模拟赛出了这题,整理一下。sto jimmyywang
由于每次选到的数都比上一个小,所以所有可达到的状态序列都是单调递减的,每次只能在序列的末尾增减一个数,如果序列中所有数的和大于 $T$,则停止操作。
尝试在每种状态间连边,从上一种状态到下一种可到达的状态连有向边。像这样($T=3,n=2$):
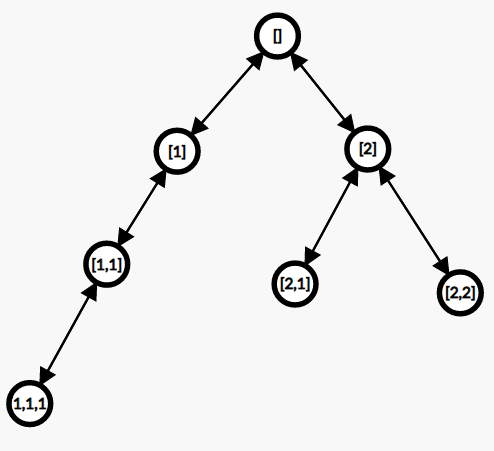
发现每一个状态删去末尾的数后,对应唯一的状态,所以所有的状态连完边后形成一个树形结构。由于存在回溯,所以树上均为双向边。叶子结点就表示已经超过阈值,没有后继状态。设状态总数为 $S$,将每个点编号为 $1$ 到 $S$,极限数据下 $S$ 约为 $1e6$。
设 $dp_x$ 表示从编号为 $x$ 的状态走到叶子结点的期望步数。那么对于每一个 $x \in leaf$,显然 $dp_x=0$(已经到达)。对于每一个非叶子非根节点 $x$ 所表示的状态,有 $P$ 的概率走到父亲,有 $\frac{1-P}{cnt_{x}} $ 的概率走到每一个儿子,其中 $cnt_{x}$ 表示 $x$ 的子节点个数,所以有如下转移:
$$dp_x=P \times (dp_{fa}+1)+\frac{1-P}{cnt_x} \times \sum_{y \in son}(dp_y+1)$$
化简以后得到:
$$dp_x=1 + P \times dp_{fa} + \frac{1-P}{cnt_x} \times \sum_{y \in son}dp_y$$
这个转移有后效性。尝试用待定系数法将 $dp_x$ 用 $dp_{fa}$ 表示。
设 $dp_x = k_x \times dp_{fa} + b_x$,代入上式得:
$$dp_x=1 + P \times dp_{fa} + \frac{1-P}{cnt_x} \times \sum_{y \in son}(k_y \times dp_x + b_y)$$
化简得:
$$dp_x = \frac{P}{1-\frac{1-P}{cnt_x} \times \sum_{y \in son}k_y} \times dp_{fa} + \frac{1 + \frac{1-P}{cnt_x} \sum_{y \in son}b_y}{1 - \frac{1-P}{cnt_x} \sum_{y \in son}k_y}$$
所以:
$$k_x = \frac{P}{1-\frac{1-P}{cnt_x} \times \sum_{y \in son}k_y}$$
$$b_x = \frac{1 + \frac{1-P}{cnt_x} \sum_{y \in son}b_y}{1 - \frac{1-P}{cnt_x} \sum_{y \in son}k_y}$$
回溯时转移 $b_x$ 和 $k_x$ 即可。
由于根节点(初始状态:空序列)没有父亲,所以在根节点时 $P = 0$, $b_{root}$ 即为答案。
时间复杂度 $O(S)$。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int SIZE = 2000005;
double P, b[SIZE], k[SIZE];
int n, m, a[SIZE], iid;
bool cmp(int x, int y){
return x > y;
}
void deal(int now, int id, int sum){
if(sum > m) return;
int x = id, cnt = n-now+1;
double sb = 0, sk = 0, t = (1.0-P);
for(int i = now; i <= n; i++){
int y = ++iid;
deal(i, y, sum+a[i]);
sb += b[y]; sk += k[y];
}
if(x == 1) P = 0, t = 1.0;
t = t / (double)cnt;
k[x] = P/(1.0-t*(double)sk);
b[x] = (1.0+t*(double)sb)/(1.0-t*(double)sk);
}
int main(){
while(~scanf("%lf%d%d", &P, &m, &n)){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
sort(a+1, a+n+1, cmp);
iid = 1;
deal(1, 1, 0);
printf("%.3lf\n", b[1]);
}
return 0;
}