杂谈
- 传统的并行计算要的是:投入更多机器,数据大小不变,计算速度更快。
- 分布式计算要求:投入更多的机器,能处理更大的数据。
- 换句话说二者的出发点从一开始就不同,一个强调 high performance, 一个强调 scalability.
本过程实现的MapReduce是通过Go语言实现的,本人第一次接触Go,可能在码风等问题上有不太友好的地方。
这个课程想学很久了,最近抽出一点点时间,开个坑,做一些lab。在开始之前,一定要看论文,听课程。附上中翻链接
MapReduce是一个软件框架,基于该框架可以更容易地编写应用程序,这些应用程序运行在十分大的集群上,并以可靠的、具有容错能力的方式并行处理TB级别的数据集。
软件框架、并行处理、可靠且容错、大规模集群、海量数据集
因为是第一次接触Go语言,所以在处理语法特性上还有所生疏。(不过感觉大部分特性都能现查)只是听过程的话是可以理解的,落实到代码处理会有很多的问题。整体的代码量不是特别大,可能是我实现的有点复杂,看来是窝太菜惹。
开始之前
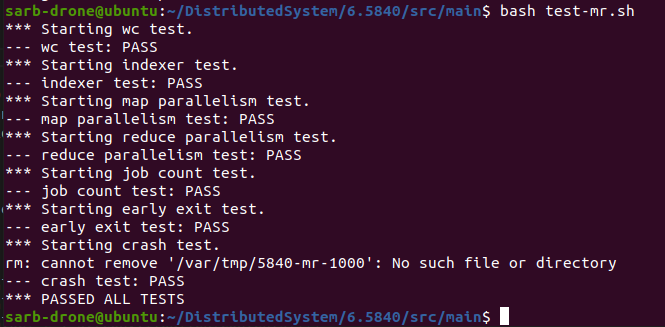
记录一下测试过程:
- 跑通程序:
- 运行coordinator
go run -race mrcoordinator.go pg-*.txt
- 运行worker
go build -race -buildmode=plugin ../mrapps/wc.go
go run -race mrworker.go wc.so
- 测试脚本
bash test-mr.sh
bash test-mr-many.sh 200
整个的实验过程我是在Linux环境下做的。调试的过程中大佬的博客给了很准确的定位调错分析。
在git上下载的压缩包解压之后有go语言较新版本的安装包,可以使用那个配环境。配环境的过程一定要谨慎一些,我最开始就因为没配好环境所以寄了一次 T_T。官方lab指导
记得根据官方指导看一下自己的环境有没有配置完善。
MapReduce的过程主要是理解论文中给的那幅图,我把它放到这里:
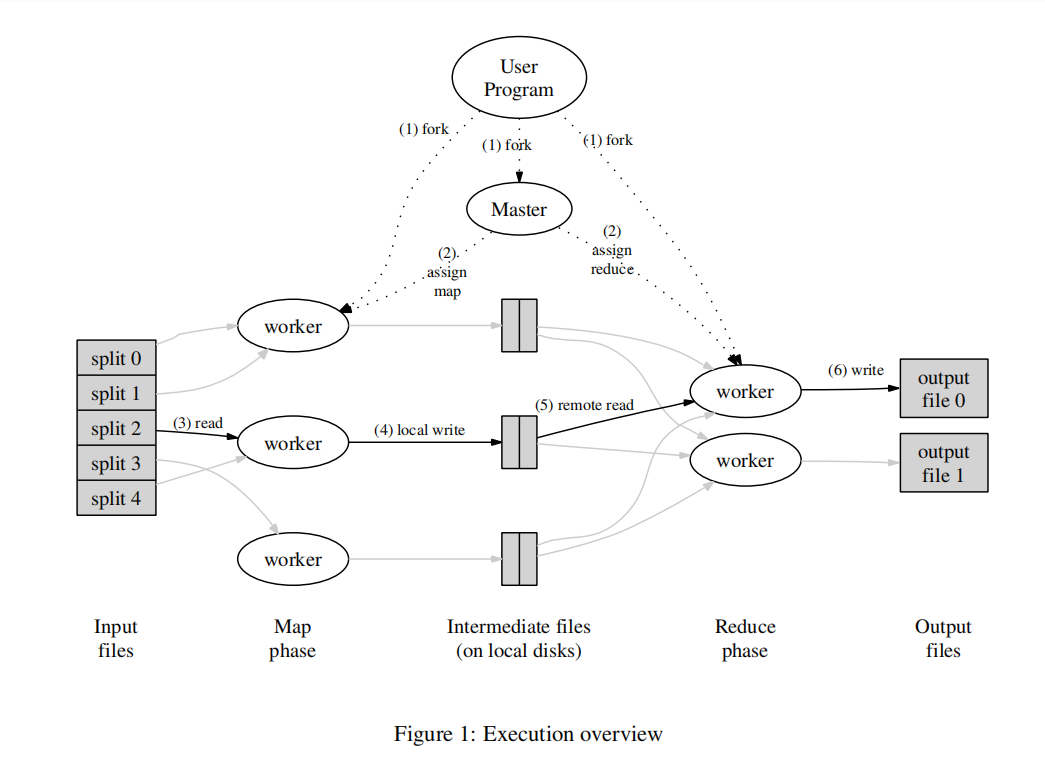
同时论文在3.1节Execution Overview中介绍了这个总体的实现过程思路。我们要做的就是根据论文的思路把这个过程用Go语言实现一遍。
- 在Linux中的默认sort排序是大小写不敏感的,在这个lab我们应该对于大小写敏感。可以采用以下命令:
export LC_ALL=C
实验过程
1. 大体结构
我们通过看实验指导可以知道我们需要做的内容主要是包括三个文件中,coordinator.go,worker.go,rpc.go,只看文件名字大概就可以理解他们各自所主要负责的部分了。
coordinator(协调者)只有一个,worker(工作者)的数量至少为一个,worker之间是并行执行的关系。彼此之间通过RPC协议来通信。coordinator向worker分配任务(Map或Reduce任务),然后worker执行任务并写入指定的文件。
这里coordinator有个规划,一般来说是,在某个worker在一定时间期限内未完成任务的时候,我们选择将这个worker上所执行的任务分配给别的worker从而实现总体系统的可用性。
2. RPC消息结构
认为RPC消息有三种情况:与Map任务相关,与Reduce任务相关,与Worker状态相关。
我们在划分传递消息的时候。分别地,对Map任务定义了MapRequest,MapResponse,MapTaskState三种消息格式;对Reduce任务定义了ReduceRequest,ReduceResponse,ReduceTaskState;对Worker状态相关的消息我们仅保留NReduce,WorkId信息。
其中对于MapRequest和ReduceRequest,这两种消息我们其实是不用分配信息的:因为我们在接到这个信息的目的是需要向其分配任务,那么选择随机分配就可以了,不用采取根据消息类型而区别的情况。(仅对于该lab来说)
【Click to check Codes】
type MapRequest struct {
// random
}
type ReduceRequest struct {
// random
}
type MapResponse struct {
Filename string
State string
}
type ReduceResponse struct {
ReduceId int
Filenames []string // array
State string
}
type MapTaskState struct {
Filename string
WorkerId int
TaskId int
State string
}
type ReduceTaskState struct {
ReduceId int
State string
}
type WorkerInfo struct {
NReduce int
WorkId int
}
3. Coordinator Process
- 首先定义一下Coordinator的结构体格式:
var void interface{}
type stringArray []string // make a type
type Coordinator struct {
files []string
reduceId int
midfFilesMap map[int]stringArray // reduceId
midFilesList []int // unfinished & rpc Sent
mapSend map[string]interface{}
reduceSend map[int]interface{} // reduceId
nReduce int
Finish bool // make sure is finished
mtx sync.Mutex // lock
}
网络上有的做法是将sync.Mutex互斥锁放到了外面,那样应该或许也是可以的()。这里把互斥锁放到了Coordinator结构体里面,方便实现Mutex跟着Coordinator Process进程走的作用。
- 然后是分配WorkerId的方法:
func (c *Coordinator) AssignWorkerId(i *int, woinfo *WorkerInfo) error {
c.mtx.Lock()
woinfo.WorkId = c.reduceId
woinfo.NReduce = c.nReduce
c.reduceId++
c.mtx.Unlock()
return nil
}
- 分发MapTask任务的方法和分发Reduce任务的方法:
// return the first File's name
func (c *Coordinator) AssignMapTask(req *MapRequest, resp *MapResponse) error {
c.mtx.Lock()
if len(c.files) == 0 {
resp.Filename = ""
if len(c.mapSend) == 0 {
resp.State = "done"
// fmt.Println("map task done.")
}
} else {
resp.Filename = c.files[0]
c.files = c.files[1:]
f := mapAfterFuncWrapper(c, resp.Filename)
c.mapSend[resp.Filename] = time.AfterFunc(time.Second*20, f)
}
c.mtx.Unlock()
// fmt.Printf("c.files: %v\n", c.files)
// fmt.Printf("c.mapSend: %v\n", c.mapSend)
return nil
}
// before reduce, return midFile's filename
func (c *Coordinator) AssignReduceTask(req *ReduceRequest, resp *ReduceResponse) error {
c.mtx.Lock()
if len(c.midFilesList) == 0 {
resp.ReduceId = -1
resp.Filenames = nil
if len(c.reduceSend) == 0 {
resp.State = "done"
// fmt.Println("reduce task done")
}
} else {
resp.ReduceId = c.midFilesList[0]
c.midFilesList = c.midFilesList[1:]
resp.Filenames = c.midFilesMap[resp.ReduceId]
f := reduceAfterFuncWrapper(c, resp.ReduceId)
c.reduceSend[resp.ReduceId] = time.AfterFunc(time.Second*20, f)
}
// fmt.Printf("c.midFiles: %v\n", c.midFilesList)
// fmt.Printf("c.reduceSend: %v\n", c.reduceSend)
c.mtx.Unlock()
return nil
}
- map处理完毕之后调用查看,防止在运行过程中崩溃,如果彻底崩溃了,设置10s超时,再把这个元素加回去, 直到全部文件结束了之后,得到全部的中间文件名list。
这里我们定义MapTaskResp方法:
func (c *Coordinator) MapTaskResp(state *MapTaskState, resp *MapResponse) error {
c.mtx.Lock()
if state.State == "done" {
delete(c.mapSend, state.Filename) // finish, so delete
for i := 0; i < c.nReduce; i++ {
name := fmt.Sprintf("%s-%d-%d_%d", "mr-mid", state.WorkerId, state.TaskId, i) // print to mid-Files
_, Finish := c.midFilesMap[i]
if !Finish {
c.midFilesMap[i] = stringArray{}
}
c.midFilesMap[i] = append(c.midFilesMap[i], name)
}
} else {
// Failed, remake
c.files = append(c.files, state.Filename)
// delete(c.mapSend, state.filename)
}
c.mtx.Unlock()
return nil
}
ReduceStateResp方法同理:
func (c *Coordinator) ReduceStateResp(state *ReduceTaskState, resp *ReduceResponse) error {
c.mtx.Lock()
if state.State == "done" {
delete(c.reduceSend, state.ReduceId)
if len(c.reduceSend) == 0 && len(c.midFilesList) == 0 && !c.Finish {
c.Finish = true
}
} else {
// Failed, remake
c.midFilesList = append(c.midFilesList, state.ReduceId)
// delete(c.mapSend, state.filename)
}
c.mtx.Unlock()
return nil
}
- 定义检测完成的方法
Done:
func (c *Coordinator) Done() bool {
c.mtx.Lock()
ret := c.Finish
c.mtx.Unlock()
return ret
}
- 生成初始的Coordinator结构体,用于操作,
MakeCoordinator方法:
func MakeCoordinator(files []string, nReduce int) *Coordinator {
c := Coordinator{}
c.nReduce = nReduce
c.files = files
c.midFilesMap = map[int]stringArray{}
c.midFilesList = []int{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
c.mtx = sync.Mutex{}
c.mapSend = make(map[string]interface{})
c.reduceSend = make(map[int]interface{})
c.server()
return &c
}
- 最后是对于crash exit的处理方法。
这个点卡了我很久,看了别人的代码才明白的。关键就是在多次分配任务后(要支持这个操作),如果两个worker执行一个task都执行完了,根据重复情况,判断完成的文件里是否已经存在,存在就直接不管。
相应的实现方法是mapAfterFuncWrapper和reduceAfterFuncWrapper两个方法:(相应的调用过程在上面已经写了)
func mapAfterFuncWrapper(c *Coordinator, filename string) func() {
return func() {
c.mtx.Lock()
fmt.Printf("map task %v 超时重试\n", filename)
c.files = append(c.files, filename)
c.mtx.Unlock()
}
}
func reduceAfterFuncWrapper(c *Coordinator, reduceId int) func() {
return func() {
c.mtx.Lock()
fmt.Printf("reduce task %v 超时重试\n", reduceId)
c.midFilesList = append(c.midFilesList, reduceId)
c.mtx.Unlock()
}
}
4. worker的实现
- 映射方式采用的是hash映射(有点像cache那样):
func ihash(key string) int {
h := fnv.New32a()
h.Write([]byte(key))
return int(h.Sum32() & 0x7fffffff)
}
- 获取中间文件的这一步方法,这里采用的是json编码再解码的方式(按照lab的要求)
func WorkerMap(mapf func(string, string) []KeyValue, c *rpc.Client) {
retryTimes := 0
taskid := 0
for retryTimes < 3 {
req := MapRequest{}
resp := MapResponse{}
err2 := c.Call("Coordinator.AssignMapTask", &req, &resp)
if err2 != nil {
fmt.Printf("err2: %v\n", err2)
time.Sleep(time.Second)
retryTimes++
continue
}
retryTimes = 0
if resp.State == "done" {
return
}
if resp.Filename == "" {
// empty but not done -- problem!
time.Sleep(time.Second)
continue
}
// write to disk
req2 := MapTaskState{resp.Filename, workerInfo.WorkId, taskid, "done"}
resp2 := MapResponse{}
f, err := os.Open(resp.Filename)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
req2.State = "nosuchfile"
c.Call("Coordinator.MapTaskResp", &req2, &resp2)
continue
}
defer f.Close() // out the function
content, err := ioutil.ReadAll(f)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot read %v", resp.Filename)
req2.State = "filereaderr"
c.Call("Coordinator.MapTaskResp", &req2, &resp2)
}
kvs := mapf(resp.Filename, string(content))
encs := []*json.Encoder{}
midFiles = []*os.File{}
// create temp,make sure final is mr-mid-{workid}-{taskid}_{nreduceid} (after finish)
// in ReduceTask nreduceid is the symbol
for i := 0; i < workerInfo.NReduce; i++ {
f, _ := os.CreateTemp("", "di-mp")
midFiles = append(midFiles, f)
}
for i := 0; i < workerInfo.NReduce; i++ {
encs = append(encs, json.NewEncoder(midFiles[i]))
}
for _, kv := range kvs {
encs[ihash(kv.Key)%workerInfo.NReduce].Encode(kv)
}
for i := 0; i < workerInfo.NReduce; i++ {
name := fmt.Sprintf("%s-%d-%d_%d", "mr-mid", workerInfo.WorkId, taskid, i)
os.Rename(midFiles[i].Name(), name)
}
req2.Filename = resp.Filename
req2.TaskId = taskid
req2.State = "done"
err = c.Call("Coordinator.MapTaskResp", &req2, &resp2)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err: %v\n", err)
}
taskid++
// then send to MapTaskResp
}
}
- 类似地,有WorkerReduce方法:
func WorkerReduce(reducef func(string, []string) string, client *rpc.Client) {
// retry & finish by a series attemps
RESTARTREDUCE:
retryTimes := 0
for retryTimes < 3 {
req := ReduceRequest{}
var resp ReduceResponse
err2 := client.Call("Coordinator.AssignReduceTask", &req, &resp)
if err2 != nil {
fmt.Printf("err2: %v\n", err2)
time.Sleep(time.Second)
retryTimes++
continue
}
retryTimes = 0
if resp.State == "done" {
return
}
if resp.ReduceId == -1 {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
continue
}
// resp.Filename is the midFiles
// like serial, transfer to coordinate and combine it
req2 := ReduceTaskState{resp.ReduceId, ""}
resp2 := ReduceResponse{}
resp2.ReduceId = resp.ReduceId
reduceId := resp2.ReduceId
name := fmt.Sprintf("%s-%d", "mr-out", reduceId)
outtmpfile, _ := os.CreateTemp("", "di-out")
kva := []KeyValue{}
jsonParseState := true
for _, filename := range resp.Filenames {
f, err := os.Open(filename)
defer f.Close()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("mid file open wrong:", err)
req2.State = "nosuchfile"
client.Call("Coordinator.ReduceStateResp", &req2, &resp2)
goto RESTARTREDUCE
}
d := json.NewDecoder(f)
for {
var kv KeyValue
if err := d.Decode(&kv); err != nil {
if err == io.EOF {
break
}
fmt.Println("json parse:", err)
req2.State = "jsonparseerr"
client.Call("Coordinator.ReduceStateResp", &req2, &resp2)
jsonParseState = false
break
}
kva = append(kva, kv)
}
}
if jsonParseState {
sort.Sort(byKey(kva))
i := 0
for i < len(kva) {
j := i + 1
for j < len(kva) && kva[i].Key == kva[j].Key {
j++
}
vv := []string{}
for k := i; k < j; k++ {
vv = append(vv, kva[k].Value)
}
s := reducef(kva[i].Key, vv)
fmt.Fprintf(outtmpfile, "%v %v\n", kva[i].Key, s)
i = j
}
} else {
goto RESTARTREDUCE
}
req2.State = "done"
req2.ReduceId = resp.ReduceId
err := client.Call("Coordinator.ReduceStateResp", &req2, &resp2)
if err == nil {
os.Rename(outtmpfile.Name(), name)
}
}
}
- 在我们测试的时候,实际调用的是
Worker函数,我们把之前写的方法加上去,就实现了Worker方法:
func Worker(mapf fun(string, string) []KeyValue, reducef func(string, []string) string) {
i := 0
c, _ := rpc.DialHTTP("tcp", "127.0.0.1"+":1234")
defer c.Close()
c.Call("Coordinator.AssignWorkerId", &i, &workerInfo)
time.Sleep(time.Second)
WorkerMap(mapf, c)
WorkerReduce(reducef, c)
}
5. 实验效果
短暂地挖个坑。
一开始是crash exit过不去
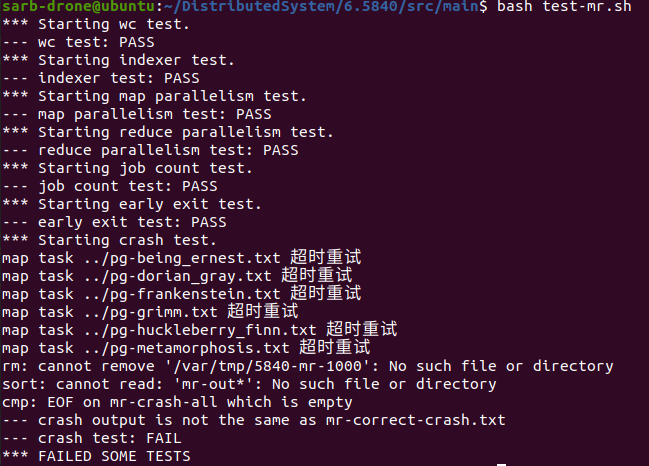
修改之后就可以ALL PASS了