粗略看了下kernel/kprobes.c下的register_kprobe方法。
逻辑:
-
调用
kprobe_addr方法来根据symbol或者addr+offset来获取需要劫持的地址,symbol和addr不能同时设置,symbol是利用kprobe_lookup_name -> kallsyms_lookup_name来查找内核中的符号地址。 -
检查这个kprobe是否重注册了?
持有
kprobe_mutex锁,并搜索kprobe_table哈希表。先通过
get_kprobe获取原劫持指令的哈希节点(黑色),然后遍历下面的劫持后指令的链表节点(红色节点)。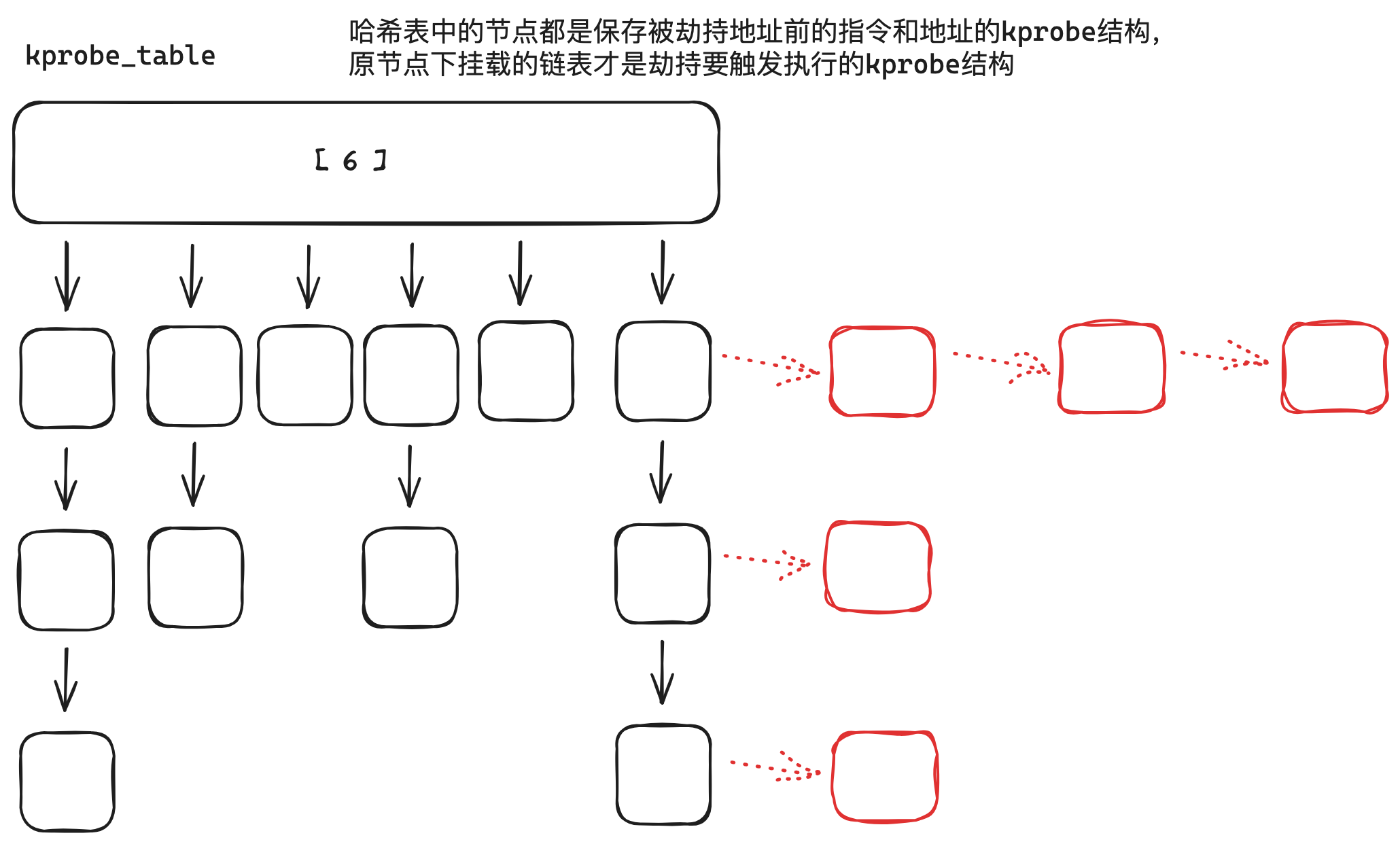
-
确保用户只能设置kprobe的标志位flags上的
KPROBE_FLAG_DISABLEE位为0或者1。设置重启用次数nmissed为0,初始化list链表节点。 -
检查劫持的内核地址是否安全?(
check_kprobe_address_safe)判断标准:
不能是ftrace的代码、不能是内核text段、不能在kprobe_blacklist上,该地址不能被预留的,不能是bug对应的地址,如果是module代码,则必须保存模块代码没被卸载。
-
如果该地址已经被劫持过,则调用
register_aggr_kprobe方法直接插入到对应的链表节点。 -
持有
kprobe_mutex锁。 -
再次根据劫持地址获取kprobe,如果已经存在kprobe则跳过。
-
初始化哈希链表节点hlist,并加入
kprobe_table。 -
如果
kprobe_all_disarmed选项没设置或者kprobe没被禁用,则调用arm_kprobe方法插入指令。arm_kprobe方法:#define __arm_kprobe(p) arch_arm_kprobe(p) static int arm_kprobe(struct kprobe *kp) { if (unlikely(kprobe_ftrace(kp))) return arm_kprobe_ftrace(kp); cpus_read_lock(); mutex_lock(&text_mutex); __arm_kprobe(kp); // 调用架构对应的插入指令方法 mutex_unlock(&text_mutex); cpus_read_unlock(); return 0; }x86架构下的
arch_arm_kprobe方法:#define BREAKPOINT_INSTRUCTION 0xcc void arch_arm_kprobe(struct kprobe *p) { text_poke(p->addr, ((unsigned char []){BREAKPOINT_INSTRUCTION}), 1); }x86架构下对
int3指令的处理方法do_int3:dotraplinkage void notrace do_int3(struct pt_regs *regs, long error_code) { #ifdef CONFIG_DYNAMIC_FTRACE /* * ftrace must be first, everything else may cause a recursive crash. * See note by declaration of modifying_ftrace_code in ftrace.c */ if (unlikely(atomic_read(&modifying_ftrace_code)) && ftrace_int3_handler(regs)) return; #endif if (poke_int3_handler(regs)) return; /* * Use ist_enter despite the fact that we don't use an IST stack. * We can be called from a kprobe in non-CONTEXT_KERNEL kernel * mode or even during context tracking state changes. * * This means that we can't schedule. That's okay. */ ist_enter(regs); RCU_LOCKDEP_WARN(!rcu_is_watching(), "entry code didn't wake RCU"); #ifdef CONFIG_KGDB_LOW_LEVEL_TRAP if (kgdb_ll_trap(DIE_INT3, "int3", regs, error_code, X86_TRAP_BP, SIGTRAP) == NOTIFY_STOP) goto exit; #endif /* CONFIG_KGDB_LOW_LEVEL_TRAP */ #ifdef CONFIG_KPROBES // 这里判断是否需要进行kprobe回调 if (kprobe_int3_handler(regs)) goto exit; #endif if (notify_die(DIE_INT3, "int3", regs, error_code, X86_TRAP_BP, SIGTRAP) == NOTIFY_STOP) goto exit; cond_local_irq_enable(regs); do_trap(X86_TRAP_BP, SIGTRAP, "int3", regs, error_code, NULL); cond_local_irq_disable(regs); exit: ist_exit(regs); } NOKPROBE_SYMBOL(do_int3);
执行中断指令int3时如何回调到kprobe对应的方法:
arch/arc/kernel/kprobes.c文件中定义的几个变量:
每个cpu中都存在一份自己的变量:current_kprobe指向当前执行的kprobe指针,kprobe_ctlblk指向当前kprobe执行控制块

// 控制块状态
/* kprobe_status settings */
#define KPROBE_HIT_ACTIVE 0x00000001
#define KPROBE_HIT_SS 0x00000002
#define KPROBE_REENTER 0x00000004
#define KPROBE_HIT_SSDONE 0x00000008
/*
* Interrupts are disabled on entry as trap3 is an interrupt gate and they
* remain disabled throughout this function.
*/
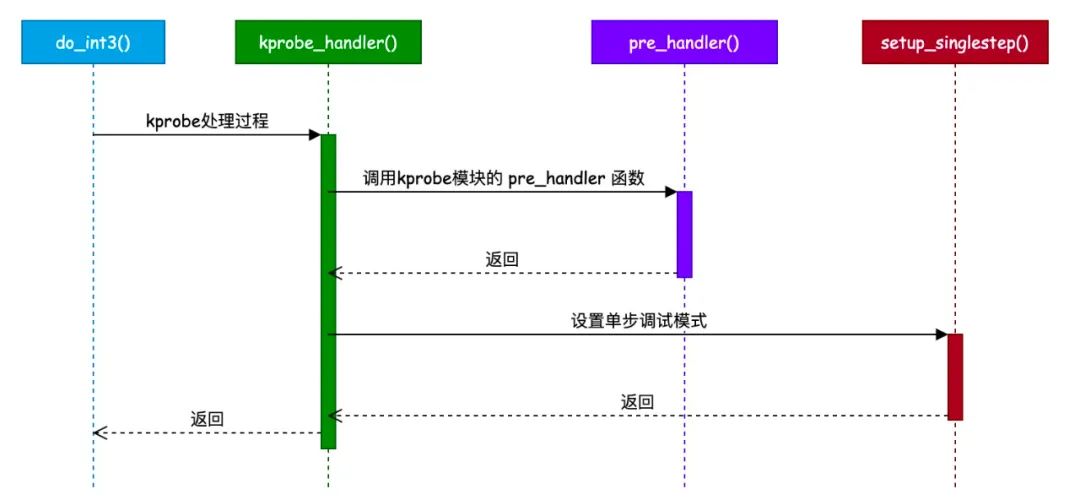
int kprobe_int3_handler(struct pt_regs *regs)
{
kprobe_opcode_t *addr;
struct kprobe *p;
struct kprobe_ctlblk *kcb;
if (user_mode(regs))
return 0;
// 获取当前指令地址
addr = (kprobe_opcode_t *)(regs->ip - sizeof(kprobe_opcode_t));
/*
* We don't want to be preempted for the entire duration of kprobe
* processing. Since int3 and debug trap disables irqs and we clear
* IF while singlestepping, it must be no preemptible.
*/
// 获取kprobe执行控制块
kcb = get_kprobe_ctlblk();
// 从kprobe_table中根据地址搜索kprobe
p = get_kprobe(addr);
if (p) {
// 判断当前是否在执行kprobe? 就是判断current_kprobe是否为NULL
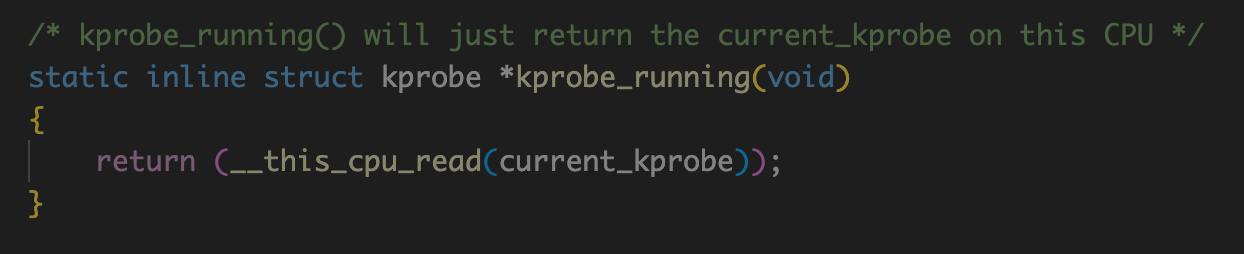
if (kprobe_running()) {
// 如果控制块当前记录了为重进入, 那么会直接panic,
// 其他状态则nmissed+1, 设置当前kprobe_ctlblk保存当前kprobe,
// 并设置ip
if (reenter_kprobe(p, regs, kcb))
return 1;
} else {
set_current_kprobe(p, regs, kcb);
kcb->kprobe_status = KPROBE_HIT_ACTIVE;
/*
* If we have no pre-handler or it returned 0, we
* continue with normal processing. If we have a
* pre-handler and it returned non-zero, that means
* user handler setup registers to exit to another
* instruction, we must skip the single stepping.
*/
if (!p->pre_handler || !p->pre_handler(p, regs))
// 设置ip到kprobe对应的处理方法地址
setup_singlestep(p, regs, kcb, 0);
else
reset_current_kprobe();
return 1;
}
} else if (*addr != BREAKPOINT_INSTRUCTION) {
/*
* The breakpoint instruction was removed right
* after we hit it. Another cpu has removed
* either a probepoint or a debugger breakpoint
* at this address. In either case, no further
* handling of this interrupt is appropriate.
* Back up over the (now missing) int3 and run
* the original instruction.
*/
regs->ip = (unsigned long)addr;
return 1;
} /* else: not a kprobe fault; let the kernel handle it */
return 0;
}
NOKPROBE_SYMBOL(kprobe_int3_handler);
kprobe_running:判断当前cpu中的current_kprobe变量是否为NULL。