Timofey has an apple tree growing in his garden; it is a rooted tree of n vertices with the root in vertex 11 (the vertices are numbered from 11 to n). A tree is a connected graph without loops and multiple edges.
This tree is very unusual — it grows with its root upwards. However, it's quite normal for programmer's trees.
The apple tree is quite young, so only two apples will grow on it. Apples will grow in certain vertices (these vertices may be the same). After the apples grow, Timofey starts shaking the apple tree until the apples fall. Each time Timofey shakes the apple tree, the following happens to each of the apples:
Let the apple now be at vertex u.
- If a vertex u has a child, the apple moves to it (if there are several such vertices, the apple can move to any of them).
- Otherwise, the apple falls from the tree.
It can be shown that after a finite time, both apples will fall from the tree.
Timofey has q assumptions in which vertices apples can grow. He assumes that apples can grow in vertices x and y, and wants to know the number of pairs of vertices (a, b) from which apples can fall from the tree, where a — the vertex from which an apple from vertex x will fall, b — the vertex from which an apple from vertex y will fall. Help him do this.
The first line contains integer t (1≤t≤1041≤≤104) — the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains integer n (2≤n≤2⋅1052≤≤2⋅105) — the number of vertices in the tree.
Then there are n−1−1 lines describing the tree. In line i there are two integers ui and vi (1≤ui,vi≤n1≤,≤, ui≠vi≠) — edge in tree.
The next line contains a single integer q (1≤q≤2⋅1051≤≤2⋅105) — the number of Timofey's assumptions.
Each of the next q lines contains two integers xi and yi (1≤xi,yi≤n1≤,≤) — the supposed vertices on which the apples will grow for the assumption i.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n does not exceed 2⋅1052⋅105. Similarly, It is guaranteed that the sum of q does not exceed 2⋅1052⋅105.
For each Timofey's assumption output the number of ordered pairs of vertices from which apples can fall from the tree if the assumption is true on a separate line.
2 2 1 4 4 1 2
1 2 1 4 2
In the first example:
- For the first assumption, there are two possible pairs of vertices from which apples can fall from the tree: (4,4),(5,4)(4,4),(5,4).
- For the second assumption there are also two pairs: (5,4),(5,5)(5,4),(5,5).
- For the third assumption there is only one pair: (4,4)(4,4).
- For the fourth assumption, there are 44 pairs: (4,4),(4,5),(5,4),(5,5)(4,4),(4,5),(5,4),(5,5).
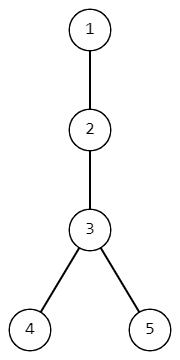 Tree from the first example.
Tree from the first example.For the second example, there are 44 of possible pairs of vertices from which apples can fall: (2,3),(2,2),(3,2),(3,3)(2,3),(2,2),(3,2),(3,3). For the second assumption, there is only one possible pair: (2,3)(2,3). For the third assumption, there are two pairs: (3,2),(3,3)(3,2),(3,3).
// Apple Tree // 树形搜索,建立根节点和子节点,dfs内u代表当前的节点,v代表父节点 // 如果搜到父节点的话就返回 // 使用邻接表建立树 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std; const int N=1e6+10,mod=1e9+7; string s; int n,t,a[N],f[N],res,num,ans,m,q; int idx,h[N],e[N],ne[N]; bool vis[N]; void add(int a,int b) { e[idx]=b,ne[idx]=h[a],h[a]=idx++; } void dfs(int u,int v) { bool flag=false; for(int i=h[u];i!=-1;i=ne[i]){ int x=e[i]; if(e[i]==v) continue; flag=true,dfs(x,u); f[u]+=f[x]; } if(!flag) f[u]=1; } signed main() { std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0); cin>>t; while(t--){ cin>>n; for(int i=0;i<=n+5;i++) h[i]=-1,e[i]=ne[i]=f[i]=0; for(int i=1;i<n;i++){ int x,y; cin>>x>>y; add(x,y),add(y,x); } dfs(1,0); cin>>m; while(m--){ cin>>ans>>num; cout<<f[ans]*f[num]<<endl; } } return 0; }