Software industry & market
16.1 Economical characteristics of software
Software evolution
Software will be evolution, not involution.
- Hardware will be worn - Bathtub curve (1)
- Software will be deteriorated(退化) - Sail curve (2)
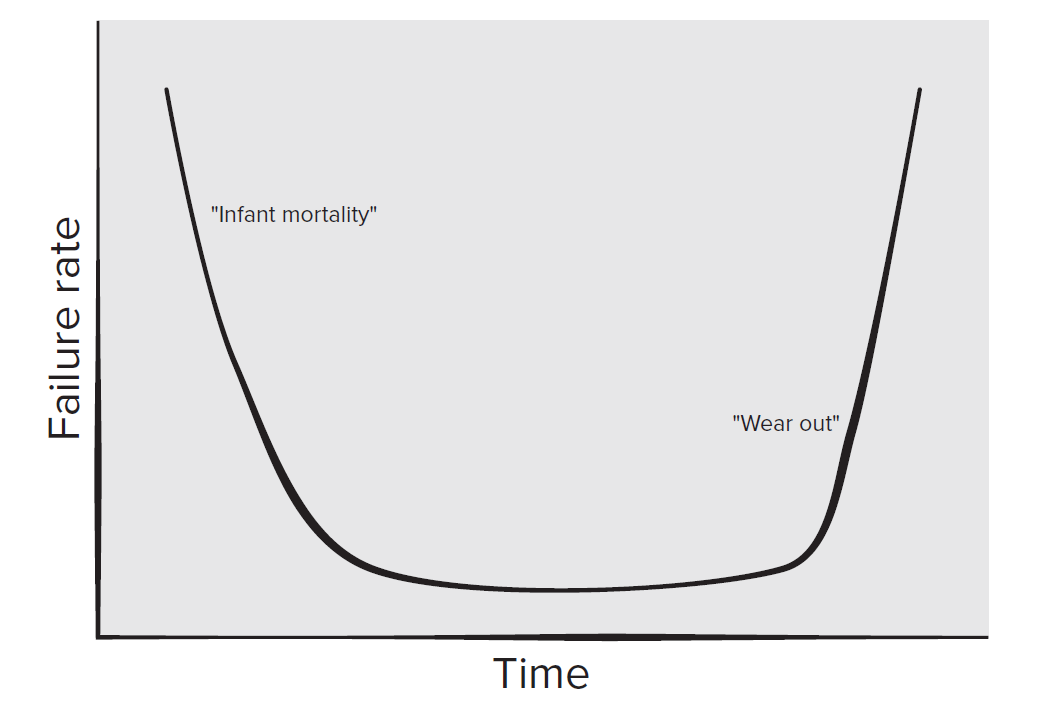
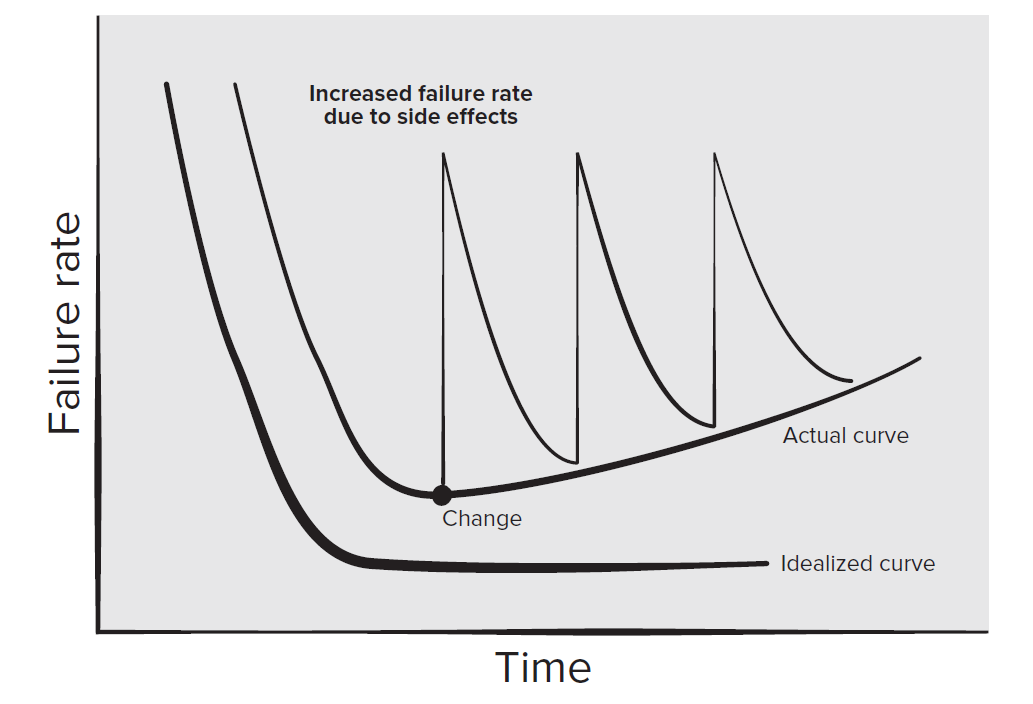
The marginal cost of software is Zero
Marginal cost of software, also called incremental cost, refers to the cost to be paid for each additional unit of software product production.
The source code development cost of the first software product is high, but the cost of copying the source code is close to zero, and the quality of the copy is the same as that of the first product.
16.2 Sources of Software Value
The objects processed by software include:
- data
- information
- knowledge
- intelligence
Different views on Software Quality
- A priori view(先验论): quality is recognizable, but undefined.
- User view: quality is just to achieve the goal.
- Developer's point of view: quality is the consistency between products and specifications.
- Product view: quality is related to the internal characteristics of products.
- Value based view: quality depends on the amount the customer is willing to pay.
16.3 Paradigm of SEE Analysis
Goal-Plan-Metrics in balance
- Goals in software engineering economics are mostly business goals or business objectives. Goals apply to operational planning.
- Metrics are a well-founded evaluation of resources and time that will be needed to achieve stated goals. e.g., Effort, Schedule, Cost Estimation and Maintenance Cost Estimation.
Estimation is a periodic activity, should be continually revised during a project. - Plan describes the activities and milestones that are necessary in order to reach the goals of a project. The plan should be in line with the goal and the estimate.
Estimates are done based on the initial goals. The plan tries to match the goals and the estimates. This is an iterative process.