1、什么是regmap?
Linux引入regmap是为了统一管理内核的i2c,spi等总线,将i2c、spi驱动做了一次重构,把I/O读写的重复逻辑在regmap中实现。只需初始化时指定总线类型、寄存器位宽等关键参数,即可通过regmap模型接口来操作器件寄存器。
将i2c、spi、mmio、irq等抽象出统一接口regmap_read,regmap_write,regmap_update_bits等接口,从而提高代码的可重用性;regmap是在Linux内核为减少慢速I/O驱动上的重复逻辑,提供的一种通用接口来操作底层硬件寄存器的模型框架。
此外,如果在regmap中使用cache,会减少底层低速I/O的操作次数,提高访问效率,但是会降低操作的实时性。
2、regmap的架构
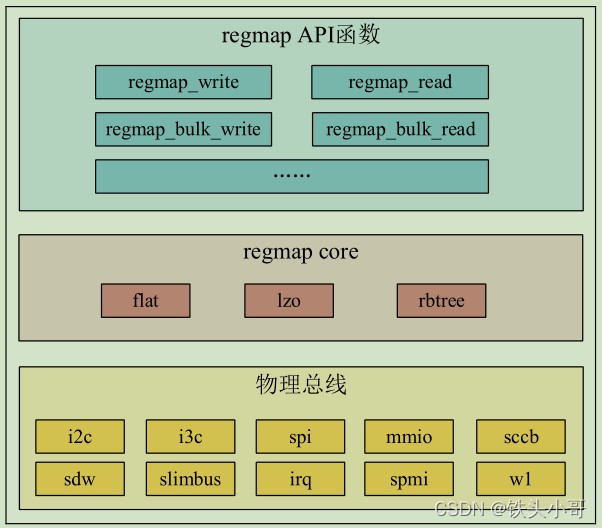
regmap框架主要分为三层,如上图所示:
- 底层物理总线:regmap对不同的物理总线进行封装,目前regmap支持的物理总线有i2c、i3c、spi、mmio、sccb等
- regmap核心层:用于实现regmap,链接API抽象层和物理层
- regmap API抽象层,向驱动编写人员提供API接口,驱动编写人员使用这些API接口来操作具体的芯片设备,也是驱动编写人员重点要掌握的。
3、regmap数据结构
相关的代码路径:
include/linux/regmap.h
drivers/base/regmap/
3.1 regmap结构体
Linux内核将regmap框架抽象为regmap结构体,如下:
Path:drivers/base/regmap/internal.h
struct regmap {
union {
struct mutex mutex;
struct {
spinlock_t spinlock;
unsigned long spinlock_flags;
};
struct {
raw_spinlock_t raw_spinlock;
unsigned long raw_spinlock_flags;
};
};
regmap_lock lock;
regmap_unlock unlock;
void *lock_arg; /* This is passed to lock/unlock functions */
gfp_t alloc_flags;
unsigned int reg_base;
struct device *dev; /* Device we do I/O on */
void *work_buf; /* Scratch buffer used to format I/O */
struct regmap_format format; /* Buffer format */
const struct regmap_bus *bus;
void *bus_context;
const char *name;
bool async;
spinlock_t async_lock;
wait_queue_head_t async_waitq;
struct list_head async_list;
struct list_head async_free;
int async_ret;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_FS
bool debugfs_disable;
struct dentry *debugfs;
const char *debugfs_name;
unsigned int debugfs_reg_len;
unsigned int debugfs_val_len;
unsigned int debugfs_tot_len;
struct list_head debugfs_off_cache;
struct mutex cache_lock;
#endif
unsigned int max_register;
bool (*writeable_reg)(struct device *dev, unsigned int reg);
bool (*readable_reg)(struct device *dev, unsigned int reg);
bool (*volatile_reg)(struct device *dev, unsigned int reg);
bool (*precious_reg)(struct device *dev, unsigned int reg);
bool (*writeable_noinc_reg)(struct device *dev, unsigned int reg);
bool (*readable_noinc_reg)(struct device *dev, unsigned int reg);
const struct regmap_access_table *wr_table;
const struct regmap_access_table *rd_table;
const struct regmap_access_table *volatile_table;
const struct regmap_access_table *precious_table;
const struct regmap_access_table *wr_noinc_table;
const struct regmap_access_table *rd_noinc_table;
int (*reg_read)(void *context, unsigned int reg, unsigned int *val);
int (*reg_write)(void *context, unsigned int reg, unsigned int val);
int (*reg_update_bits)(void *context, unsigned int reg,
unsigned int mask, unsigned int val);
/* Bulk read/write */
int (*read)(void *context, const void *reg_buf, size_t reg_size,
void *val_buf, size_t val_size);
int (*write)(void *context, const void *data, size_t count);
bool defer_caching;
unsigned long read_flag_mask;
unsigned long write_flag_mask;
/* number of bits to (left) shift the reg value when formatting*/
int reg_shift;
int reg_stride;
int reg_stride_order;
/* regcache specific members */
const struct regcache_ops *cache_ops;
enum regcache_type cache_type;
/* number of bytes in reg_defaults_raw */
unsigned int cache_size_raw;
/* number of bytes per word in reg_defaults_raw */
unsigned int cache_word_size;
/* number of entries in reg_defaults */
unsigned int num_reg_defaults;
/* number of entries in reg_defaults_raw */
unsigned int num_reg_defaults_raw;
/* if set, only the cache is modified not the HW */
bool cache_only;
/* if set, only the HW is modified not the cache */
bool cache_bypass;
/* if set, remember to free reg_defaults_raw */
bool cache_free;
struct reg_default *reg_defaults;
const void *reg_defaults_raw;
void *cache;
/* if set, the cache contains newer data than the HW */
bool cache_dirty;
/* if set, the HW registers are known to match map->reg_defaults */
bool no_sync_defaults;
struct reg_sequence *patch;
int patch_regs;
/* if set, converts bulk read to single read */
bool use_single_read;
/* if set, converts bulk write to single write */
bool use_single_write;
/* if set, the device supports multi write mode */
bool can_multi_write;
/* if set, raw reads/writes are limited to this size */
size_t max_raw_read;
size_t max_raw_write;
struct rb_root range_tree;
void *selector_work_buf; /* Scratch buffer used for selector */
struct hwspinlock *hwlock;
/* if set, the regmap core can sleep */
bool can_sleep;
};
使用regmap_init_xxxxx等接口函数,根据regmap_config和bus结构体的数据来初始化regmap结构体。
3.2 regmap_config结构体
// include/linux/regmap.h
struct regmap_config {
const char *name; // 可选,寄存器名字
int reg_bits; // 寄存器地址位宽,必须填写
int reg_stride; // 寄存器操作宽度,比如为1时,所有寄存器可操作,为2时,只有2^n可操作
int pad_bits;
int val_bits; // 寄存器值的位宽,必须填写
// 可选,判断寄存器是否可写,可读,是否可缓冲等回调
bool (*writeable_reg)(struct device *dev, unsigned int reg);
bool (*readable_reg)(struct device *dev, unsigned int reg);
bool (*volatile_reg)(struct device *dev, unsigned int reg);
bool (*precious_reg)(struct device *dev, unsigned int reg);
regmap_lock lock;
regmap_unlock unlock;
void *lock_arg;
// 寄存器读写方法,可选
int (*reg_read)(void *context, unsigned int reg, unsigned int *val);
int (*reg_write)(void *context, unsigned int reg, unsigned int val);
bool fast_io;
unsigned int max_register;
const struct regmap_access_table *wr_table; //可选,可写寄存器
const struct regmap_access_table *rd_table;//可选,可读寄存器
const struct regmap_access_table *volatile_table;
const struct regmap_access_table *precious_table;
const struct reg_default *reg_defaults;
unsigned int num_reg_defaults;
enum regcache_type cache_type; // 缓冲方式
const void *reg_defaults_raw;
unsigned int num_reg_defaults_raw;
u8 read_flag_mask;
u8 write_flag_mask;
bool use_single_rw;
bool can_multi_write;
enum regmap_endian reg_format_endian;
enum regmap_endian val_format_endian;
const struct regmap_range_cfg *ranges;
unsigned int num_ranges;
};
4、使用案例
/* 1. 配置信息 */
static const struct regmap_config regmap_config =
{
.reg_bits = 8,
.val_bits = 8,
.max_register = 255,
.cache_type = REGCACHE_NONE,
.volatile_reg = false,
};
/* 2. 注册regmap实例 */
regmap = regmap_init_i2c(i2c_client, ®map_config);
/* 3. 访问操作 */
regmap_raw_read(regmap, reg, &data, size);
/* 4. 注销regmap */
regmap_exit(regmap);
参考链接
1、https://www.cnblogs.com/schips/p/linix_regmap.html
2、https://blog.csdn.net/zhuyong006/article/details/80931397
3、https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44182115/article/details/123331499
4、https://www.cnblogs.com/schips/p/using_regmap_in_linux_kernel.html
5、https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/550695692