reduce--->归纳
mapreduce必须构建在hdfs之上的一种大数据离线计算框架
在线:实时数据处理
离线:数据处理时效性没有在线那么强,但是相对也需要很快得到结果
mapreduce不会马上得到结果,他会有一定的延时(磁盘IO)
如果数据量小,使用mapreduce反而不合适
杀鸡焉用宰牛刀
原始数据-->map(Key,Value)-->Reduce
分布式计算
将大的数据切分成多个小数据,交给更多的节点参与运算
计算向数据靠拢
二、MapReduce架构特点
MapReduce1.x

主节点,单点,负责调度所有的作业和监控整个集群的资源负载。
TaskTracker
从节点,自身节点资源管理和JobTracker进行心跳联系,汇报资源和获取task。
Client
以作业为单位,规划作业计算分布,提交作业资源到HDFS,最终提交作业到JobTracker。
Slot(槽):
属于JobTracker分配的资源(计算能力、IO能力等)。
不管任务大小,资源是恒定的,不灵活但是好管理。
Task(MapTask-->ReduceTask):
开始按照MR的流程执行业务。
当任务完成时,JobTracker告诉TaskTracker回收资源。
MapReduce1.x的弊端
1.JobTracker负载过重,存在单点故障。
2.资源管理和计算调度强耦合,其它计算框架难以复用其资源管理。
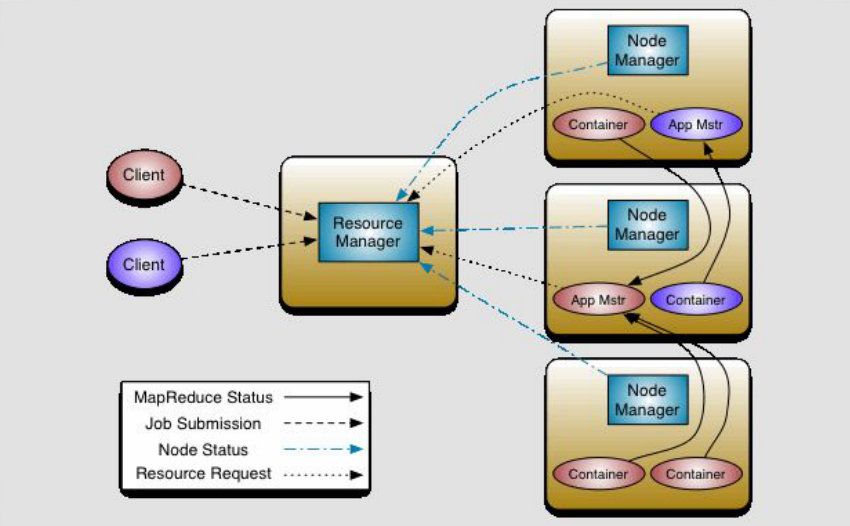
ResourceManager: 资源协调框架的管理者,分为主节点和备用节点(防止单点故障,主备的切换基于ZK的管理),它时刻与NodeManager保持心跳,接受NodeManager的汇报(NodeManager当前节点的资源情况)。
当有外部框架要使用资源的时候直接访问ResourceManager即可。
如果是有MR任务,先去ResourceManager申请资源,ResourceManager根据汇报分配资源,例如资源在NodeManager1,那么NodeManager1要负责开辟资源。
Yarn(NodeManager): Yarn(Yet Another Resource Negotiator,另一种资源协调者),统一管理资源。以后其他的计算框架可以直接访问yarn获取当前集群的空闲节点。
每个DataNode上默认有一个NodeManager,NodeManager汇报自己的信息到ResourceManager。
Container: 它是动态分配的,2.X资源的代名词。
ApplicationMaster: 我们本次任务的主导者,负责调度本次被分配的资源Container。当所有的节点任务全部完成,applicaion告诉ResourceManager请求杀死当前ApplicationMaster线程,本次任务的所有资源都会被释放。
Task(MapTask--ReduceTask): 开始按照MR的流程执行业务,当任务完成时,ApplicationMaster接收当前节点的反馈。
YARN【Yet Another Resource Negotiator】:Hadoop 2.0新引入的资源管理系统,直接从MRv1演化而来的。
核心思想:将MRv1中JobTracker的资源管理和任务调度两个功能分开,分别由ResourceManager和ApplicationMaster进程实现:
ResourceManager:负责整个集群的资源管理和调度。
ApplicationMaster:负责应用程序相关的事务,比如任务调度、任务监控和容错等。
三、MR的计算流程
计算1T数据中每个单词出现的次数---->wordcount
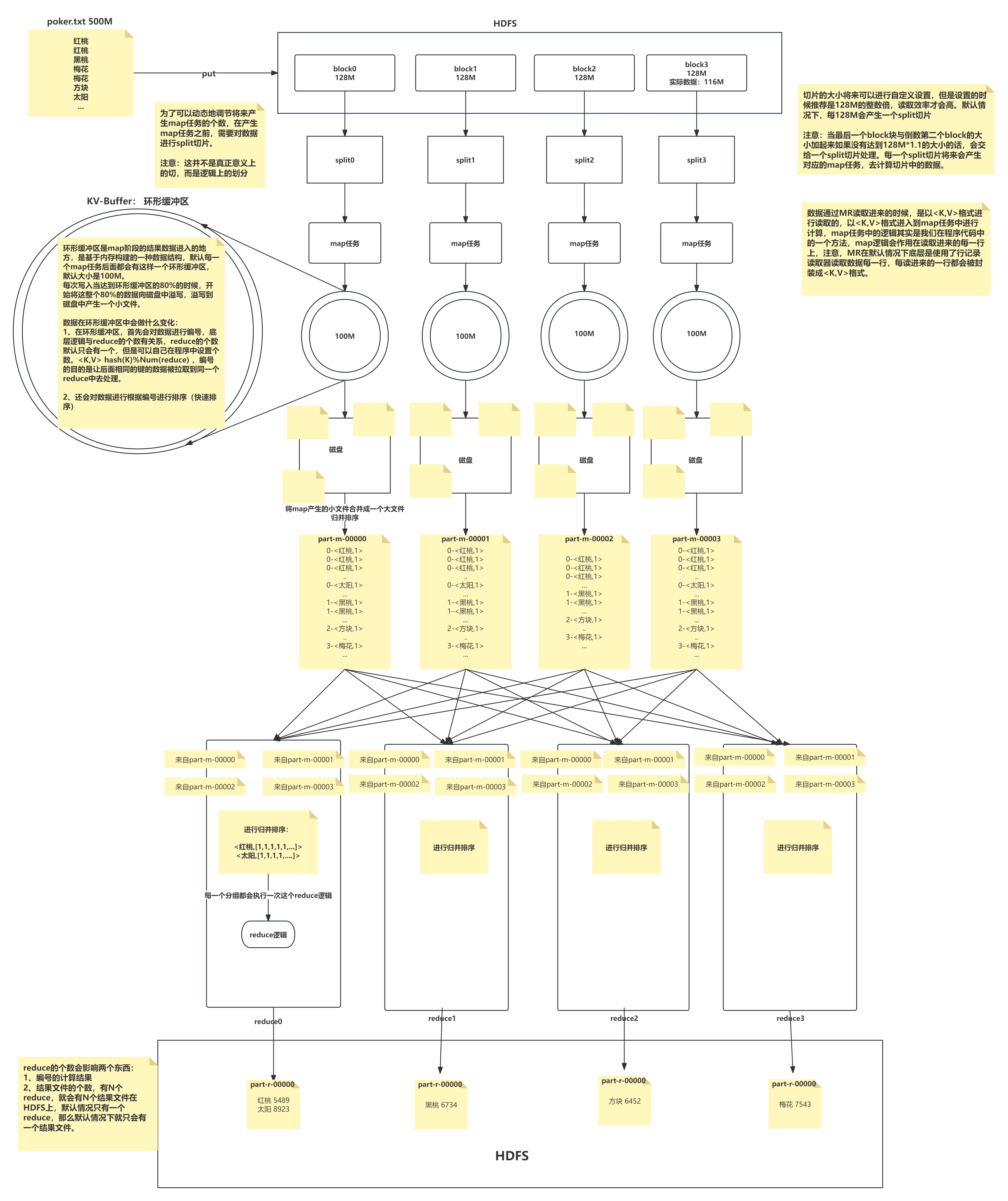
1T数据被切分成块存放在HDFS上,每一个块有128M大小
因为数据存储到HDFS上不可变,所以有可能块的数量和集群的计算能力不匹配
我们需要一个动态调整本次参与计算节点数量的一个单位
在不改变现在数据存储的情况下,可以控制参与计算的节点数目
通过切片大小可以达到控制计算节点数量的目的
有多少个切片就会执行多少个Map任务
一般切片大小为Block的整数倍(2 1/2)
防止多余创建和很多的数据连接
如果Split大小 > Block大小 ,计算节点少了
如果Split大小 < Block大小 ,计算节点多了
默认情况下,Split切片的大小等于Block的大小 ,默认128M,如果读取到最后一个block块的时候,与前一个blokc块组合起来的大小小于128M*1.1的话,他们结合生一个split切片,生成一个map任务
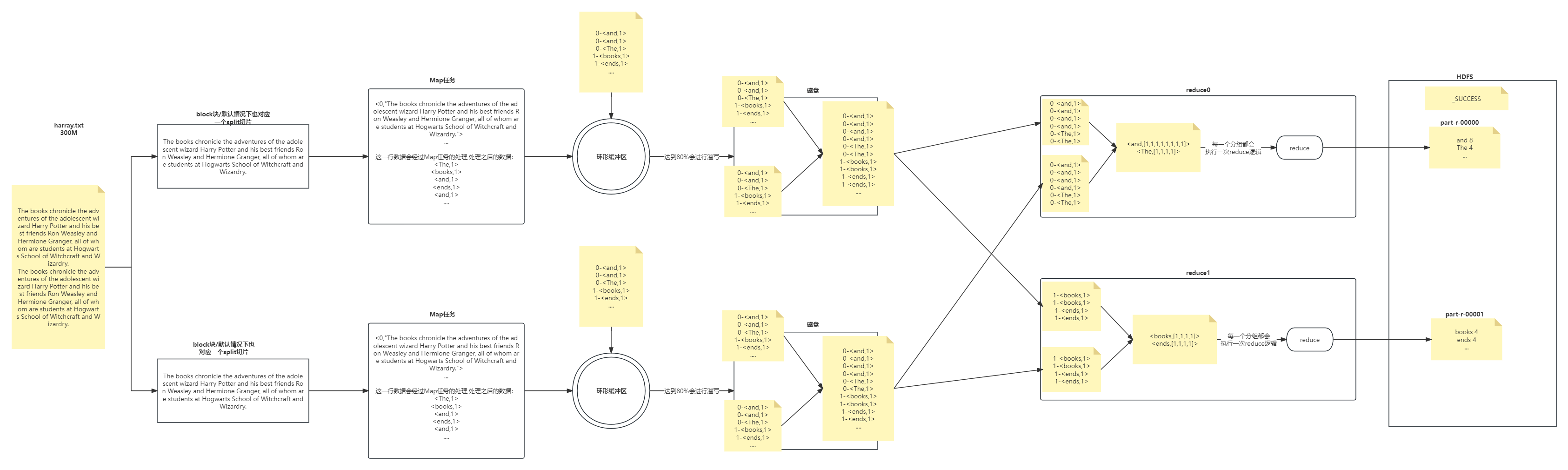
我们可以根据自己书写的分词逻辑(空格,逗号等分隔),计算每个单词出现的次数(wordcount)
the books chronicle the adventures of the adolescent wizard Harry Potter and his best friends Ron Weasley and Hermione Granger, all of whom are students at Hogwarts School of Witchcraft and Wizardry
the 1
books 1
chronicle 1
the 1
adventures 1
of 1
...
Wizardry 1
如果把数据都直接放到硬盘,效率太低
环形缓冲区(KV-Buffer)
可以循环利用这块内存区域,减少数据溢写时map的停止时间
每一个Map可以独享的一个内存区域
在内存中构建一个环形数据缓冲区(kvBuffer),默认大小为100M
设置缓冲区的阈值为80%(设置阈值的目的是为了同时写入和写出),当缓冲区的数据达到80M开始向外溢写到硬盘
溢写的时候还有20M的空间可以被使用效率并不会被减缓
而且将数据循环写到硬盘,不用担心OOM问题
说完这个先说溢写,合并,拉取(分析出问题得到结论),再说中间的分区排序
6 分区Partition(环形缓冲区做的)
根据Key直接计算出对应的Reduce
分区的数量和Reduce的数量是相等的
hash(key) % partation(reduce的数量) = num
默认分区的算法是Hash然后取余
Object的hashCode()—equals()
如果两个对象equals,那么两个对象的hashcode一定相等
如果两个对象的hashcode相等,但是对象不一定equlas
7 排序Sort(环形缓冲区做的,快速排序,对前面分区后的编号进行排序,使得相同编号的在一起)
对要溢写的数据进行排序(QuickSort)
按照先Partation后Key的顺序排序–>相同分区在一起,相同Key的在一起
我们将来溢写出的小文件也都是有序的
8 溢写Spill
将内存中的数据循环写到硬盘,不用担心OOM问题
每次会产生一个80M的文件
如果本次Map产生的数据较多,可能会溢写多个文件
9 合并Merge
因为溢写会产生很多有序(分区 key)的小文件,而且小文件的数目不确定
后面向reduce传递数据带来很大的问题
所以将小文件合并成一个大文件,将来拉取的数据直接从大文件拉取即可
合并小文件的时候同样进行排序(归并 排序),最终产生一个有序的大文件
0 组合器Combiner
a. 集群的带宽限制了mapreduce作业的数量,因此应该尽量避免map和reduce任务之间的数据传输,hadoop允许用户对map的输出数据进行处理,用户可自定义combiner函数(如同map函数和reduce函数一般),其逻辑一般和reduce函数一样,combiner的输入是map的输出,combiner的输出作为reduce的输入,很多情况下可以i直接将reduce函数作为conbiner函数来试用(job.setCombinerClass(FlowCountReducer.class))。
b. combiner属于优化方案,所以无法确定combiner函数会调用多少次,可以在环形缓存区溢出文件时调用combiner函数,也可以在溢出的小文件合并成大文件时调用combiner,但是要保证不管调用多少次,combiner函数都不影响最终的结果,所以不是所有处理逻辑都可以i使用combiner组件,有些逻辑如果试用了conbiner函数会改变最后reduce的输出结果(如求几个数的平均值,就不能先用conbiner求一次各个map输出结果的平均值,再求这些平均值的平均值,那样会导致结果的错误)。
c. combiner的意义就是对每一个maptask的输出进行局部汇总,以减小网络传输量:
原先传给reduce的数据时a1 a1 a1 a1 a1
第一次combiner组合后变成a(1,1,1,1,1)
第二次combiner后传给reduce的数据变为a(5,5,6,7,23,...)
11
我们需要将Map的临时结果拉取到Reduce节点
第一种方式:两两合并
第二种方式:相同的进一个reduce
第三种对第二种优化,排序
第四种对第三种优化:如果一个reduce处理两种key,而key分布一个首一个尾,解决不连续的问题,给个编号,这个编号怎么算呢,`回到分区,排序`
相同的Key必须拉取到同一个Reduce节点
但是一个Reduce节点可以有多个Key
未排序前拉取数据的时候必须对Map产生的最终的合并文件做全序遍历
而且每一个reduce都要做一个全序遍历
12 合并Merge
因为reduce拉取的时候,会从多个map拉取数据
那么每个map都会产生一个小文件,这些小文件(文件与文件之间无序,文件内部有序)
为了方便计算(没必要读取N个小文件),需要合并文件
归并算法合并成2个
相同的key都在一起
13 归并Reduce
将文件中的数据读取到内存中
一次性将相同的key全部读取到内存中
直接将相同的key得到结果–>最终结果
14 写出Output
每个reduce将自己计算的最终结果都会存放到HDFS上
四、分词器
#maven添加依赖,父依赖 pom.xml
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.hankcs/hanlp -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.hankcs</groupId>
<artifactId>hanlp</artifactId>
<version>portable-1.7.8</version>
</dependency>
#子依赖 pom.xml
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-assembly-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.3.0</version>
<configuration>
<descriptorRefs>
<!-- 打包出来的带依赖jar包名称 -->
<descriptorRef>jar-with-dependencies</descriptorRef>
</descriptorRefs>
</configuration>
<!--下面是为了使用 mvn package命令,如果不加则使用mvn assembly-->
<executions>
<execution>
<id>make-assemble</id>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>single</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
combiner发生在map端的reduce操作。
作用是减少map端的输出,减少shuffle过程中网络传输的数据量,提高作业的执行效率。
combiner仅仅是单个map task的reduce,没有对全部map的输出做reduce。 如果不用combiner,那么,所有的结果都是reduce完成,效率会相对低下。
使用combiner,先完成的map会在本地聚合,提升速度。
注意:Combiner的输出是Reducer的输入,Combiner绝不能改变最终的计算结果。所以,Combine适合于等幂操作,比如累加,最大值等。求平均数不适合
ctrl+alt+方向键:查看上一个或者下一个方法
ctrl+shift+alt+c: 拷贝方法的全名 com.shujia.airPM25.Pm25Avg#main
ctrl+alt+b:查看当前接口的实现类
1 Split
带着问题看源码:
1、map的数量和切片的数量一样?
2、split的大小可以自己调节吗?算法是什么?
源代码的分析从提交任务开始
job.waitForCompletion(true);
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job#waitForCompletion
/**
* Submit the job to the cluster and wait for it to finish.
* @param verbose print the progress to the user
* @return true if the job succeeded
* @throws IOException thrown if the communication with the
* <code>JobTracker</code> is lost
*/
public boolean waitForCompletion(boolean verbose) throws IOException, InterruptedException,ClassNotFoundException {
//判断当前的状态
if (state == JobState.DEFINE) {
//=============关键代码================
submit();
}
//监控任务的运行状态
if (verbose) {
monitorAndPrintJob();
} else {
// get the completion poll interval from the client.
int completionPollIntervalMillis =
Job.getCompletionPollInterval(cluster.getConf());
while (!isComplete()) {
try {
Thread.sleep(completionPollIntervalMillis);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
}
}
}
//返回任务状态
return isSuccessful();
}
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job#submit
public void submit() throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
//确认当前任务的状态
ensureState(JobState.DEFINE);
//mapreduce1.x和2.x,但是2的时候将1的好多方法进行了优化
setUseNewAPI();
//获取当前任务所运行的集群
connect();
//创建Job的提交器
final JobSubmitter submitter = getJobSubmitter(cluster.getFileSystem(), cluster.getClient());
status = ugi.doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<JobStatus>() {
public JobStatus run() throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
//提交任务到系统去执行
//Internal method for submitting jobs to the system
//===========关键代码============
return submitter.submitJobInternal(Job.this, cluster);
}
});
//任务的状态修改为运行
state = JobState.RUNNING;
LOG.info("The url to track the job: " + getTrackingURL());
}
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.JobSubmitter#submitJobInternal
//validate the jobs output specs
//检查一下输出路径存不存在呀,有没有权限之类的
checkSpecs(job);
//生成并设置新的JobId
JobID jobId = submitClient.getNewJobID();
job.setJobID(jobId);
//获取任务的提交目录
Path submitJobDir = new Path(jobStagingArea, jobId.toString());
// Create the splits for the job
LOG.debug("Creating splits at " + jtFs.makeQualified(submitJobDir));
//===========关键代码============ 197行
int maps = writeSplits(job, submitJobDir);
//设置map的数量,其中map的数量就等于切片的数量
conf.setInt(MRJobConfig.NUM_MAPS, maps);
LOG.info("number of splits:" + maps);
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.JobSubmitter#writeSplits
private int writeSplits(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.JobContext job,Path jobSubmitDir) throws IOException,InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
//获取作业的配置文件
JobConf jConf = (JobConf)job.getConfiguration();
int maps;
//今后我们看源码的时候,想都不要想,看新的方式
if (jConf.getUseNewMapper()) {
//===========关键代码============
maps = writeNewSplits(job, jobSubmitDir);
} else {
maps = writeOldSplits(jConf, jobSubmitDir);
}
return maps;
}
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.JobSubmitter#writeNewSplits
private <T extends InputSplit> int writeNewSplits(JobContext job, Path jobSubmitDir) throws IOException,InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
//获取集群配置
Configuration conf = job.getConfiguration();
//通过反射工具获取文件读取器对象
//===========关键代码============ job 的实现类
//org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat --> input
//job->org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.task.JobContextImpl#getInputFormatClass
InputFormat<?, ?> input = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(job.getInputFormatClass(), conf);
//获取到切片
//===========关键代码============ getSplits
List<InputSplit> splits = input.getSplits(job);
//转成数组
T[] array = (T[]) splits.toArray(new InputSplit[splits.size()]);
// sort the splits into order based on size, so that the biggest
// go first
Arrays.sort(array, new SplitComparator());
JobSplitWriter.createSplitFiles(jobSubmitDir, conf,
jobSubmitDir.getFileSystem(conf), array);
//返回的是数组的长度,对应着切片的数量,回到197行验证
return array.length;
}
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.task.JobContextImpl#getInputFormatClass
/**
* Get the {@link InputFormat} class for the job.
*
* @return the {@link InputFormat} class for the job.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Class<? extends InputFormat<?,?>> getInputFormatClass() throws ClassNotFoundException {
return (Class<? extends InputFormat<?,?>>)
//getClass的操作是如果有值返回值,没有的话使用默认值
conf.getClass(INPUT_FORMAT_CLASS_ATTR, TextInputFormat.class);
}
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat#getSplits
/**
* Generate the list of files and make them into FileSplits.
* @param job the job context
* @throws IOException
*/
public List<InputSplit> getSplits(JobContext job) throws IOException {
StopWatch sw = new StopWatch().start();
//开始计算两个变量(一个切片最少有一个字节,一个最小切片值也是1)
//1
long minSize = Math.max(getFormatMinSplitSize(), getMinSplitSize(job));
//Long.MAX_VALUE
long maxSize = getMaxSplitSize(job);
// generate splits
//创建一个List存放切片
List<InputSplit> splits = new ArrayList<InputSplit>();
//获取本次计算中所有的要计算的文件
List<FileStatus> files = listStatus(job);
//首先取出一个文件
for (FileStatus file: files) {
//获取文件路径
Path path = file.getPath();
//获取文件大小
long length = file.getLen();
if (length != 0) {
BlockLocation[] blkLocations;
if (file instanceof LocatedFileStatus) {
blkLocations = ((LocatedFileStatus) file).getBlockLocations();
} else {
FileSystem fs = path.getFileSystem(job.getConfiguration());
//获取文件块的信息
blkLocations = fs.getFileBlockLocations(file, 0, length);
}
//判断文件是否可以被切分,比如文件被压缩了,需要解压缩才可以
if (isSplitable(job, path)) {
//获取单个块的大小
long blockSize = file.getBlockSize();
//开始计算切片大小,这里可以验证切片大小与block大小一样
//思考如何生成256M的切片
//如果切片小于blocksize-->将maxsize小于blocksize
//如果切片大于blocksize-->将minsize大于blocksize
long splitSize = computeSplitSize(blockSize, minSize, maxSize);
//将文件大小分配给bytesRemaining
long bytesRemaining = length;
//private static final double SPLIT_SLOP = 1.1; // 10% slop
while (((double) bytesRemaining)/splitSize > SPLIT_SLOP) {
int blkIndex = getBlockIndex(blkLocations, length-bytesRemaining);
//制作切片
//封装切片对象并将其存放到list中
//makeSplit(路径,偏移量,切片大小,块的位置,备份的位置);
splits.add(makeSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, splitSize,
blkLocations[blkIndex].getHosts(),
blkLocations[blkIndex].getCachedHosts()));
bytesRemaining -= splitSize;
}
//如果最后一个文件过小没有大于1.1,就与上一个一起生成切片
if (bytesRemaining != 0) {
int blkIndex = getBlockIndex(blkLocations, length-bytesRemaining);
splits.add(makeSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, bytesRemaining,
blkLocations[blkIndex].getHosts(),
blkLocations[blkIndex].getCachedHosts()));
}
} else { // not splitable
//如果文件不可切,就生成一个切片
splits.add(makeSplit(path, 0, length, blkLocations[0].getHosts(),
blkLocations[0].getCachedHosts()));
}
} else {
//Create empty hosts array for zero length files
splits.add(makeSplit(path, 0, length, new String[0]));
}
}
// Save the number of input files for metrics/loadgen
job.getConfiguration().setLong(NUM_INPUT_FILES, files.size());
sw.stop();
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Total # of splits generated by getSplits: " + splits.size()
+ ", TimeTaken: " + sw.now(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
}
//返回切片(后面的代码我们跟不进去了,是yarn上面的了)
return splits;
}
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat#computeSplitSize
protected long computeSplitSize(long blockSize, long minSize,
long maxSize) {
//blockSize--128M
//maxSize--56M ----> 56M
//minSize--256M ----> 256M
return Math.max(minSize, Math.min(maxSize, blockSize));
}
2 Map源码-MapTask
带着问题:
1、map读取数据按照行读取数据?验证一下
2、如果切片把一行数据放在了两个切片中呢?怎么办?
3、map里面的第一个参数类型是LongWritable?哪里指定的?
org.apache.hadoop.mapred.MapTask
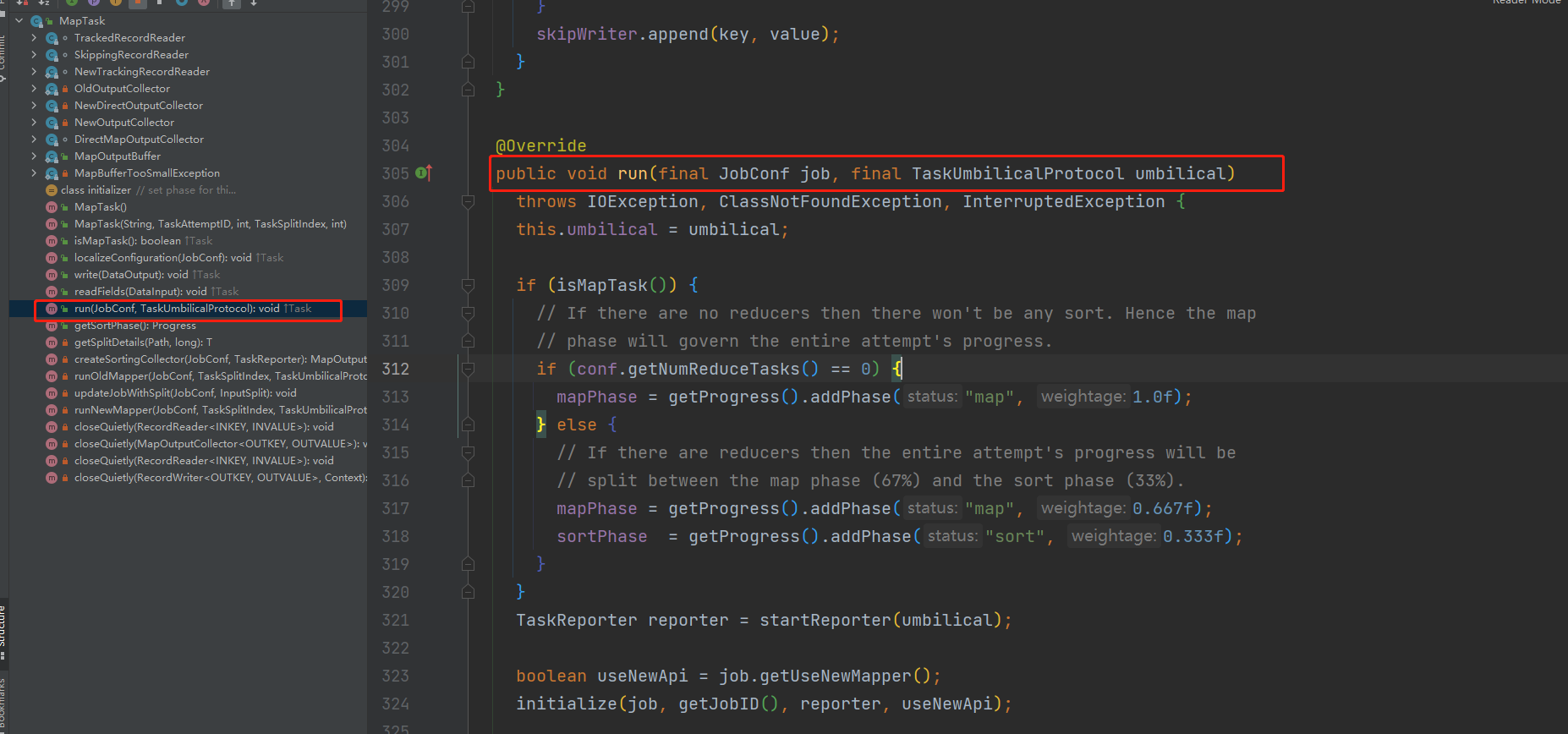
@Override
public void run(final JobConf job, final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
this.umbilical = umbilical;
//判断是否为Map任务
if (isMapTask()) {
// If there are no reducers then there won't be any sort. Hence the map
// phase will govern the entire attempt's progress.
//判断reduce数量是否等于0,有可能等于0的如果我们只是清洗数据,就不需要
if (conf.getNumReduceTasks() == 0) {
//map所占的比例100%,没有reducce就不用分区了
mapPhase = getProgress().addPhase("map", 1.0f);
} else {
// If there are reducers then the entire attempt's progress will be
// split between the map phase (67%) and the sort phase (33%).
//如果有reduce的话分区排序
mapPhase = getProgress().addPhase("map", 0.667f);
sortPhase = getProgress().addPhase("sort", 0.333f);
}
}
//任务报告一下,说明我要处理多少数据
TaskReporter reporter = startReporter(umbilical);
//使用新api
boolean useNewApi = job.getUseNewMapper();
//===========关键代码============
//使用新api进行初始化
initialize(job, getJobID(), reporter, useNewApi);
// check if it is a cleanupJobTask
if (jobCleanup) {
runJobCleanupTask(umbilical, reporter);
return;
}
if (jobSetup) {
runJobSetupTask(umbilical, reporter);
return;
}
if (taskCleanup) {
runTaskCleanupTask(umbilical, reporter);
return;
}
if (useNewApi) {
//===========关键代码============
runNewMapper(job, splitMetaInfo, umbilical, reporter);
} else {
runOldMapper(job, splitMetaInfo, umbilical, reporter);
}
done(umbilical, reporter);
}
org.apache.hadoop.mapred.Task#initialize
public void initialize(JobConf job, JobID id,
Reporter reporter,
boolean useNewApi) throws IOException,
ClassNotFoundException,
InterruptedException {
//获取作业的上下文
jobContext = new JobContextImpl(job, id, reporter);
//获取任务的上下文
taskContext = new TaskAttemptContextImpl(job, taskId, reporter);
if (getState() == TaskStatus.State.UNASSIGNED) {
setState(TaskStatus.State.RUNNING);
}
if (useNewApi) {
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("using new api for output committer");
}
//创建了一个outputFormat对象
outputFormat = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getOutputFormatClass(), job);
committer = outputFormat.getOutputCommitter(taskContext);
} else {
committer = conf.getOutputCommitter();
}
Path outputPath = FileOutputFormat.getOutputPath(conf);
if (outputPath != null) {
if ((committer instanceof FileOutputCommitter)) {
FileOutputFormat.setWorkOutputPath(conf,
((FileOutputCommitter)committer).getTaskAttemptPath(taskContext));
} else {
FileOutputFormat.setWorkOutputPath(conf, outputPath);
}
}
committer.setupTask(taskContext);
Class<? extends ResourceCalculatorProcessTree> clazz =
conf.getClass(MRConfig.RESOURCE_CALCULATOR_PROCESS_TREE,
null, ResourceCalculatorProcessTree.class);
pTree = ResourceCalculatorProcessTree
.getResourceCalculatorProcessTree(System.getenv().get("JVM_PID"), clazz, conf);
LOG.info(" Using ResourceCalculatorProcessTree : " + pTree);
if (pTree != null) {
pTree.updateProcessTree();
initCpuCumulativeTime = pTree.getCumulativeCpuTime();
}
}
org.apache.hadoop.mapred.MapTask#runNewMapper
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private <INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>
void runNewMapper(final JobConf job,
final TaskSplitIndex splitIndex,
final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical,
TaskReporter reporter
) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException,
InterruptedException {
// make a task context so we can get the classes
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext taskContext =
new org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.task.TaskAttemptContextImpl(job,
getTaskID(),
reporter);
// make a mapper--com.shujia.MyMapper
//对应自己写的map类 TaskAttemptContextImpl
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE> mapper =
(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getMapperClass(), job);
// make the input format
//org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE> inputFormat =
(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getInputFormatClass(), job);
// rebuild the input split
//获取切片
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit split = null;
split = getSplitDetails(new Path(splitIndex.getSplitLocation()),
splitIndex.getStartOffset());
LOG.info("Processing split: " + split);
//===========关键代码============ NewTrackingRecordReader
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE> input =
new NewTrackingRecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE>
(split, inputFormat, reporter, taskContext);
job.setBoolean(JobContext.SKIP_RECORDS, isSkipping());
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordWriter output = null;
// get an output object
if (job.getNumReduceTasks() == 0) {
//如果reduce数量等于0,直接输出
output =
new NewDirectOutputCollector(taskContext, job, umbilical, reporter);
} else {
//如果reduce数量不等于0,待会来看,看下面的初始化
output = new NewOutputCollector(taskContext, job, umbilical, reporter);
}
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.MapContext<INKEY, INVALUE, OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>
mapContext =
new MapContextImpl<INKEY, INVALUE, OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>(job, getTaskID(),
input, output,
committer,
reporter, split);
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>.Context
mapperContext =
new WrappedMapper<INKEY, INVALUE, OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>().getMapContext(
mapContext);
try {
//===========关键代码============
//初始化的时候有意识的将第一行省略了
input.initialize(split, mapperContext);
//实际上调用的就是我们自己重写的map方法
//===========关键代码============
mapper.run(mapperContext);
mapPhase.complete();
setPhase(TaskStatus.Phase.SORT);
statusUpdate(umbilical);
input.close();
input = null;
output.close(mapperContext);
output = null;
} finally {
closeQuietly(input);
closeQuietly(output, mapperContext);
}
}
NewTrackingRecordReader(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit split,
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<K, V> inputFormat,
TaskReporter reporter,
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext taskContext)
throws InterruptedException, IOException {
this.reporter = reporter;
this.inputRecordCounter = reporter
.getCounter(TaskCounter.MAP_INPUT_RECORDS);
this.fileInputByteCounter = reporter
.getCounter(FileInputFormatCounter.BYTES_READ);
List <Statistics> matchedStats = null;
if (split instanceof org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit) {
matchedStats = getFsStatistics(((org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit) split)
.getPath(), taskContext.getConfiguration());
}
fsStats = matchedStats;
long bytesInPrev = getInputBytes(fsStats);
//===========关键代码============
//真正工作的人是谁,创建一个记录读取器
//返回的是一个行记录读取器
this.real = inputFormat.createRecordReader(split, taskContext);
long bytesInCurr = getInputBytes(fsStats);
fileInputByteCounter.increment(bytesInCurr - bytesInPrev);
}
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordReader
@Override
public RecordReader<LongWritable, Text>
createRecordReader(InputSplit split,
TaskAttemptContext context) {
String delimiter = context.getConfiguration().get(
"textinputformat.record.delimiter");
byte[] recordDelimiterBytes = null;
if (null != delimiter)
recordDelimiterBytes = delimiter.getBytes(Charsets.UTF_8);
return new LineRecordReader(recordDelimiterBytes);
}
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.LineRecordReader#initialize
public void initialize(InputSplit genericSplit,
TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException {
FileSplit split = (FileSplit) genericSplit;
Configuration job = context.getConfiguration();
this.maxLineLength = job.getInt(MAX_LINE_LENGTH, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
//获取开始的位置
start = split.getStart();
end = start + split.getLength();
final Path file = split.getPath();
// open the file and seek to the start of the split
//获取分布式文件系统
final FileSystem fs = file.getFileSystem(job);
//获取一个输入流
fileIn = fs.open(file);
CompressionCodec codec = new CompressionCodecFactory(job).getCodec(file);
if (null!=codec) {
isCompressedInput = true;
decompressor = CodecPool.getDecompressor(codec);
if (codec instanceof SplittableCompressionCodec) {
final SplitCompressionInputStream cIn =
((SplittableCompressionCodec)codec).createInputStream(
fileIn, decompressor, start, end,
SplittableCompressionCodec.READ_MODE.BYBLOCK);
in = new CompressedSplitLineReader(cIn, job,
this.recordDelimiterBytes);
start = cIn.getAdjustedStart();
end = cIn.getAdjustedEnd();
filePosition = cIn;
} else {
in = new SplitLineReader(codec.createInputStream(fileIn,
decompressor), job, this.recordDelimiterBytes);
filePosition = fileIn;
}
} else {
//读取偏移量
fileIn.seek(start);
in = new UncompressedSplitLineReader(
fileIn, job, this.recordDelimiterBytes, split.getLength());
filePosition = fileIn;
}
// If this is not the first split, we always throw away first record
// because we always (except the last split) read one extra line in
// next() method.
//解决第二个问题 从第二行开始读,把切片的第一行将给上一个切片去读
if (start != 0) {
//返回的start正好是下一行数据的开头
start += in.readLine(new Text(), 0, maxBytesToConsume(start));
}
this.pos = start;
}
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.map.WrappedMapper
@Override
public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
return mapContext.nextKeyValue();
}
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.task.MapContextImpl#MapContextImpl
@Override
public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//最终调用的是LineRecordReader中的nextKeyValue方法
return reader.nextKeyValue();
}
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.LineRecordReader
public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException {
if (key == null) {
key = new LongWritable();
}
//设置当前的偏移量
key.set(pos);
if (value == null) {
value = new Text();
}
int newSize = 0;
// We always read one extra line, which lies outside the upper
// split limit i.e. (end - 1)
//循环读取数据
while (getFilePosition() <= end || in.needAdditionalRecordAfterSplit()) {
if (pos == 0) {
newSize = skipUtfByteOrderMark();
} else {
//pos是当前数据的定位,value是数据
newSize = in.readLine(value, maxLineLength, maxBytesToConsume(pos));
pos += newSize;
}
if ((newSize == 0) || (newSize < maxLineLength)) {
break;
}
// line too long. try again
LOG.info("Skipped line of size " + newSize + " at pos " +
(pos - newSize));
}
if (newSize == 0) {
//如果本次啥也没有读到,返回false
key = null;
value = null;
return false;
} else {
//读到了返回true
return true;
}
}
//看完这里回到map方法,key就是数据的偏移量,value就是一行数据,context上下文,写到环形缓冲区,map结束
带着问题:
1、分区的数量和reduce数量一样?
2、环形缓冲区内存大小100M?80%溢写?可以自己设置吗?
3、排序是快速排序?
/**
* Generate an output key/value pair.
*/
public void write(KEYOUT key, VALUEOUT value
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
output.write(key, value);
}
通过参数的个数
org.apache.hadoop.mapred.MapTask.NewOutputCollector#NewOutputCollector
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
NewOutputCollector(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.JobContext jobContext,
JobConf job,
TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical,
TaskReporter reporter
) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//========关键代码=============
collector = createSortingCollector(job, reporter);
partitions = jobContext.getNumReduceTasks();
if (partitions > 1) {
//========关键代码============= 分区器
partitioner = (org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner<K,V>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(jobContext.getPartitionerClass(), job);
} else {
partitioner = new org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner<K,V>() {
@Override
public int getPartition(K key, V value, int numPartitions) {
return partitions - 1;
}
};
}
}
org.apache.hadoop.mapred.MapTask#createSortingCollector
private <KEY, VALUE> MapOutputCollector<KEY, VALUE>
createSortingCollector(JobConf job, TaskReporter reporter)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
MapOutputCollector.Context context =
new MapOutputCollector.Context(this, job, reporter);
//========关键代码==========
Class<?>[] collectorClasses = job.getClasses(
JobContext.MAP_OUTPUT_COLLECTOR_CLASS_ATTR, MapOutputBuffer.class);
int remainingCollectors = collectorClasses.length;
Exception lastException = null;
for (Class clazz : collectorClasses) {
try {
if (!MapOutputCollector.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
throw new IOException("Invalid output collector class: " + clazz.getName() +
" (does not implement MapOutputCollector)");
}
Class<? extends MapOutputCollector> subclazz =
clazz.asSubclass(MapOutputCollector.class);
LOG.debug("Trying map output collector class: " + subclazz.getName());
MapOutputCollector<KEY, VALUE> collector =
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(subclazz, job);
//====================进行初始化===============
collector.init(context);
LOG.info("Map output collector class = " + collector.getClass().getName());
//返回MapOutputBuffer
return collector;
} catch (Exception e) {
String msg = "Unable to initialize MapOutputCollector " + clazz.getName();
if (--remainingCollectors > 0) {
msg += " (" + remainingCollectors + " more collector(s) to try)";
}
lastException = e;
LOG.warn(msg, e);
}
}
throw new IOException("Initialization of all the collectors failed. " +
"Error in last collector was :" + lastException.getMessage(), lastException);
}
org.apache.hadoop.mapred.MapTask.MapOutputBuffer#init
public void init(MapOutputCollector.Context context
) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
job = context.getJobConf();
reporter = context.getReporter();
mapTask = context.getMapTask();
mapOutputFile = mapTask.getMapOutputFile();
sortPhase = mapTask.getSortPhase();
spilledRecordsCounter = reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.SPILLED_RECORDS);
partitions = job.getNumReduceTasks();
rfs = ((LocalFileSystem)FileSystem.getLocal(job)).getRaw();
//sanity checks
//溢写
final float spillper =
job.getFloat(JobContext.MAP_SORT_SPILL_PERCENT, (float)0.8);
final int sortmb = job.getInt(JobContext.IO_SORT_MB, 100);
indexCacheMemoryLimit = job.getInt(JobContext.INDEX_CACHE_MEMORY_LIMIT,
INDEX_CACHE_MEMORY_LIMIT_DEFAULT);
if (spillper > (float)1.0 || spillper <= (float)0.0) {
throw new IOException("Invalid \"" + JobContext.MAP_SORT_SPILL_PERCENT +
"\": " + spillper);
}
if ((sortmb & 0x7FF) != sortmb) {
throw new IOException(
"Invalid \"" + JobContext.IO_SORT_MB + "\": " + sortmb);
}
//默认排序器是快速排序
sorter = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(job.getClass("map.sort.class",
QuickSort.class, IndexedSorter.class), job);
// buffers and accounting
//100左移2位 ×2^20
int maxMemUsage = sortmb << 20;
//对16进行取余,让这个数字变成16的整数倍
maxMemUsage -= maxMemUsage % METASIZE;
//环形缓冲区100M
//并且设置环形缓冲区的一些初始值
kvbuffer = new byte[maxMemUsage];
bufvoid = kvbuffer.length;
kvmeta = ByteBuffer.wrap(kvbuffer)
.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder())
.asIntBuffer();
setEquator(0);
bufstart = bufend = bufindex = equator;
kvstart = kvend = kvindex;
//双重索引,大家课下可以自己了解
maxRec = kvmeta.capacity() / NMETA;
softLimit = (int)(kvbuffer.length * spillper);
bufferRemaining = softLimit;
LOG.info(JobContext.IO_SORT_MB + ": " + sortmb);
LOG.info("soft limit at " + softLimit);
LOG.info("bufstart = " + bufstart + "; bufvoid = " + bufvoid);
LOG.info("kvstart = " + kvstart + "; length = " + maxRec);
// k/v serialization
//如果是自己自定义的类型,需要自定义排序器
comparator = job.getOutputKeyComparator();
keyClass = (Class<K>)job.getMapOutputKeyClass();
valClass = (Class<V>)job.getMapOutputValueClass();
//
serializationFactory = new SerializationFactory(job);
keySerializer = serializationFactory.getSerializer(keyClass);
keySerializer.open(bb);
valSerializer = serializationFactory.getSerializer(valClass);
valSerializer.open(bb);
// output counters
mapOutputByteCounter = reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.MAP_OUTPUT_BYTES);
mapOutputRecordCounter =
reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.MAP_OUTPUT_RECORDS);
fileOutputByteCounter = reporter
.getCounter(TaskCounter.MAP_OUTPUT_MATERIALIZED_BYTES);
// compression
if (job.getCompressMapOutput()) {
Class<? extends CompressionCodec> codecClass =
job.getMapOutputCompressorClass(DefaultCodec.class);
codec = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(codecClass, job);
} else {
codec = null;
}
// combiner
final Counters.Counter combineInputCounter =
reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.COMBINE_INPUT_RECORDS);
combinerRunner = CombinerRunner.create(job, getTaskID(),
combineInputCounter,
reporter, null);
if (combinerRunner != null) {
final Counters.Counter combineOutputCounter =
reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.COMBINE_OUTPUT_RECORDS);
combineCollector= new CombineOutputCollector<K,V>(combineOutputCounter, reporter, job);
} else {
combineCollector = null;
}
spillInProgress = false;
minSpillsForCombine = job.getInt(JobContext.MAP_COMBINE_MIN_SPILLS, 3);
spillThread.setDaemon(true);
spillThread.setName("SpillThread");
spillLock.lock();
try {
spillThread.start();
while (!spillThreadRunning) {
spillDone.await();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new IOException("Spill thread failed to initialize", e);
} finally {
spillLock.unlock();
}
if (sortSpillException != null) {
throw new IOException("Spill thread failed to initialize",
sortSpillException);
}
}
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.task.JobContextImpl#getPartitionerClass 默认是hash分区
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Class<? extends Partitioner<?,?>> getPartitionerClass()
throws ClassNotFoundException {
return (Class<? extends Partitioner<?,?>>)
conf.getClass(PARTITIONER_CLASS_ATTR, HashPartitioner.class);
}
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.partition.HashPartitioner
public class HashPartitioner<K, V> extends Partitioner<K, V> {
/** Use {@link Object#hashCode()} to partition. */
public int getPartition(K key, V value,
int numReduceTasks) {
return (key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks;
}
}
output-->NewOutputCollector--->write
@Override
public void write(K key, V value) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
collector.collect(key, value,
partitioner.getPartition(key, value, partitions));
}
MapOutputBuffer
/**
* Serialize the key, value to intermediate storage.
* When this method returns, kvindex must refer to sufficient unused
* storage to store one METADATA.
*/
public synchronized void collect(K key, V value, final int partition
) throws IOException {
reporter.progress();
if (key.getClass() != keyClass) {
throw new IOException("Type mismatch in key from map: expected "
+ keyClass.getName() + ", received "
+ key.getClass().getName());
}
if (value.getClass() != valClass) {
throw new IOException("Type mismatch in value from map: expected "
+ valClass.getName() + ", received "
+ value.getClass().getName());
}
if (partition < 0 || partition >= partitions) {
throw new IOException("Illegal partition for " + key + " (" +
partition + ")");
}
checkSpillException();
bufferRemaining -= METASIZE;
if (bufferRemaining <= 0) {
// start spill if the thread is not running and the soft limit has been
// reached
spillLock.lock();
try {
do {
if (!spillInProgress) {
final int kvbidx = 4 * kvindex;
final int kvbend = 4 * kvend;
// serialized, unspilled bytes always lie between kvindex and
// bufindex, crossing the equator. Note that any void space
// created by a reset must be included in "used" bytes
final int bUsed = distanceTo(kvbidx, bufindex);
final boolean bufsoftlimit = bUsed >= softLimit;
if ((kvbend + METASIZE) % kvbuffer.length !=
equator - (equator % METASIZE)) {
// spill finished, reclaim space
resetSpill();
bufferRemaining = Math.min(
distanceTo(bufindex, kvbidx) - 2 * METASIZE,
softLimit - bUsed) - METASIZE;
continue;
} else if (bufsoftlimit && kvindex != kvend) {
// spill records, if any collected; check latter, as it may
// be possible for metadata alignment to hit spill pcnt
//====开始溢写====================
startSpill();
final int avgRec = (int)
(mapOutputByteCounter.getCounter() /
mapOutputRecordCounter.getCounter());
// leave at least half the split buffer for serialization data
// ensure that kvindex >= bufindex
final int distkvi = distanceTo(bufindex, kvbidx);
final int newPos = (bufindex +
Math.max(2 * METASIZE - 1,
Math.min(distkvi / 2,
distkvi / (METASIZE + avgRec) * METASIZE)))
% kvbuffer.length;
setEquator(newPos);
bufmark = bufindex = newPos;
final int serBound = 4 * kvend;
// bytes remaining before the lock must be held and limits
// checked is the minimum of three arcs: the metadata space, the
// serialization space, and the soft limit
bufferRemaining = Math.min(
// metadata max
distanceTo(bufend, newPos),
Math.min(
// serialization max
distanceTo(newPos, serBound),
// soft limit
softLimit)) - 2 * METASIZE;
}
}
} while (false);
} finally {
spillLock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public void close(TaskAttemptContext context
) throws IOException,InterruptedException {
try {
//===============关键代码===============
collector.flush();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cnf) {
throw new IOException("can't find class ", cnf);
}
collector.close();
}
}
collector--->MapOutputBuffer
public void flush() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException,
InterruptedException {
LOG.info("Starting flush of map output");
if (kvbuffer == null) {
LOG.info("kvbuffer is null. Skipping flush.");
return;
}
spillLock.lock();
try {
while (spillInProgress) {
reporter.progress();
spillDone.await();
}
checkSpillException();
final int kvbend = 4 * kvend;
if ((kvbend + METASIZE) % kvbuffer.length !=
equator - (equator % METASIZE)) {
// spill finished
resetSpill();
}
if (kvindex != kvend) {
kvend = (kvindex + NMETA) % kvmeta.capacity();
bufend = bufmark;
LOG.info("Spilling map output");
LOG.info("bufstart = " + bufstart + "; bufend = " + bufmark +
"; bufvoid = " + bufvoid);
LOG.info("kvstart = " + kvstart + "(" + (kvstart * 4) +
"); kvend = " + kvend + "(" + (kvend * 4) +
"); length = " + (distanceTo(kvend, kvstart,
kvmeta.capacity()) + 1) + "/" + maxRec);
sortAndSpill();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new IOException("Interrupted while waiting for the writer", e);
} finally {
spillLock.unlock();
}
assert !spillLock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
// shut down spill thread and wait for it to exit. Since the preceding
// ensures that it is finished with its work (and sortAndSpill did not
// throw), we elect to use an interrupt instead of setting a flag.
// Spilling simultaneously from this thread while the spill thread
// finishes its work might be both a useful way to extend this and also
// sufficient motivation for the latter approach.
try {
spillThread.interrupt();
spillThread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new IOException("Spill failed", e);
}
// release sort buffer before the merge
kvbuffer = null;
//当最后一个数据写出后,开始对溢写的小文件进行合并
mergeParts();
Path outputPath = mapOutputFile.getOutputFile();
fileOutputByteCounter.increment(rfs.getFileStatus(outputPath).getLen());
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void run(JobConf job, final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical)
throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
job.setBoolean(JobContext.SKIP_RECORDS, isSkipping());
//reduce的三个阶段
if (isMapOrReduce()) {
copyPhase = getProgress().addPhase("copy");
sortPhase = getProgress().addPhase("sort");
reducePhase = getProgress().addPhase("reduce");
}
// start thread that will handle communication with parent
TaskReporter reporter = startReporter(umbilical);
boolean useNewApi = job.getUseNewReducer();
//初始化信息
initialize(job, getJobID(), reporter, useNewApi);
// check if it is a cleanupJobTask
if (jobCleanup) {
runJobCleanupTask(umbilical, reporter);
return;
}
if (jobSetup) {
runJobSetupTask(umbilical, reporter);
return;
}
if (taskCleanup) {
runTaskCleanupTask(umbilical, reporter);
return;
}
// Initialize the codec
codec = initCodec();
RawKeyValueIterator rIter = null;
ShuffleConsumerPlugin shuffleConsumerPlugin = null;
Class combinerClass = conf.getCombinerClass();
CombineOutputCollector combineCollector =
(null != combinerClass) ?
new CombineOutputCollector(reduceCombineOutputCounter, reporter, conf) : null;
Class<? extends ShuffleConsumerPlugin> clazz =
job.getClass(MRConfig.SHUFFLE_CONSUMER_PLUGIN, Shuffle.class, ShuffleConsumerPlugin.class);
shuffleConsumerPlugin = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(clazz, job);
LOG.info("Using ShuffleConsumerPlugin: " + shuffleConsumerPlugin);
ShuffleConsumerPlugin.Context shuffleContext =
new ShuffleConsumerPlugin.Context(getTaskID(), job, FileSystem.getLocal(job), umbilical,
super.lDirAlloc, reporter, codec,
combinerClass, combineCollector,
spilledRecordsCounter, reduceCombineInputCounter,
shuffledMapsCounter,
reduceShuffleBytes, failedShuffleCounter,
mergedMapOutputsCounter,
taskStatus, copyPhase, sortPhase, this,
mapOutputFile, localMapFiles);
//=================关键代码=========================
shuffleConsumerPlugin.init(shuffleContext);
rIter = shuffleConsumerPlugin.run();
// free up the data structures
mapOutputFilesOnDisk.clear();
sortPhase.complete(); // sort is complete
setPhase(TaskStatus.Phase.REDUCE);
statusUpdate(umbilical);
Class keyClass = job.getMapOutputKeyClass();
Class valueClass = job.getMapOutputValueClass();
RawComparator comparator = job.getOutputValueGroupingComparator();
if (useNewApi) {
runNewReducer(job, umbilical, reporter, rIter, comparator,
keyClass, valueClass);
} else {
runOldReducer(job, umbilical, reporter, rIter, comparator,
keyClass, valueClass);
}
shuffleConsumerPlugin.close();
done(umbilical, reporter);
}