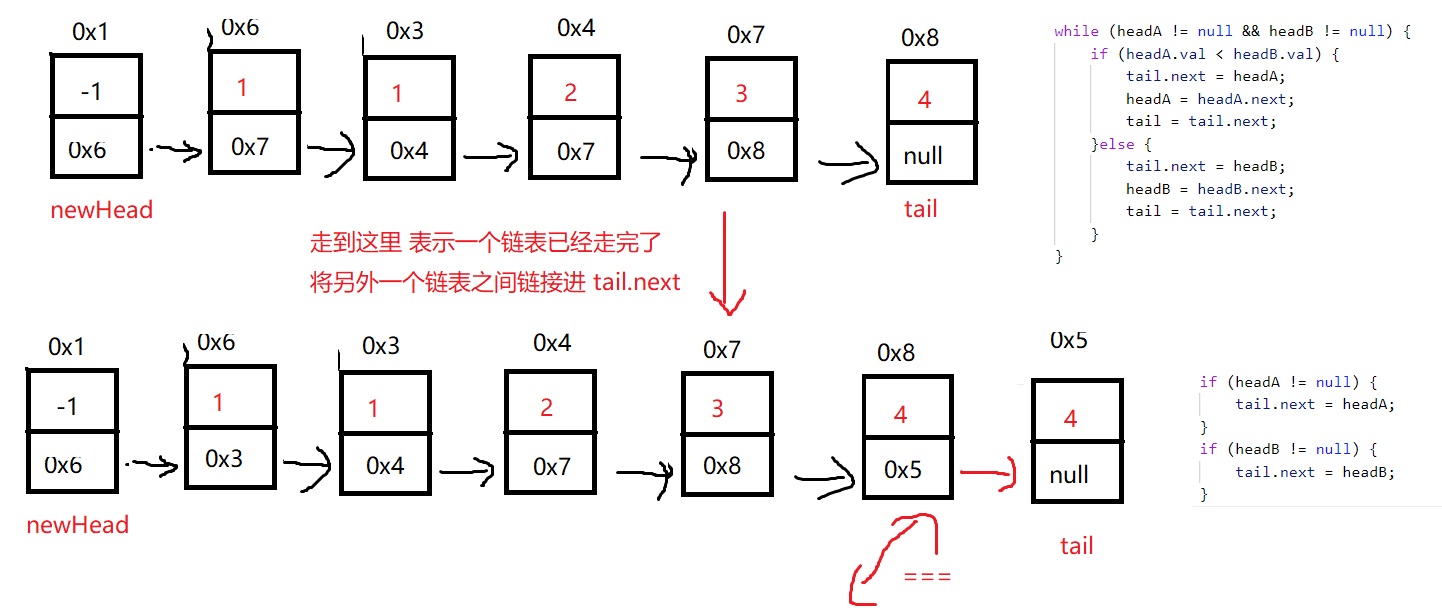
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode tail = newHead;
while (headA != null && headB != null) {
if (headA.val < headB.val) {
tail.next = headA;
headA = headA.next;
tail = tail.next;
}else {
tail.next = headB;
headB = headB.next;
tail = tail.next;
}
}
if (headA != null) {
tail.next = headA;
}
if (headB != null) {
tail.next = headB;
}
return newHead.next;
}
}6. 分割链表
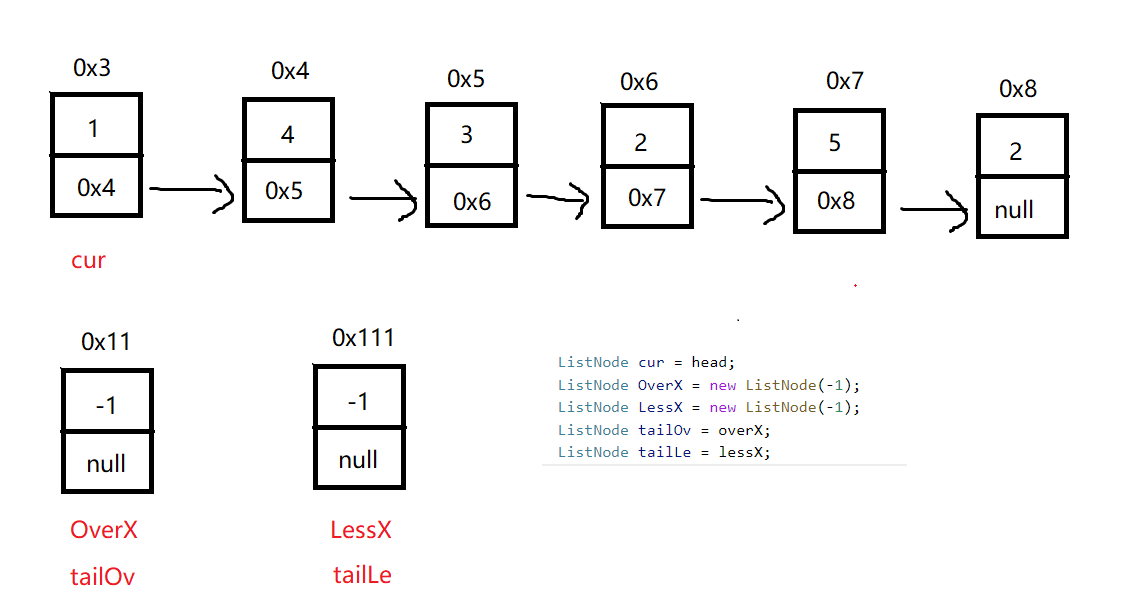
使用虚拟节点:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode overX = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode lessX = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode tailOv = overX;
ListNode tailLe = lessX;
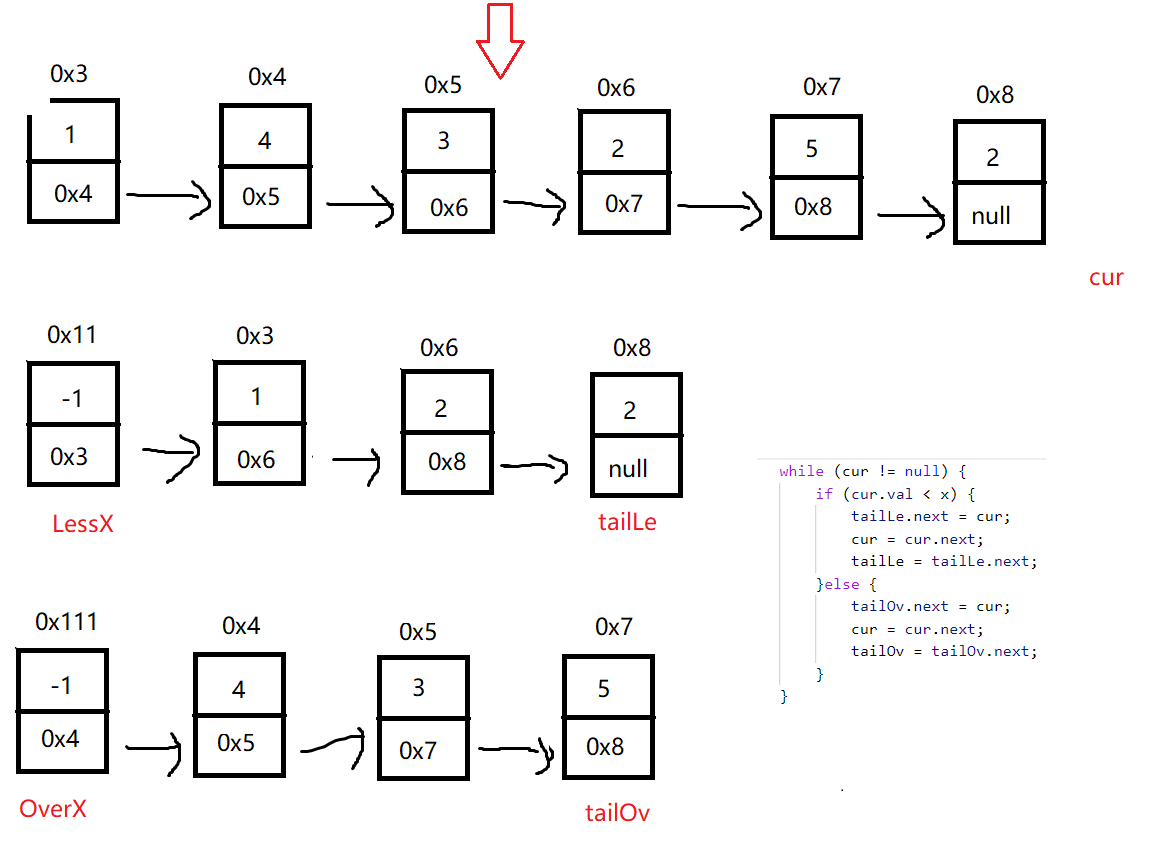
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val < x) {
tailLe.next = cur;
cur = cur.next;
tailLe = tailLe.next;
}else {
tailOv.next = cur;
cur = cur.next;
tailOv = tailOv.next;
}
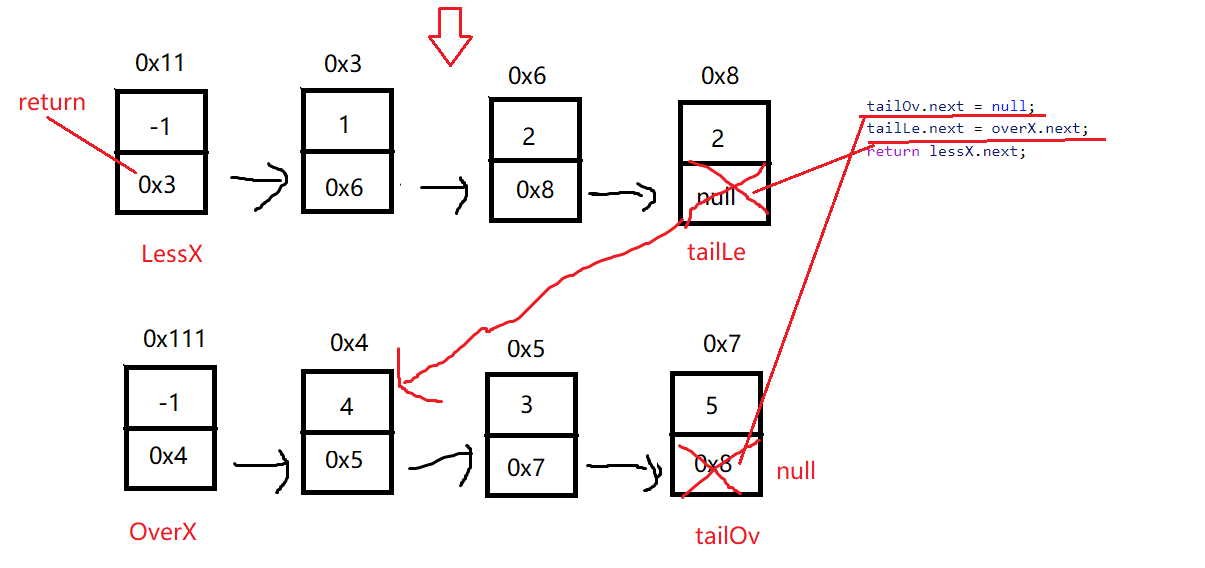
}
tailOv.next = null;
tailLe.next = overX.next;
return lessX.next;
}
}不使用虚拟节点:
解决思路与上面一样 只是多了些判断
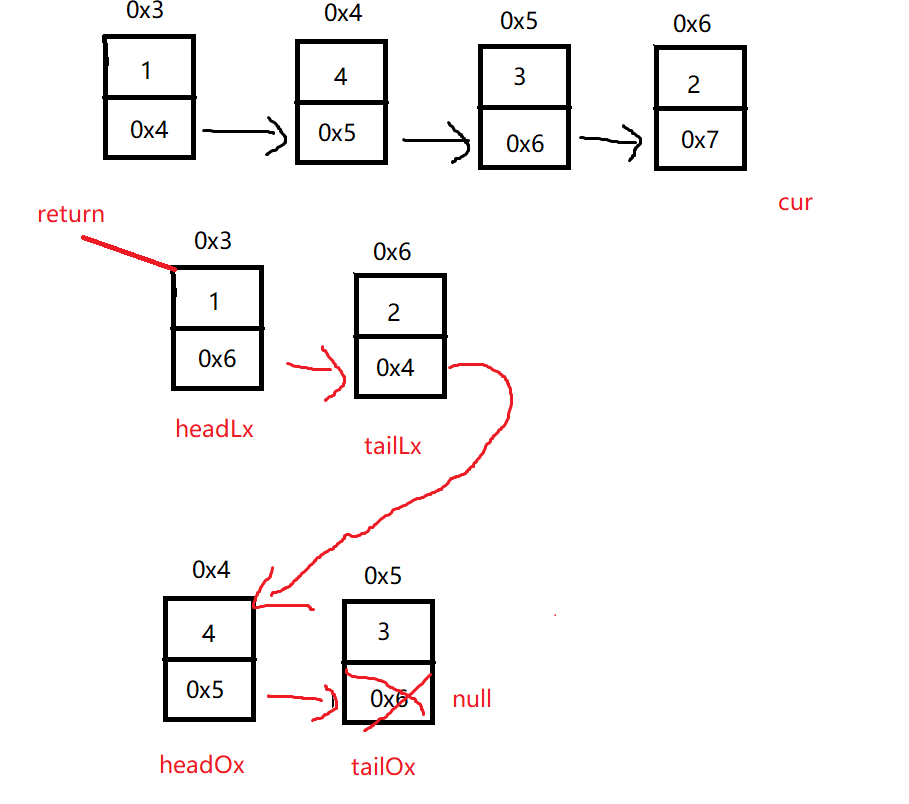
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
// 处理空链表
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode headOx = null;
ListNode headLx = null;
ListNode tailOx = null;
ListNode tailLx = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val < x){
// < x
if (headLx == null) {
headLx = cur;
tailLx = headLx;
}else {
tailLx.next = cur;
tailLx = tailLx.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}else {
// >= x
if (headOx == null) {
headOx = cur;
tailOx = headOx;
}else {
tailOx.next = cur;
tailOx = tailOx.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
// 分割链表后可能 headLx为空 或者 headOx为空,但是不可能都为空
if (headLx == null) {
return headOx;
}
// 走到这里表示< x 的链表不为空,直接链接headOx
// 可以直接链接是因为 无论 val > x 链表是否有节点都对结果不影响
// 为空: headOx = null, tailLx.next = headOx(null)
tailLx.next = headOx;
// 但是最后需要判断 因为最后一个节点得置空
if (tailOx != null)
tailOx.next = null;
return headLx;
}
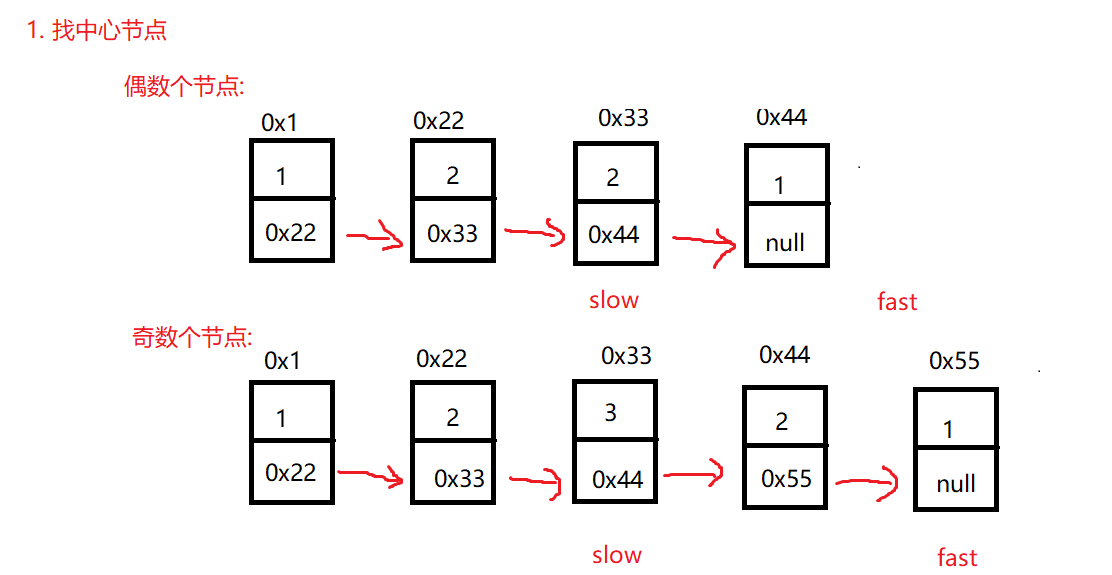
}7. 回文链表
方法1: 思路
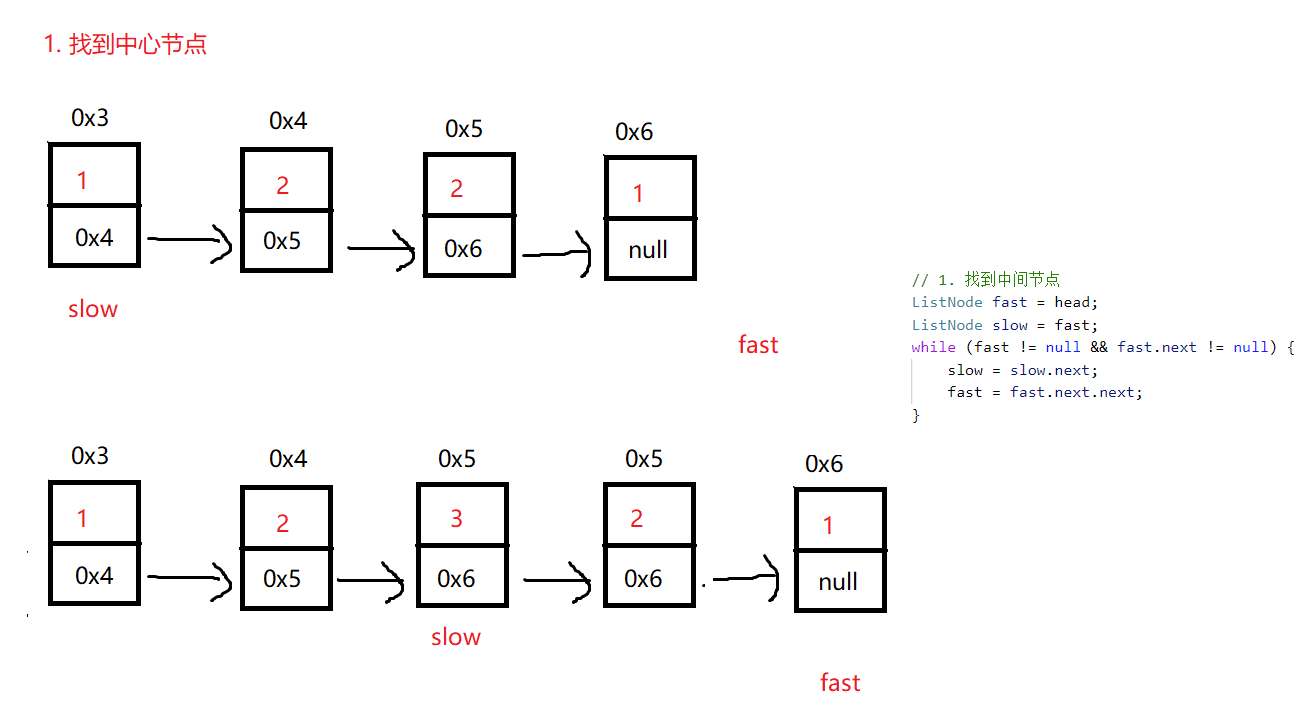
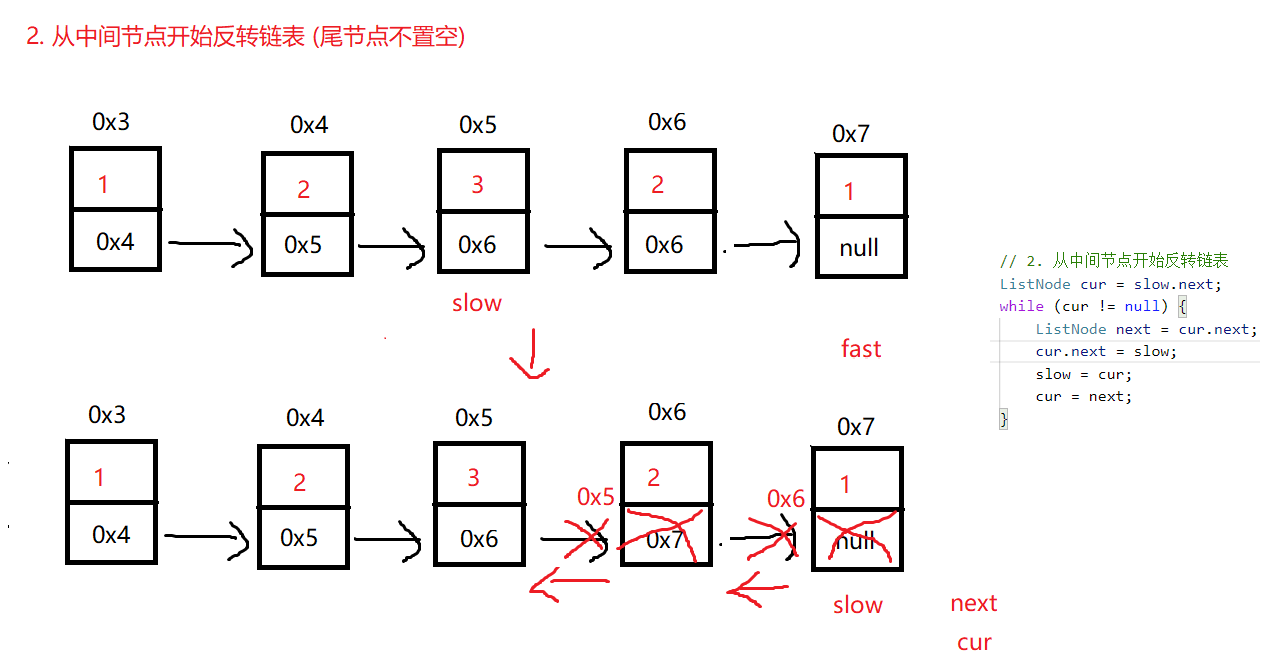
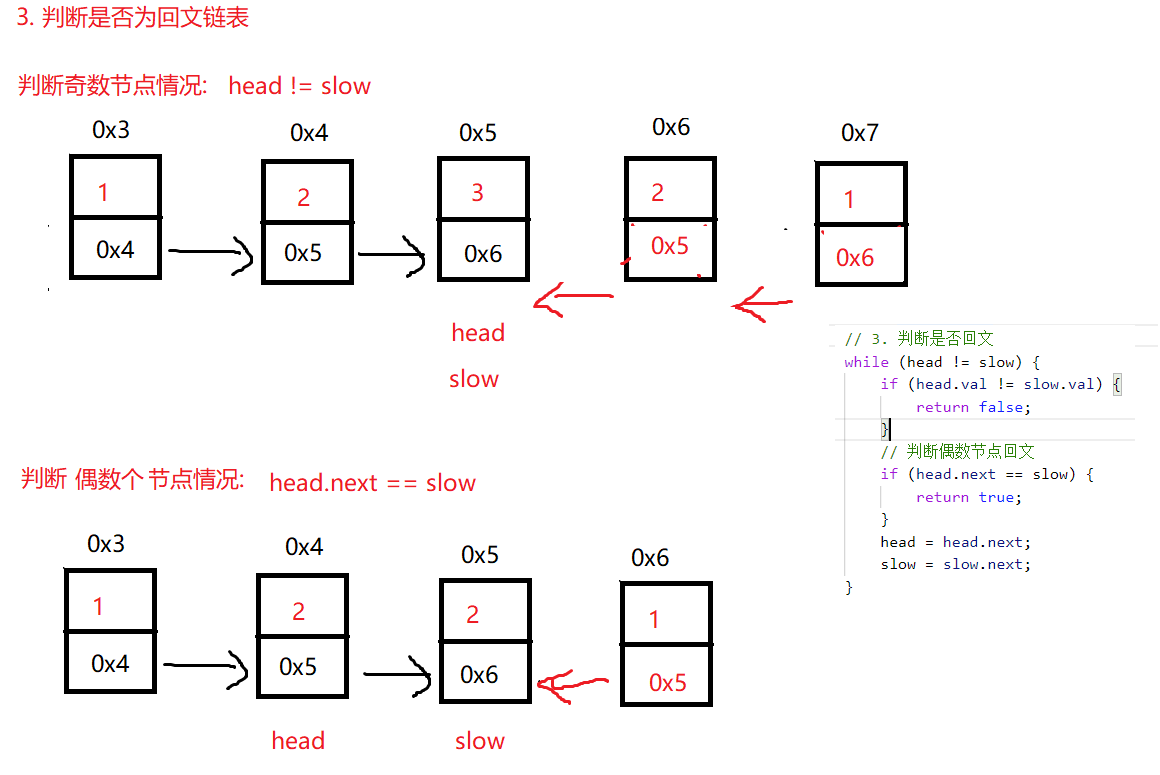
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, L istNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
// 1. 找到中间节点
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = fast;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// 2. 从中间节点开始反转链表
ListNode cur = slow.next;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = slow;
slow = cur;
cur = next;
}
// 3. 判断是否回文
while (head != slow) {
if (head.val != slow.val) {
return false;
}
// 判断偶数节点回文
if (head.next == slow) {
return true;
}
head = head.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
// 走到这表示奇数个节点链表为回文
return true;
}
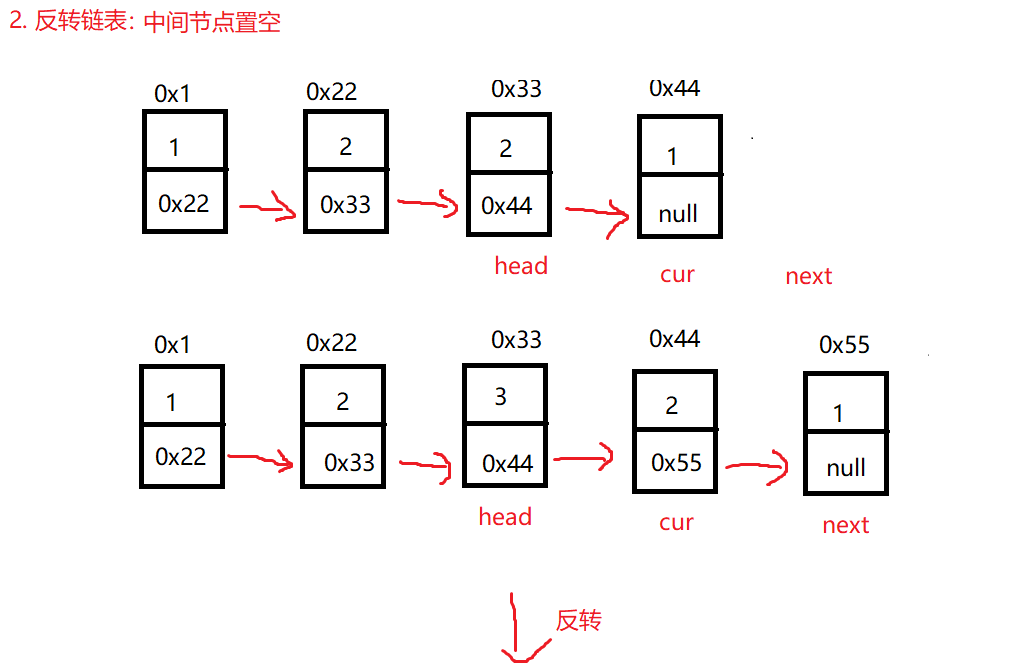
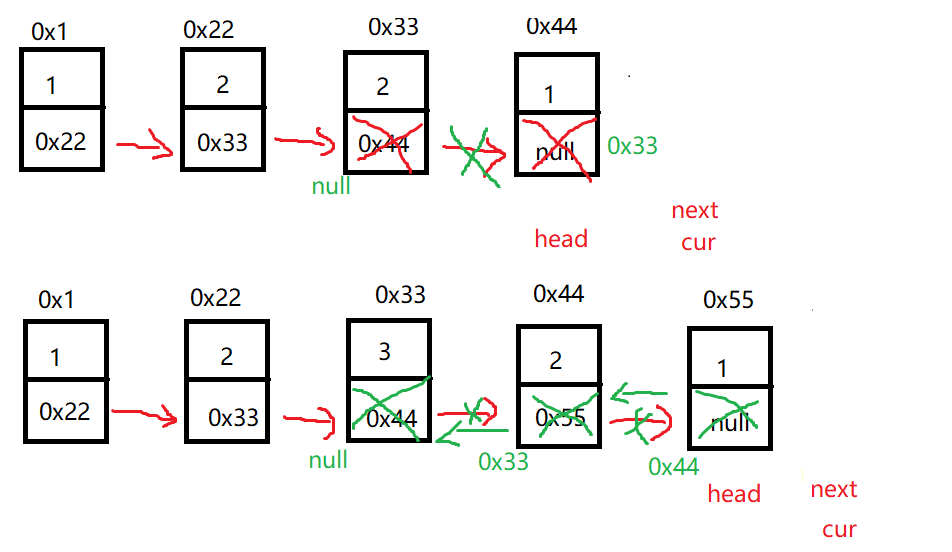
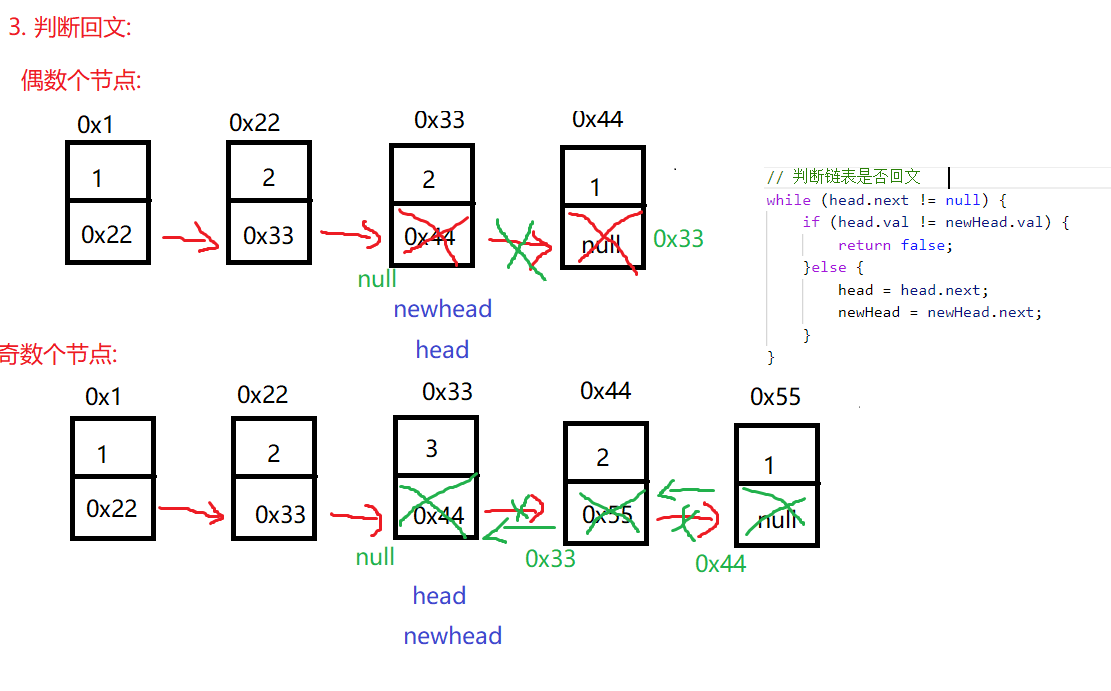
}方法2:
解题的思路与方法1一样 只是在反转链表时将中间节点置空 然后判断回文
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode findMiddleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = fast;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head.next;
head.next = null;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = head;
head = cur;
cur = next;
}
return head;
}
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
ListNode midNode = findMiddleNode(head);
ListNode newHead = reverseList(midNode);
// 判断链表是否回文
while (head.next != null) {
if (head.val != newHead.val) {
return false;
}else {
head = head.next;
newHead = newHead.next;
}
}
return true;
}
}8. 相交链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
// 1. 计算两个链表长度
ListNode curL = headA; // curL指向长链表
ListNode curS = headB; // curS指向短链表
int lenL = 0;
int lenS = 0;
while (curL != null) {
lenL++;
curL = curL.next;
}
while (curS != null) {
lenS++;
curS = curS.next;
}
curL = headA;
curS = headB;
// 2. 让curL先走差距步
int gap = lenL - lenS;
if (gap < 0) {
curL = headB;
curS = headA;
gap = lenS - lenL;
}
while (gap != 0) {
curL = curL.next;
gap--;
}
// 3. 同时走 判断链表是否相交
// 判断方法1:
// while (curL != null && curS != null) {
// if (curL == curS) {
// return curL;
// }
// curL = curL.next;
// curS = curS.next;
// }
// return null;
// 判断方法2:
while (curL != null && curS != null && curL != curS) {
curL = curL.next;
curS = curS.next;
}
if (curL == curS && curL == null) return null;
return curL;
}
}9. 环形链表
解题思路:
slow慢指针一次走一步 fast快指针一次走两步, 如果快指针与慢指针在圈内相遇 该链表就是环形链表
问题:
1. 为什么可以用快慢指针思路解这道题 ?
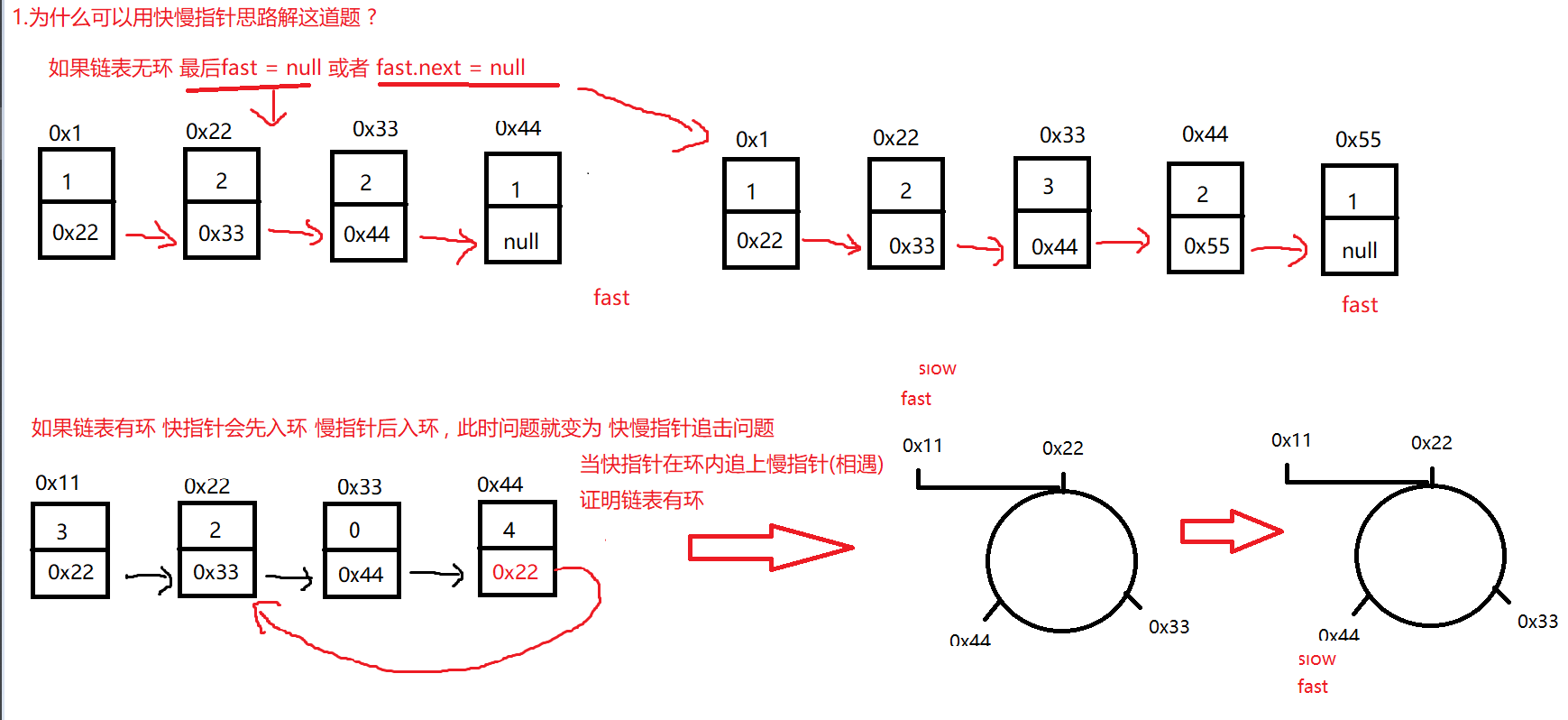
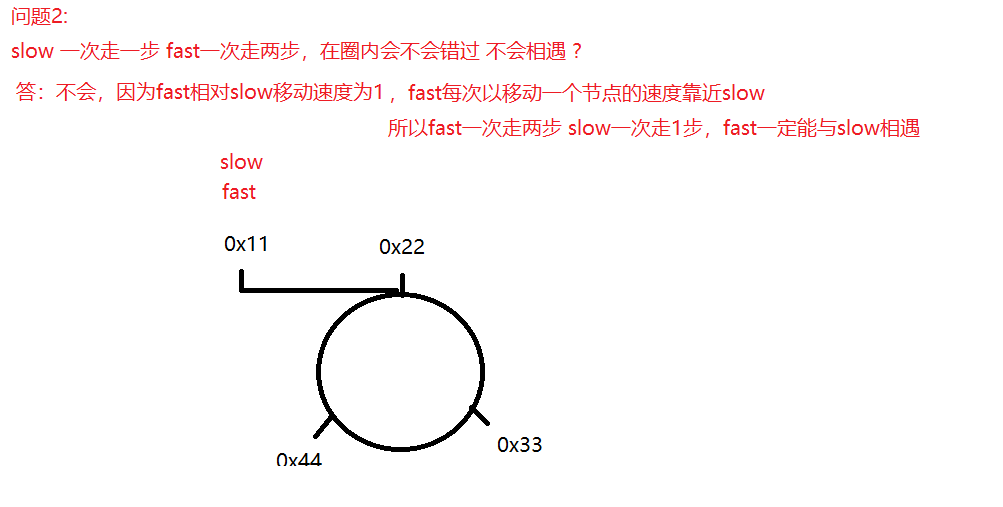
slow 一次走一步 fast一次走两步,在圈内会不会错过 不会相遇 ?
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = slow;
// 有可能链表不是环形
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}10. 找环形链表入口点
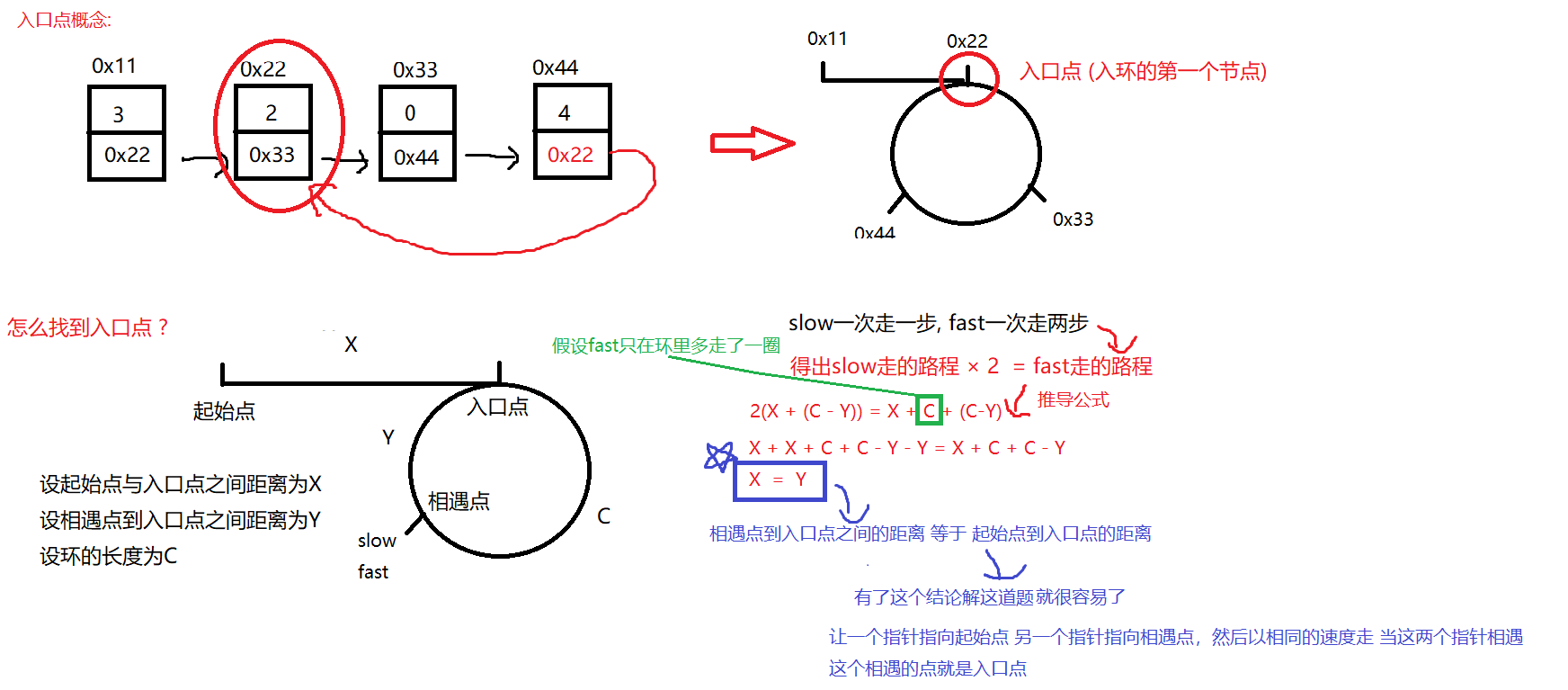
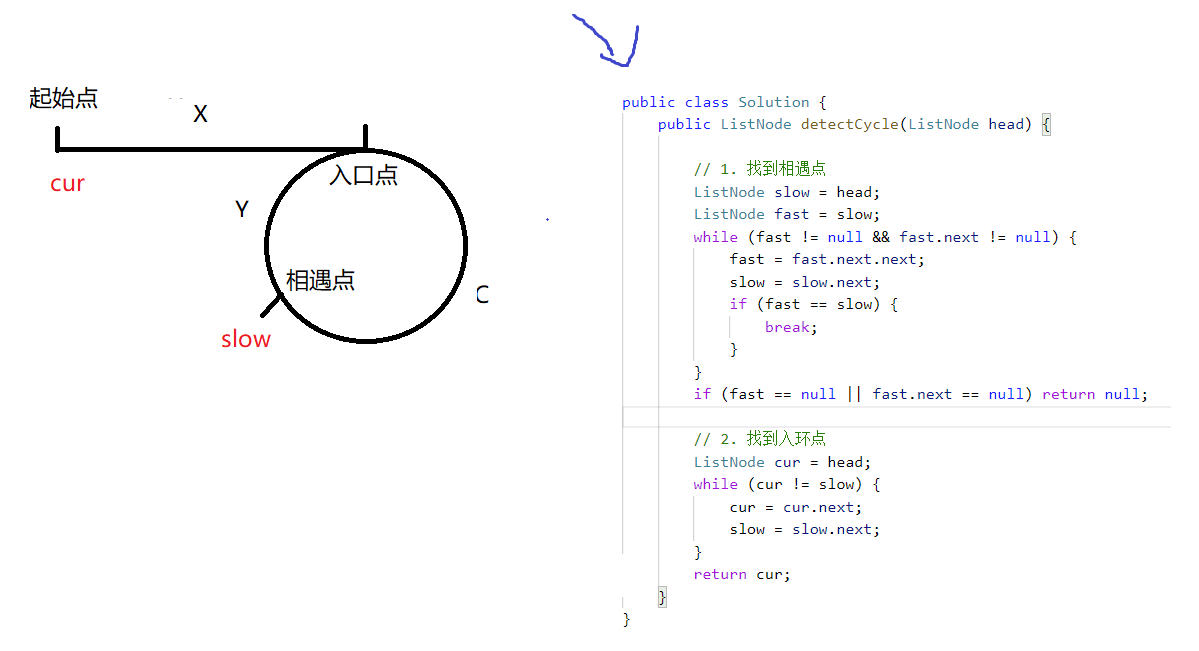
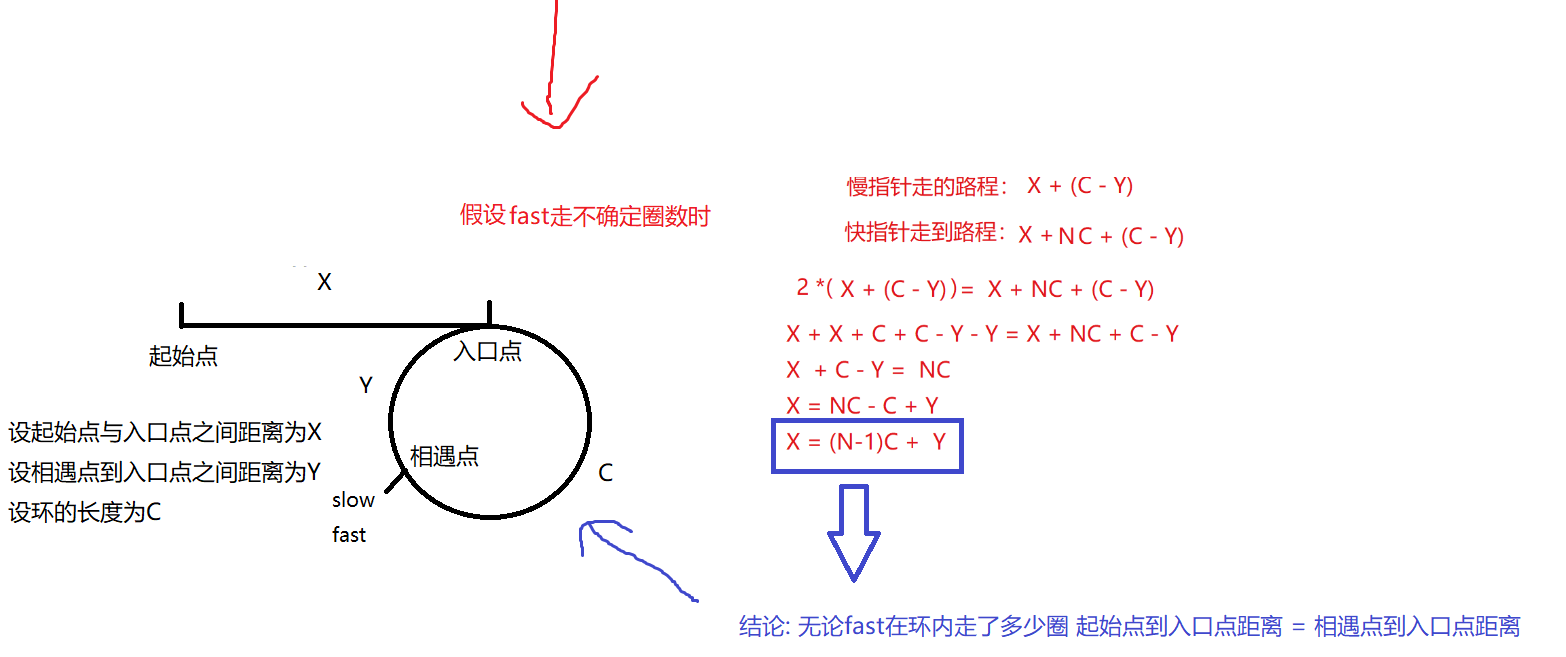
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
// 1. 找到相遇点
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = slow;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) {
break;
}
}
// 走到这里 有两种情况:
// 1. fast走到null(偶数节点) 或者 fast.next = null(奇数节点) ——》 无环
// 2. fast与slow相遇后break
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) return null;
// 2. 找到入环点
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != slow) {
cur = cur.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return cur;
}
}