前言
在工作中,尤其是对于经常操作数据的项目来说,可能会经常出现操作表格的需求,因为用户需要导出数据来查看汇报信息,这时就可以通过POI进行操作。
Apache POI 是用Java编写的免费开源的跨平台的Java API,Apache POI提供API给Java程序对Microsoft Office格式档案读和写的功能,其中使用最多的就是使用POI操作Excel文件
本篇文章并不是教大家了解学习POI,而是为大家介绍一个POI的工具类,方便大家开发节省时间。
首先简单来看下是如何通过POI操作导入Excel的,代码如下:
public boolean importExcel(MultipartFile file, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
log.info("开始导入");
// 解析文件获得workbook
InputStream in = file.getInputStream();
Workbook workbook = WorkbookFactory.create(in);
// 解析Excel第一sheet页
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
// 获取totalRows数据总行数
int totalRows = sheet.getPhysicalNumberOfRows();
if(totalRows <= 1){
log.info("数据为空");
return false;
}
for (int i = 1; i < totalRows; i++) {
// 获取第i行
Row currentRow = sheet.getRow(i);
// 获取第1列数据的值 [注意:poi解析中下标是从0开始的,也就是说第一行和第一列的下标为0]
String str = currentRow.getCell(0).getStringCellValue();
// ...
}
log.info("导入结束");
return true;
}
上面是粗略的展示了POI获取Excel中数据的写法,通过上面代码发现其实在解析Excel中有很多代码我们可以提取出来作为工具类来进行使用,下面展开工具类的介绍。
POI导入
前提介绍:POI导入工具类依据Swagger的一些注解进行编写,所以不了解Swagger的可以查看我之前的文章。
1.导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml-schemas</artifactId>
<version>4.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-scratchpad</artifactId>
<version>4.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>4.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>4.1.2</version>
</dependency>
2.工具类代码
- ApiModelProperty注解工具
public class ApiModelPropertyUtils {
/**
* 获取参数名称与ApiModelProperty注解的值的对应关系
*
* @param clz 类的Class类型
* @return
*/
public static LinkedHashMap<String, String> getApiModelPropertyValueAndFieldName(Class<?> clz) {
return getApiModelPropertyValueAndFieldName(clz, null);
}
/**
* 获取参数名称与ApiModelProperty注解的值的对应关系
*
* @param clz 类的Class类型
* @param replaceMap 需要进行替换的表头元素, key是原始值,value是新值
* @return
*/
public static LinkedHashMap<String, String> getApiModelPropertyValueAndFieldName(Class<?> clz, HashMap<String, String> replaceMap) {
Field[] fields = clz.getDeclaredFields();
LinkedHashMap<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(fields.length);
for (Field field : fields) {
if (field == null) {
continue;
}
ApiModelProperty apiModelProperty = field.getAnnotation(ApiModelProperty.class);
if (apiModelProperty == null) {
continue;
}
String apiModelPropertyValue = apiModelProperty.value();
if(replaceMap != null && StringUtils.isNotBlank(replaceMap.get(apiModelPropertyValue))){
apiModelPropertyValue = replaceMap.get(apiModelPropertyValue);
}
map.put(apiModelPropertyValue, field.getName());
}
return map;
}
/**
* 获取参数名称与ApiModelProperty注解的值的对应关系
*
* @param variableObj
* @return
*/
public static LinkedHashMap<String, Object> getApiModelPropertyValueAndFieldValue(Object variableObj) throws IllegalAccessException {
Field[] fields = variableObj.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
LinkedHashMap<String, Object> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(fields.length);
for (Field field : fields) {
if (field == null) {
continue;
}
field.setAccessible(true);
Object value = field.get(variableObj);
ApiModelProperty apiModelProperty = field.getAnnotation(ApiModelProperty.class);
if (apiModelProperty != null) {
map.put(apiModelProperty.value(), value);
}
}
return map;
}
}
- 导入excel工具类
@Slf4j
public class ImpExcelUtil {
private static final int MAX_RANGE = 20;
/**
* 检查文件类型
* @param file
* @return
*/
private static Workbook checkFileTypeAndGetWorkBook(MultipartFile file) throws Exception {
// 解析文件
String suffix = Objects.requireNonNull(file.getResource().getFilename()).substring(file.getResource().getFilename().indexOf(".") + 1);
String xls = "xls";String xlsx = "xlsx";
Workbook workbook;
if (xls.equals(suffix)) {
workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(file.getInputStream());
} else if (xlsx.equals(suffix)) {
workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(file.getInputStream());
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("文件类型不正确");
}
return workbook;
}
/**
* 拿到不同类型单元格中的值
* 1. 字符串: 字符串
* 2. 布尔: toString
* 3. 数值(double): 格式化后的字符串
* @param cell 获取的单元格
* @return 单元格中的值
*/
public static String getCellValue(Cell cell) {
String resultValue = "";
// 判空
if (Objects.isNull(cell)) {
return resultValue;
}
// 拿到单元格类型
CellType cellType = cell.getCellType();
switch (cellType) {
// 字符串类型
case STRING:
resultValue = StringUtils.isEmpty(cell.getStringCellValue()) ? "" : cell.getStringCellValue().trim();
break;
// 布尔类型
case BOOLEAN:
resultValue = String.valueOf(cell.getBooleanCellValue());
break;
// 数值类型
case NUMERIC:
resultValue = new DecimalFormat("#.######").format(cell.getNumericCellValue());
break;
// 取空串
default:
break;
}
return resultValue;
}
/**
* 通过excel生成数据
*
* @param workbook excel
* @param sheetNum sheet页数
* @param tClass T的class类型
* @param map 参数名称与Excel表中的列头的对应关系
* @param <T> 需要返回的对象类型
* @return 需要返回的对象类型的列表
* @throws IllegalAccessException
* @throws InstantiationException
* @throws InvocationTargetException
*/
public static <T> List<T> buildDataListByExcel(Workbook workbook, int sheetNum, Class<T> tClass, Map<String, String> map) throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException {
List<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(sheetNum);
Map<Integer, Method> columnNumMethodNameMap = new HashMap<>(16);
for (int i = 0; i < sheet.getPhysicalNumberOfRows(); i++) {
// 获取工作表中的某一行,通过下标获取
Row row = sheet.getRow(i);
// 跳过空行
if (row == null) { continue;}
// 对第一行进行处理,获取参数方法与列顺序的对应
if (i == 0) {
for (int j = 0; j < MAX_RANGE; j++) {
Cell cell = row.getCell(j);
// 跳过空数据
if (cell == null) {
continue;
}
String cellStr = getCellValue(cell);
Method[] methods = tClass.getMethods();
for (int m = 0; m < methods.length - 1; m++) {
Method method = methods[m];
String fieldName = map.get(cellStr);
// 跳过没有对应关系的列
if (StringUtils.isBlank(fieldName)) {
continue;
}
// 拼装为set方法的名称,获取set方法,如果匹配,放入
String methodName = "set" + fieldName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + fieldName.substring(1);
if (method.getName().equals(methodName)) {
columnNumMethodNameMap.put(j, methods[m]);
}
}
}
continue;
}
// 遍历一个行中的所有列
T t = tClass.newInstance();
boolean isNullFlag = false;
for (int j = 0; j < MAX_RANGE; j++) {
// 获取一行中的某个单元格,通过下标获取
Cell cell = row.getCell(j);
if (cell == null) {
continue;
}
// 获取单元格中的内容
String value = ImpExcelUtil.getCellValue(cell);
// 获取方法
Method method = columnNumMethodNameMap.get(j);
// 如果方法、方法的参数为空,直接跳过
if (method == null || method.getParameters() == null || method.getParameters().length <= 0
|| method.getParameters()[0] == null || StringUtils.isBlank(value)) {
continue;
}
Class<?> clz = method.getParameters()[0].getType();
// 对类型进行匹配,然后执行方法,进行数据插入
try {
if (BigDecimal.class.equals(clz)) {
method.invoke(t, new BigDecimal(value));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("传入的'"+ value +"'类型不符合,请检查!!!");
}
if (Long.class.equals(clz)) {
method.invoke(t, Long.parseLong(value));
} else if (String.class.equals(clz)) {
method.invoke(t, value);
} else if (Double.class.equals(clz)) {
method.invoke(t, Double.parseDouble(value));
} else if (Integer.class.equals(clz)) {
method.invoke(t, Integer.parseInt( value));
} else if (Boolean.class.equals(clz)) {
method.invoke(t, Boolean.parseBoolean(value));
} else {
continue;
}
isNullFlag = true;
}
if (isNullFlag) {
list.add(t);
}
}
return list;
}
}
3.使用
- 首先创建接收的实体类,图下:
@Data
public class UserVo {
@ApiModelProperty(value = "账号", dataType = "String")
private String account;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "密码", dataType = "String")
private String userPassword;
}
- 然后创建一个模板,如下图
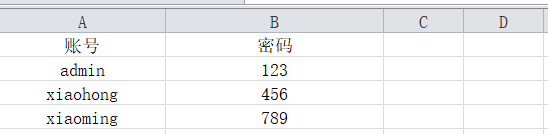
注意:第一行的表头要和@ApiModelProperty中的value值相同
- 编写导入接口及方法实现
@PostMapping("/importExcelTest")
@ResponseBody
Boolean importExcelTest(@RequestBody MultipartFile file, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
return service.importExcelTest(file, request);
}
public Boolean importExcelTest(MultipartFile file, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//检查文件类型
Workbook workbook = ImpExcelUtil.checkFileTypeAndGetWorkBook(file);
//获取参数名称与ApiModelProperty注解的值的对应关系
LinkedHashMap<String, String> map = ApiModelPropertyUtils.getApiModelPropertyValueAndFieldName(UserVo.class);
List<UserVo> importList = ImpExcelUtil.buildDataListByExcel(workbook, 0, UserVo.class, map);
// ...
return true;
}
- 通过debug查看最后获取的
importList的值

通过上面的工具类可以很好的获得Excel表格中导入的数据,之后开发人员直接操作获取到的数据就可以了,很是方便。
微信搜索【君耀软件设计】了解更多