Inception块
在GoogLeNet中,基本的卷积块被称为Inception块(Inception block)。具体结构如下图:

这四条路径都使用合适的填充来使输入与输出的高和宽一致,最后我们将每条线路的输出在通道维度上连结,并构成Inception块的输出。在Inception块中,通常调整的超参数是每层输出通道数。
那么为什么GoogLeNet这个网络如此有效呢? 首先我们考虑一下滤波器(filter)的组合,它们可以用各种滤波器尺寸探索图像,这意味着不同大小的滤波器可以有效地识别不同范围的图像细节。 同时,我们可以为不同的滤波器分配不同数量的参数。
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
from d2l import torch as d2l
class Inception(nn.Module):
# c1--c4是每条路径的输出通道数
def __init__(self, in_channels, c1, c2, c3, c4, **kwargs):
super(Inception, self).__init__(**kwargs)
# 线路1,单1x1卷积层
self.p1_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, c1, kernel_size=1)
# 线路2,1x1卷积层后接3x3卷积层
self.p2_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, c2[0], kernel_size=1)
self.p2_2 = nn.Conv2d(c2[0], c2[1], kernel_size=3, padding=1)
# 线路3,1x1卷积层后接5x5卷积层
self.p3_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, c3[0], kernel_size=1)
self.p3_2 = nn.Conv2d(c3[0], c3[1], kernel_size=5, padding=2)
# 线路4,3x3最大汇聚层后接1x1卷积层
self.p4_1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
self.p4_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, c4, kernel_size=1)
def forward(self, x):
p1 = F.relu(self.p1_1(x))
p2 = F.relu(self.p2_2(F.relu(self.p2_1(x))))
p3 = F.relu(self.p3_2(F.relu(self.p3_1(x))))
p4 = F.relu(self.p4_2(self.p4_1(x)))
# 在通道维度上连结输出
return torch.cat((p1, p2, p3, p4), dim=1)
GoogLeNet模型
GoogLeNet一共使用9个Inception块和全局平均汇聚层的堆叠来生成其估计值。Inception块之间的最大汇聚层可降低维度。 第一个模块类似于AlexNet和LeNet,Inception块的组合从VGG继承,全局平均汇聚层避免了在最后使用全连接层。
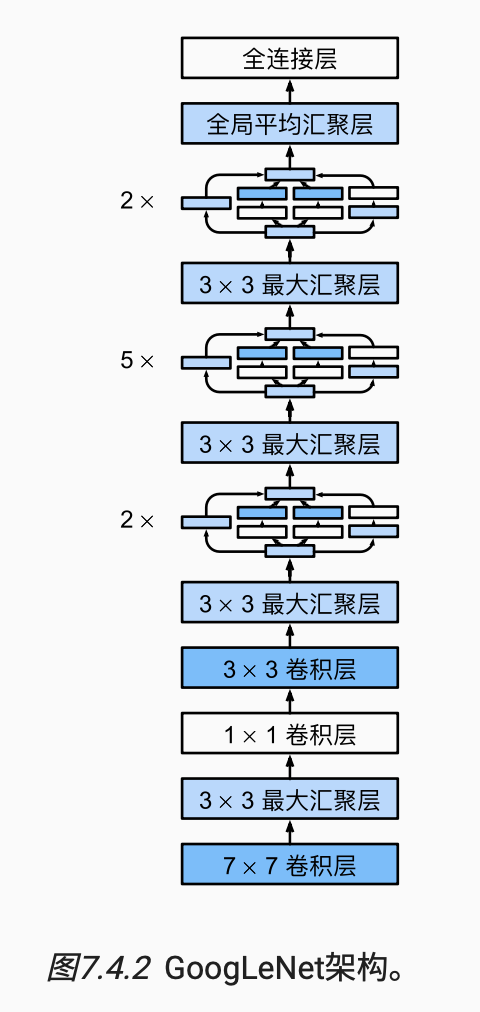
b1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1))
b2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1))
b3 = nn.Sequential(Inception(192, 64, (96, 128), (16, 32), 32),
Inception(256, 128, (128, 192), (32, 96), 64),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1))
b4 = nn.Sequential(Inception(480, 192, (96, 208), (16, 48), 64),
Inception(512, 160, (112, 224), (24, 64), 64),
Inception(512, 128, (128, 256), (24, 64), 64),
Inception(512, 112, (144, 288), (32, 64), 64),
Inception(528, 256, (160, 320), (32, 128), 128),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1))
b5 = nn.Sequential(Inception(832, 256, (160, 320), (32, 128), 128),
Inception(832, 384, (192, 384), (48, 128), 128),
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1,1)),
nn.Flatten())
net = nn.Sequential(b1, b2, b3, b4, b5, nn.Linear(1024, 10))
X = torch.rand(size=(1, 1, 96, 96))
for layer in net:
X = layer(X)
print(layer.__class__.__name__,'output shape:\t', X.shape)
Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 24, 24]) Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 192, 12, 12]) Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 480, 6, 6]) Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 832, 3, 3]) Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 1024]) Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 10])
总结
-
Inception块相当于一个有4条路径的子网络。它通过不同窗口形状的卷积层和最大汇聚层来并行抽取信息,并使用1*1卷积层减少每像素级别上的通道维数从而降低模型复杂度。
-
GoogLeNet将多个设计精细的Inception块与其他层(卷积层、全连接层)串联起来。其中Inception块的通道数分配之比是在ImageNet数据集上通过大量的实验得来的。
-
GoogLeNet和它的后继者们一度是ImageNet上最有效的模型之一:它以较低的计算复杂度提供了类似的测试精度。