package homework; import javax.swing.*; class text { public static void main(String[] a) { int i=1, j=0, k; k=i/j; try { k = i/j; // Causes division-by-zero exception //throw new Exception("Hello.Exception!"); } catch ( ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("算式错误"+ e.getMessage()); } catch (Exception e) { if (e instanceof ArithmeticException) System.out.println("算式错误"); else { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } finally { JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(null,"OK"); } } }

多层异常捕获,try-catch像if一样可以嵌套使用,catch是优先原则,先捕捉到异常后就停止不会再进行后续的catch判断。
public class CatchWho2 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { try { throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "try-catch"); } throw new ArithmeticException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("ArithmeticException"); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/try-catch"); } } }

package homework; public class text { public static void main(String args[]) { int result; try { System.out.println("in Level 1"); try { System.out.println("in Level 2"); // result=100/0; //Level 2 try { System.out.println("in Level 3"); result=100/0; //Level 3 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 3:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 3 finally"); } // result=100/0; //Level 2 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 2:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 2 finally"); } // result = 100 / 0; //level 1 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 1:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { . System.out.println("In Level 1 finally"); } } }
在Level 中,没有发生任何异常,因此不执行任何操作。
在Level 2中,发生了一个除以零的异常,该异常被第二个catch块捕获并处理。在catch块中,输出了异常的类型。无论是否发生异常,finally块都会执行,输出"In Level 2 finally"。
在Level 3中,同样发生了一个除以零的异常。这个异常被第三个catch块捕获并处理。在catch块中,输出了异常的类型。无论是否发生异常,finally块都会执行,输出"In Level 3 finally"。

当发生异常时,程序会按照从内到外的顺序执行相应的catch块,并在最后执行finally块。
package homework; public class text { public static void main(String[] args) { try{ System.out.println("in main"); throw new Exception("Exception is thrown in main"); //System.exit(0); } catch(Exception e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); System.exit(0); } finally { System.out.println("in finally"); } } }

由于System.exit(0)的存在,程序会在抛出异常后立即终止,不会继续执行后面的代码。因此,"in finally"这一行代码不会被输出。
追踪异常的传播路径
package homework; public class text { public static void main( String args[] ) { try { method1(); } catch ( Exception e ) { System.err.println( e.getMessage() + "\n" ); e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void method1() throws Exception { method2(); } public static void method2() throws Exception { method3(); } public static void method3() throws Exception { throw new Exception( "Exception thrown in method3" ); } }
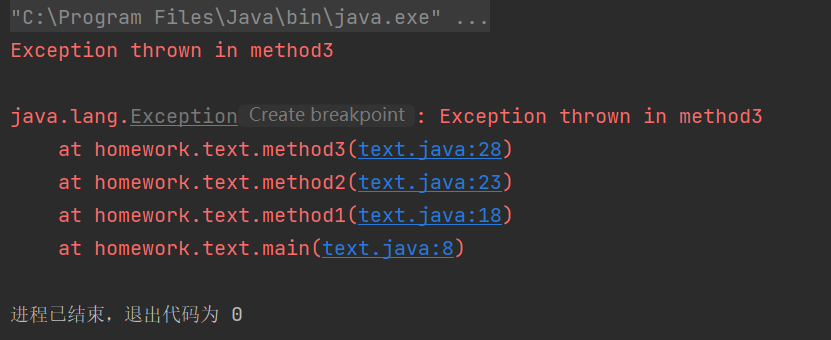
在main方法中,调用了method1方法。如果method1抛出异常,catch块将捕获该异常并打印异常信息和堆栈跟踪。
method1方法调用method2方法,method2方法调用method3方法。method3方法直接抛出一个带有消息"Exception thrown in method3"的异常。
package homework; import java.io.*; public class text { public static void main(String[] args) { try { throwsTest(); } catch(IOException e) { System.out.println("主函数异常"); } } private static void throwsTest() throws ArithmeticException,IOException { System.out.println("函数异常"); throw new IOException(); //throw new ArithmeticException(); } }

当一个方法声明抛出多个异常时,在此方法调用语句处只要catch其中任何一个异常,代码就可以正常运行