本来前一周还在做Kalman Filter的mpu6050实战,但是出于各种原因耽搁了,这周又碰上调试任务和各种作业,到现在才腾出点空总结一下这周的学习。(顺便吐槽一下,运筹学作业害的昨天两点睡的觉,悲)
其实平常的代码中一直都在用pid,但是最近用的时候才发现自己很多地方理解不够,出现了比较多的问题(这就是用祖传代码的坏处吧),所以自己花时间重新学习了一下并自己手搓了位置式和增量式的pid,感觉理解深刻了一点。
在本文,你将看到:
①对pid公式和三大参数的简单解释。
②一个简单的excel例子对pid效果的粗略展示
③手搓位置式和增量式pid的思路及方法。
一、对pid公式和三大参数的简单解释(均为离散量)
1.假设说明:对一个系统的控制量,我们假设目标值为target,当前值为position,则有误差值err=target-position
2.关于参数一:比例控制(proportional)
· 
(1)我们将Kp*(target-position)=Kp*err 记为out1(输出1),此即比例控制带来的输出量。从公式可以看到,比例控制的直接来源是误差值,误差值越大时,比例控制的效果就越明显(输出值越大),所以一般p就能够使我们的系统以较快的速度到达我们的设定值(position)。但是同时p也会有一些负面影响:比较明显的是超调和静差,另外Kp过大时还会产生震荡。
(2)关于超调:超调是由p引起的在调节过程中target>position的现象。一般当超调量越大时,系统的position到达target的时间(稳态时间)越短,反之,超调量小,系统的稳态时间越长。我们希望能同时拥有一个较小的超调量和较短的稳态时间。(3)关于静差(稳态误差):这里我们举一个例子来说明。
假设我们有一壶水,我们的目标是温度=100度,记为target,我们当前温度为20度。假设我们的热水器的输出被我们以比例控制的方法运行,比例系数为0.2,即out1=0.2*(100-position)。那么易得:
第一次输出:16度,误差值变为100-(20+16)=64,从而第二次输出:12.8度.....我们发现随着计算总能使水壶中水的温度到达100度。
但是我们当我们考虑散热时,假设每次控制间隔水的温度都会降低5度,从上面的计算中我们容易发现,当水的温度达到75度时,此时的热水器的加热量=散热量,水温会保持在75度(稳态)而不会到达我们想要的100度。
在实际情况中,我们碰到的系统大多都带有类似“散热”的因素,比如四轴无人机的阻力等等,所以静差是我们必须要消除的,由此我们引出第二个参数:积分控制。
3.关于参数二:积分控制(integral)

(1)我们将Ki*(target-position)=Ki*err 记为out2(输出2),此即积分控制带来的输出量。dt为我们控制的时间间隔。从公式我们容易发现,从系统开始调节后,积分项就在随着误差值不断累积,这也是积分控制能消除静差的关键。
(2)积分项能消除静差的原因:从前面我们知道,当我们的position和target相差不大时,比例控制的out1其实会变得较小,也就是说比例控制的作用会变得很弱。但是积分控制不同,由(1)知,积分项在不断的累加,并不会在position和target相差不大时而减小控制作用,所以引入积分项后,当position和target相差不大时,我们认为主要是积分项在起作用,当存在有误差时,积分项就会一直变大,从而积分控制的输出就会一直变大,直到到达我们的target,所以积分项能消除静差。
(3)关于积分限幅:我们已经知道积分项会不断累加,所以有可能会出现这样一种情况:积分项的累积值过大,导致积分控制对系统的控制能力过强,或者考虑另一种情况:在开始控制后,有一个较大误差,且有一个非常大的干扰来阻止其误差减小,如四轴飞行器被人固定后误差一直没变,此时随着时间的拉长,积分的输出值会越来越大,这种输出可能超过了控制系统承受范围,而且一旦这种阻力去掉,会使得输出极大,引起很大的超调和震荡。此时也容易出现问题,所以我们一般要设定一个误差值的累加上限,我们称此为积分限幅。
(4)关于积分控制的滞后性:通俗的理解是,积分项需要从系统控制开始时不断累积才能发挥作用,所以积分项的控制作用实际上是落后于系统状态的。
4.关于参数三:微分控制(derivative)

(1)我们将Kd*(errt-errt-1)记为out3(输出3),此即积分控制带来的输出量。dt为我们控制的时间间隔。从公式我们发现,微分项的来源是本次误差和上次误差的差值,有一定高数基础的人能想到这是一种变化趋势的表述,这也是微分控制能减少震荡的关键。
(2)微分项能消除震荡的关键:这里我们同样举一个例子:假设现在一辆车,我们希望它在100m后停下,我们首先不踩下刹车,这样当前它的速度是30m/s,则err1=100m,1s后err2=70m,若我们引入微分控制后,我们假设kd=0.5,则有out3=0.5*(70-100)/1=-15,从结果来看,这个就相当于我们踩下了刹车,车速会变成15m/s。其实关键就在于变化趋势的理解。
(3)微分控制的超前性:通俗的理解是,微分就代表着变化趋势,而变化趋势是先于状态变化的,所以超前。
5.pid公式:其实将前面的三个输出加起来得到的就是我们的pid公式:out=out1+out2+out3 (图源百度)

二、一个简单的excel例子对pid效果的粗略展示
我花了点时间做了一份excel表,在这里将计算得到的out直接加到了position上,所以有些不合理,但是能大概反映一些现象,见下图。
静差: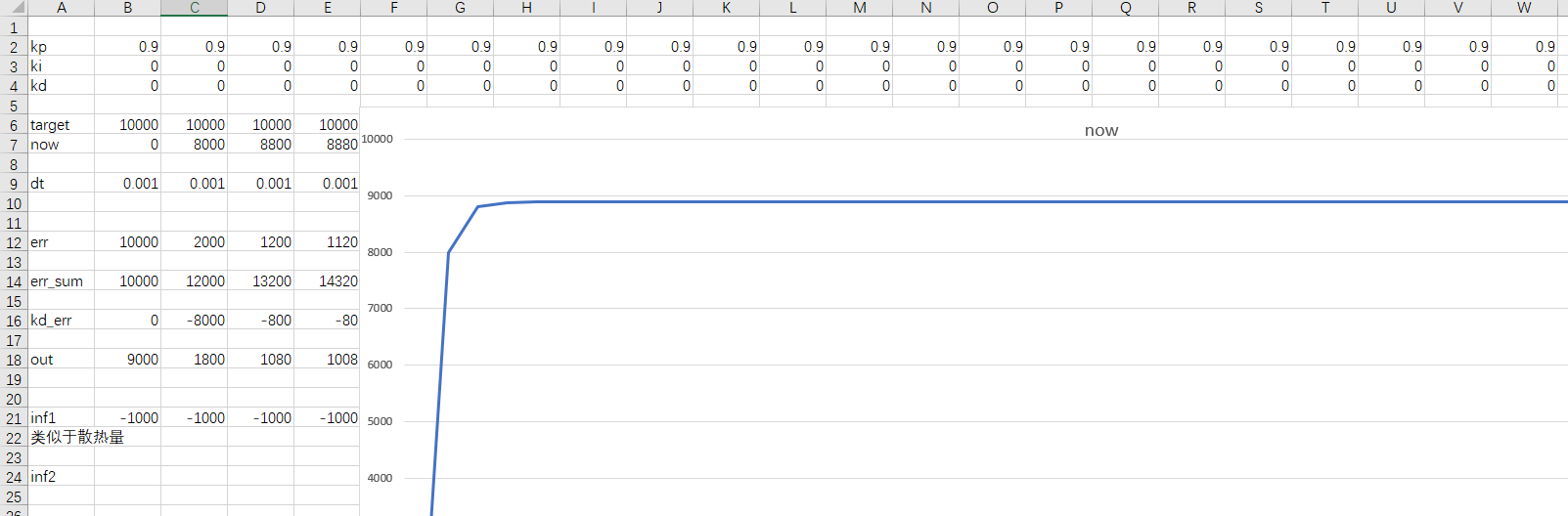
增加积分项后消除静差:
震荡: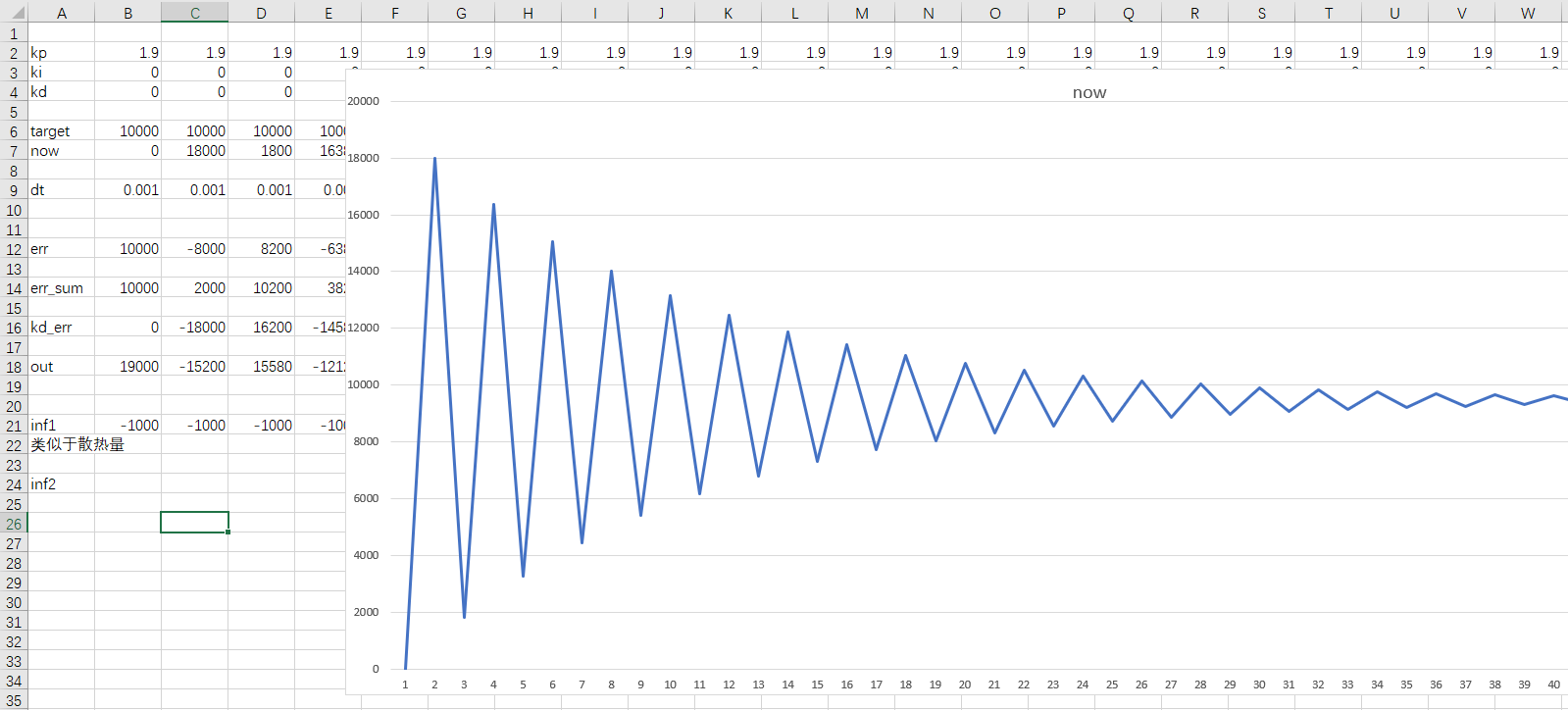
三、手搓位置式和增量式pid的思路及方法
1.位置式pid
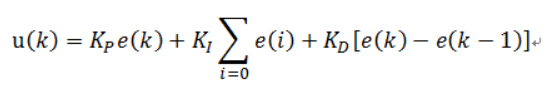
2.增量式pid
增量式pid不需要进行积分限幅,只需要进行输出限幅。(其积分项并不是累加的)
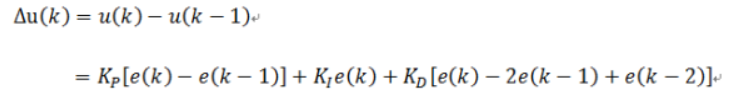
3.代码实现
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 typedef double ElemType; 4 5 #define delta_t 0.001//时间间隔 6 7 typedef struct { 8 ElemType Kp; 9 ElemType Ki; 10 ElemType Kd; 11 12 ElemType err;//误差值 13 14 ElemType integral_limit_upper;//积分上限限幅 15 ElemType integral_limit_lower;//积分下限限幅 16 ElemType integral;//积分项的误差累积和 17 18 ElemType err_last;//上次误差值 19 20 ElemType out_limit_upper;//最大输出限幅 21 ElemType out_limit_lower;//最小输出限幅 22 }pid_location_struct; 23 24 /*位置式pid初始化*/ 25 void pid_location_struct_init(pid_location_struct* pid_struct, ElemType Kp, ElemType Ki, ElemType Kd,ElemType out_limit_upper, ElemType out_limit_lower) { 26 pid_struct->Kp = Kp; 27 pid_struct->Ki = Ki; 28 pid_struct->Kd = Kd; 29 30 pid_struct->err = 0; 31 32 33 pid_struct->integral = 0; 34 pid_struct->integral_limit_upper = 100;//可更改 35 pid_struct->integral_limit_lower = 0; 36 37 pid_struct->err_last = 0; 38 pid_struct->out_limit_upper = out_limit_upper; 39 pid_struct->out_limit_lower = out_limit_lower; 40 } 41 42 /*位置式pid计算*/ 43 ElemType pid_location_cal(pid_location_struct* pid_struct, ElemType position, ElemType target) { 44 45 ElemType p_out = 0; 46 ElemType i_out = 0; 47 ElemType d_out = 0; 48 ElemType pid_cal_result = 0; 49 50 /*比例控制*/ 51 pid_struct->err = target - position;//误差更新 52 p_out = (pid_struct->Kp) * (pid_struct->err); 53 54 /*积分控制*/ 55 if (pid_struct->Ki != 0) { 56 pid_struct->integral += pid_struct->err;//积分误差累积 57 if (pid_struct->integral > pid_struct->integral_limit_upper) {//积分限幅 58 pid_struct->integral = pid_struct->integral_limit_upper; 59 } 60 else if (pid_struct->integral < pid_struct->integral_limit_lower) { 61 pid_struct->integral = pid_struct->integral_limit_lower; 62 } 63 i_out = (pid_struct->Ki) * (pid_struct->integral) * delta_t; 64 } 65 else { 66 i_out = 0; 67 } 68 69 /*微分控制*/ 70 if (pid_struct->Kd != 0) { 71 d_out = (pid_struct->Kd) * (pid_struct->err - pid_struct->err_last) / delta_t; 72 pid_struct->err_last = pid_struct->err;//上次误差更新 73 } 74 else { 75 d_out = 0; 76 } 77 78 /*pid结果输出*/ 79 pid_cal_result = p_out + i_out + d_out; 80 if (pid_cal_result > pid_struct->out_limit_upper) { 81 pid_cal_result = pid_struct->out_limit_upper; 82 } 83 else if(pid_cal_result< pid_struct->out_limit_lower){ 84 pid_cal_result = pid_struct->out_limit_lower; 85 } 86 return pid_cal_result; 87 } 88 89 typedef struct { 90 ElemType Kp; 91 ElemType Ki; 92 ElemType Kd; 93 94 ElemType last_out;//上次输出 95 96 ElemType err;//本次误差 97 ElemType err_last;//上次误差 98 ElemType err_last_last;//上上次误差 99 100 ElemType out_limit_upper;//最大输出限幅 101 ElemType out_limit_lower;//最小输出限幅 102 }pid_incremental_struct; 103 104 /*增量式pid初始化*/ 105 void pid_increment_struct_init(pid_incremental_struct* pid_struct, ElemType Kp, ElemType Ki, ElemType Kd, ElemType out_limit_upper, ElemType out_limit_lower) { 106 pid_struct->Kp = Kp; 107 pid_struct->Ki = Ki; 108 pid_struct->Kd = Kd; 109 110 pid_struct->last_out = 0; 111 112 pid_struct->err = 0; 113 pid_struct->err_last = 0; 114 pid_struct->err_last_last = 0; 115 116 pid_struct->out_limit_upper = out_limit_upper; 117 pid_struct->out_limit_lower = out_limit_lower; 118 } 119 120 /*增量式pid计算*/ 121 ElemType pid_incremental_cal(pid_incremental_struct* pid_struct, ElemType position, ElemType target) { 122 123 ElemType p_out = 0; 124 ElemType i_out = 0; 125 ElemType d_out = 0; 126 ElemType delta_pid_cal_result = 0;//输出量的增量 127 ElemType pid_cal_result = pid_struct->last_out;//最终输出结果 128 129 pid_struct->err = target - position;//更新本次误差 130 131 /*计算输出量*/ 132 p_out = (pid_struct->Kp) * (pid_struct->err - pid_struct->err_last); 133 i_out = (pid_struct->Ki) * (pid_struct->err); 134 d_out = (pid_struct->Kd) * (pid_struct->err - 2 * (pid_struct->err_last) + pid_struct->err_last_last); 135 136 /*更新上上次和上次误差*/ 137 pid_struct->err_last_last = pid_struct->err_last; 138 pid_struct->err_last = pid_struct->err; 139 140 /*得到最终输出结果*/ 141 delta_pid_cal_result = p_out + i_out + d_out; 142 pid_cal_result += delta_pid_cal_result; 143 144 /*输出限幅*/ 145 if (pid_cal_result > pid_struct->out_limit_upper) { 146 pid_cal_result = pid_struct->out_limit_upper; 147 } 148 else if (pid_cal_result < pid_struct->out_limit_lower) { 149 pid_cal_result = pid_struct->out_limit_lower; 150 } 151 152 return pid_cal_result; 153 }