fibonacci.go
package algorithms // Dynamic Programming func Fibonacci1(n int) int { if n <= 0 { return 0 } if n <= 2 { return 1 } previous1 := 1 previous2 := 1 currentVal := 0 for i := 3; i <= n; i++ { currentVal = previous1 + previous2 previous1 = previous2 previous2 = currentVal } return currentVal } var store = map[int]int{ 1: 1, 2: 1, } func Fibonacci2(n int) int { if n <= 0 { return 0 } if store[n] != 0 { return store[n] } val := Fibonacci2(n-2) + Fibonacci2(n-1) store[n] = val return val }
setup_test.go
package algorithms type TestCase struct { name string input any expected any }
fibonacci_test.go
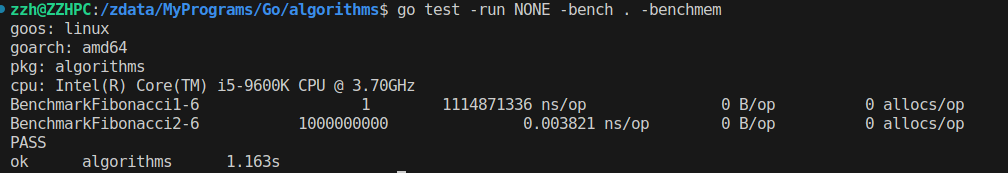
package algorithms import "testing" func BenchmarkFibonacci1(b *testing.B) { for i := 0; i < 100000; i++ { _ = Fibonacci1(i) } } func BenchmarkFibonacci2(b *testing.B) { for i := 0; i < 100000; i++ { _ = Fibonacci2(i) } } var fibo_tests = []TestCase{ {"Case 1", 0, 0}, {"Case 2", 2, 1}, {"Case 3", 3, 2}, {"Case 4", 4, 3}, {"Case 5", 5, 5}, {"Case 6", 6, 8}, {"Case 7", 7, 13}, } func TestFibonacci1(t *testing.T) { for _, tc := range fibo_tests { result := Fibonacci1(tc.input.(int)) if result != tc.expected { t.Errorf("%s failed. Input: %v Output: %v Expected: %v", tc.name, tc.input, result, tc.expected) } } } func TestFibonacci2(t *testing.T) { for _, tc := range fibo_tests { result := Fibonacci2(tc.input.(int)) if result != tc.expected { t.Errorf("%s failed. Input: %v Output: %v Expected: %v", tc.name, tc.input, result, tc.expected) } } }
Performance comparison: