问题现象
线上数据库出现数据无法写入,排查发现有一个truncate table操作导致system lock系统锁。
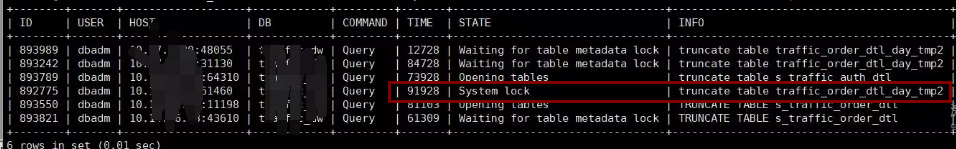
truncate引起system lock分析
truncate table通过释放存储表数据所用的数据页来删除数据,并且只在事务日志中记录页的释放,不记录每行删除的日志。
truncate是把表中数据全部清空,需要有drop权限;
truncate操作分为drop table 和create table操作;
truncate不记录二进制日志且无法回滚;
truncate如果有外键,则不能执行;
truncate结果正常显示0行受影响,表示无信息;
truncate操作将自增值重置为起始值;
truncate分区表,保留分区信息;
现象:
空间紧张,需要清除历史数据,有一个大表可以全部清空,我们知道这种操作,truncate最为擅长。但在truncate过程中,出现system lock,导致CPU升高,性能下降。
分析:
MySQL实例中的所有数据库都维护一个查询缓存,它们之间实际上没有隔离。truncate将不得不使查询缓存中的所有依赖查询失效,这可能是锁定的原因。如果查询缓存足够大,则删除缓存可能需要更长时间。
MySQL在5.5.23版本之前的处理方式即同步模式:
当要drop table的时候,会在整个操作过程中持有buffer pool的mutex,然后扫描两次LRU链表,把属于这个table的page失效掉,buffer pool中page的个数越多,持有mutex时间就会越长,对在线业务的影响也就越明显。
MySQL在5.5.23版本之后,对drop table的处理做了修改,即在扫描LRU链表过程中,如果dirty page属于drop table,那么就直接从flush list中remove掉,如果删除的page个数超过了1024个数目的话,释放buffer pool mutex,flush list mutex,释放cpu资源,重新持有mutex再释放。
buf_LRU_flush_or_remove_pages(id, BUF_REMOVE_FLUSH_NO_WRITE, 0);
buf_pool_mutex_enter(buf_pool);
err = buf_flush_or_remove_pages(buf_pool, id, flush, trx);
......
buf_pool_mutex_exit(buf_pool);
/* BUF_REMOVE_FLUSH_NO_WRITE:意思表示,只对dirty block进行remove操作,不做写入。
虽然5.5.23版本后drop table解决了该问题,但truncate操作并没有升级,还是采用5.5.23版本之前的删除方式,直到8.0版本才解决。
truncate 修改后部分代码:
Truncate calls row_discard_tablespace_for_mysql -> fil_discard_tablespace -> fil_delete_tablespace with evict_all=TRUE. When evict_all is true for the call to buf_LRU_flush_or_remove_pages then BUF_REMOVE_ALL_NO_WRITE is used.
buf_LRU_flush_or_remove_pages(
id, evict_all
? BUF_REMOVE_ALL_NO_WRITE
: BUF_REMOVE_FLUSH_NO_WRITE);
... then the slow path is used. so this stall is expected. would be nice for it to be fixed.
switch (buf_remove) {
case BUF_REMOVE_ALL_NO_WRITE:
/* A DISCARD tablespace case. Remove AHI entries
and evict all pages from LRU. */
/* Before we attempt to drop pages hash entries
one by one we first attempt to drop page hash
index entries in batches to make it more
efficient. The batching attempt is a best effort
attempt and does not guarantee that all pages
hash entries will be dropped. We get rid of
remaining page hash entries one by one below. */
buf_LRU_drop_page_hash_for_tablespace(buf_pool, id);
buf_LRU_remove_all_pages(buf_pool, id);
break;
case BUF_REMOVE_FLUSH_NO_WRITE:
/* A DROP table case. AHI entries are already
removed. No need to evict all pages from LRU
list. Just evict pages from flush list without
writing. */
buf_flush_dirty_pages(buf_pool, id);
break;
}
}
MySQL8.0针对该问题说明:
当InnoDB buffer pool比较大和innodb_adaptive_hash_index启用时,TRUNCATE TABLE操作可能由于发生了LRU扫描,删除InnoDB表的自适应散列索引项时,导致系统性能暂时下降。为了解决这个问题,TRUNCATE TABLE现在调用与DROP TABLE相同的代码删除表。因为在MySQL 5.5.23后,DROP TABLE解决了这个问题。
总结:
5.5.23版本之前,采用truncate+drop方式
5.5.23版本之后,采用drop方式
8.0版本之后,采用truncate方式