对于两组点集,要计算其旋转平移矩阵,可以用点云配准算法。
也可以用非线性优化的方法计算,不过由于待优化量包含旋转量,做迭代求雅克比矩阵时如果用欧拉角表示旋转矩阵会比较麻烦。
因此这里用李群李代数的方法求解。
李群与李代数互转公式见下图:
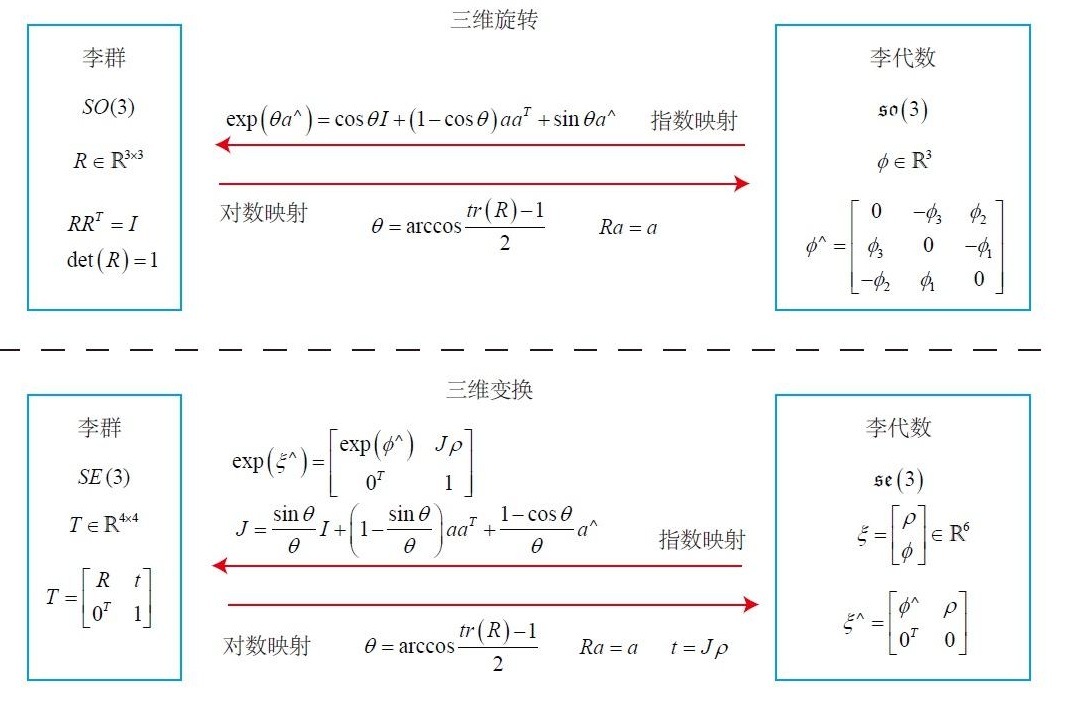
通常用三维变换SE(3)多一些,三维空间中一般都是包含旋转和平移的。
这里平移的雅克比就是单位矩阵。
旋转的雅克比是点云的反对称矩阵。
然后迭代求解即可。
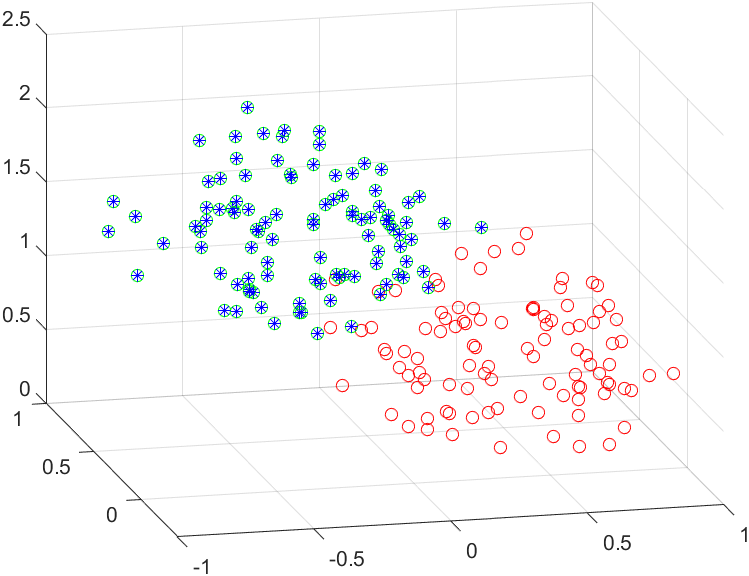
clear all;close all;clc; %生成原始点集 srcP = [rand(3,100);ones(1,100)]; %生成变换后点集 sx = rand(1,6)*2-1 R = se3_to_SE3(sx); dstP = R * srcP; plot3(srcP(1,:),srcP(2,:),srcP(3,:),'ro'); hold on; plot3(dstP(1,:),dstP(2,:),dstP(3,:),'go'); grid on; x = zeros(1,6); for i=1:100 J = calcJab(x,srcP); fx = calcCost(x,srcP,dstP); dx = inv(J'*J)*J'*fx; x = x + dx'; % x = SE3_to_se3(se3_to_SE3(x)*se3_to_SE3(dx')); end new_dstP = se3_to_SE3(x) * srcP; plot3(new_dstP(1,:),new_dstP(2,:),new_dstP(3,:),'b*'); x function J = calcJab(x,srcP) R = se3_to_SE3(x); new_P = R * srcP; J = zeros(3*size(srcP,2),6); for i=1:size(srcP,2) X = new_P(1,i); Y = new_P(2,i); Z = new_P(3,i); Jab = zeros(3,6); Jab(1:3,1:3) = eye(3,3); Jab(1:3,4:6) = -[0 -Z Y;Z 0 -X;-Y X 0]; J((i-1)*3+1:i*3,:) = Jab; end end function fx = calcCost(x,srcP,dstP) R = se3_to_SE3(x); new_P = R * srcP; fx = zeros(3*size(srcP,2),1); for i=1:size(srcP,2) dstX = dstP(1,i); dstY = dstP(2,i); dstZ = dstP(3,i); X = new_P(1,i); Y = new_P(2,i); Z = new_P(3,i); fx((i-1)*3+1:i*3) = [dstX - X;dstY - Y;dstZ - Z]; end end function se3 = SE3_to_se3( SE3 ) % UNTITLED Summary of this function goes here % Detailed explanation goes here R=SE3(1:3,1:3); theta=acos((trace(R)-1)/2); lnR=(theta/(2*sin(theta)))*(R-R'); w=[-lnR(2,3) lnR(1,3) -lnR(1,2)]; wx=[0 -w(3) w(2);w(3) 0 -w(1);-w(2) w(1) 0]; if(theta==0) Vin=eye(3); else A=sin(theta)/theta; B=(1-cos(theta))/(theta^2); Vin=eye(3)-(1/2)*wx+(1/(theta^2))*(1-(A/(2*B)))*(wx*wx); end u=Vin*SE3(1:3,4); se3=[u' w]; end function SE3 = se3_to_SE3( se3 ) % se3_SE3 Exponential Mapping from Lie Algebra to Lie Group % se3 is a 1x6 Column Vector of the form=[v1 v2 v3 w1 w2 w3] which is % defined using 6 Generator Matrices(4x4) % each of the six elements on multiplication with the generator matrices % as follows give the complete matrix: % se3 = v1*G1 + v2*G2 + v3*G3 + w1*G4 + w2*G5 + w3*G6 % To map se3 to SE3 we need to perform e^(se3) % This can be done by following the algorithm: % Algorithm w=se3(4:6)'; u=se3(1:3)'; wx=[0 -w(3) w(2);w(3) 0 -w(1);-w(2) w(1) 0]; theta=sqrt(w'*w); if(theta~=0) A=sin(theta)/theta; B=(1-cos(theta))/(theta^2); C=(1-A)/(theta^2); else A=0; B=0; C=0; end R=eye(3)+(A*wx)+(B*(wx*wx)); V=eye(3)+B*wx+C*(wx*wx); Vp=V*u; SE3=zeros(4); SE3(1:3,1:3)=R; SE3(1:3,4)=Vp; SE3(4,4)=1; end
结果如下: