1. threaded_irq引入
工作队列用起来挺简单,但是它有一个缺点:工作队列中有多个 work,前一个 work 没处理完会影响后面的 work执行,导致后面的work没法快速响应。那么可以再内核自己创建一个线程来单独处理,不跟别的 work 凑在一块了。比如在 Linux 系统中,对于存储设备比如 SD/TF 卡,它的驱动程序就是这样做的,它有自己的内核线程。用kthread_creat创建内核线程。
对于中断处理,还有另一种方法:threaded irq,线程化的中断处理。中断的处理仍然可以认为分为上半部、下半部。上半部用来处理紧急的事情,下半部用一个内核线程来处理,这个内核线程专用于这个中断。
2. threaded_irq使用
1异常中断引入 前面已经提到了threaded_irq。
你可以只提供 thread_fn,内核会提供默认的上半部处理函数irq_default_primary_handler,该函数只是返回一个IRQ_WAKE_THREAD。发生中断时,系统会立刻调用 handler 函数,然后唤醒某个内核线程,内核线程再来执行thread_fn 函数。
你也可以既提供handler函数,也提供thread_fn函数。等硬件中断到来,先执行handler函数,handler函数中返回IRQ_WAKE_THREAD去唤醒中断线程函数thread_fn。

extern int __must_check
devm_request_threaded_irq(struct device *dev, unsigned int irq,
irq_handler_t handler, irq_handler_t thread_fn,
unsigned long irqflags, const char *devname,
void *dev_id);
extern void free_irq(unsigned int, void *);
3. threaded_irq实例
驱动代码
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/major.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/stat.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/kmod.h>
#include <linux/gfp.h>
#include <linux/gpio/consumer.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/of_irq.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <linux/workqueue.h>
#include <asm/current.h>
struct gpio_key{
int gpio;
struct gpio_desc *gpiod;
int flag;
int irq;
struct timer_list key_timer;
struct tasklet_struct tasklet;
struct work_struct work;
} ;
static struct gpio_key *gpio_keys_100ask;
/* 主设备号 */
static int major = 0;
static struct class *gpio_key_class;
/* 环形缓冲区 */
#define BUF_LEN 128
static int g_keys[BUF_LEN];
static int r, w;
struct fasync_struct *button_fasync;
#define NEXT_POS(x) ((x+1) % BUF_LEN)
static int is_key_buf_empty(void)
{
return (r == w);
}
static int is_key_buf_full(void)
{
return (r == NEXT_POS(w));
}
static void put_key(int key)
{
if (!is_key_buf_full())
{
g_keys[w] = key;
w = NEXT_POS(w);
}
}
static int get_key(void)
{
int key = 0;
if (!is_key_buf_empty())
{
key = g_keys[r];
r = NEXT_POS(r);
}
return key;
}
static DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(gpio_key_wait);
static void key_timer_expire(unsigned long data)
{
/* data ==> gpio */
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = data;
int val;
int key;
val = gpiod_get_value(gpio_key->gpiod);
printk("key_timer_expire key %d %d\n", gpio_key->gpio, val);
key = (gpio_key->gpio << 8) | val;
put_key(key);
wake_up_interruptible(&gpio_key_wait);
kill_fasync(&button_fasync, SIGIO, POLL_IN);
}
static void key_tasklet_func(unsigned long data)
{
/* data ==> gpio */
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = data;
int val;
int key;
val = gpiod_get_value(gpio_key->gpiod);
printk("key_tasklet_func key %d %d\n", gpio_key->gpio, val);
}
static void key_work_func(struct work_struct *work)
{
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = container_of(work, struct gpio_key, work);
int val;
val = gpiod_get_value(gpio_key->gpiod);
printk("key_work_func: the process is %s pid %d\n",current->comm, current->pid);
printk("key_work_func key %d %d\n", gpio_key->gpio, val);
}
static ssize_t gpio_key_drv_read (struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
//printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
int err;
int key;
if (is_key_buf_empty() && (file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK))
return -EAGAIN;
wait_event_interruptible(gpio_key_wait, !is_key_buf_empty());
key = get_key();
err = copy_to_user(buf, &key, 4);
return 4;
}
static unsigned int gpio_key_drv_poll(struct file *fp, poll_table * wait)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
poll_wait(fp, &gpio_key_wait, wait);
return is_key_buf_empty() ? 0 : POLLIN | POLLRDNORM;
}
static int gpio_key_drv_fasync(int fd, struct file *file, int on)
{
if (fasync_helper(fd, file, on, &button_fasync) >= 0)
return 0;
else
return -EIO;
}
static struct file_operations gpio_key_drv = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = gpio_key_drv_read,
.poll = gpio_key_drv_poll,
.fasync = gpio_key_drv_fasync,
};
static irqreturn_t gpio_key_isr(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = dev_id;
//printk("gpio_key_isr key %d irq happened\n", gpio_key->gpio);
tasklet_schedule(&gpio_key->tasklet);
mod_timer(&gpio_key->key_timer, jiffies + HZ/50);
schedule_work(&gpio_key->work);
return IRQ_WAKE_THREAD;
}
static irqreturn_t gpio_key_thread_func(int irq, void *data)
{
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = data;
int val;
val = gpiod_get_value(gpio_key->gpiod);
printk("gpio_key_thread_func: the process is %s pid %d\n",current->comm, current->pid);
printk("gpio_key_thread_func key %d %d\n", gpio_key->gpio, val);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
static int gpio_key_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
int err;
struct device_node *node = pdev->dev.of_node;
int count;
int i;
enum of_gpio_flags flag;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
count = of_gpio_count(node);
if (!count)
{
printk("%s %s line %d, there isn't any gpio available\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
gpio_keys_100ask = kzalloc(sizeof(struct gpio_key) * count, GFP_KERNEL);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio = of_get_gpio_flags(node, i, &flag);
if (gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio < 0)
{
printk("%s %s line %d, of_get_gpio_flags fail\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpiod = gpio_to_desc(gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio);
gpio_keys_100ask[i].flag = flag & OF_GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW;
gpio_keys_100ask[i].irq = gpio_to_irq(gpio_keys_100ask[i].gpio);
setup_timer(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer, key_timer_expire, &gpio_keys_100ask[i]);
gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer.expires = ~0;
add_timer(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer);
tasklet_init(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].tasklet, key_tasklet_func, &gpio_keys_100ask[i]);
INIT_WORK(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].work, key_work_func);
}
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
//err = request_irq(gpio_keys_100ask[i].irq, gpio_key_isr, IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING | IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "100ask_gpio_key", &gpio_keys_100ask[i]);
err = request_threaded_irq(gpio_keys_100ask[i].irq, gpio_key_isr, gpio_key_thread_func, IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING | IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "100ask_gpio_key", &gpio_keys_100ask[i]);
}
major = register_chrdev(0, "100ask_gpio_key", &gpio_key_drv); /* /dev/gpio_key */
gpio_key_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "100ask_gpio_key_class");
if (IS_ERR(gpio_key_class)) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
unregister_chrdev(major, "100ask_gpio_key");
return PTR_ERR(gpio_key_class);
}
device_create(gpio_key_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "100ask_gpio_key"); /* /dev/100ask_gpio_key */
return 0;
}
static int gpio_key_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
//int err;
struct device_node *node = pdev->dev.of_node;
int count;
int i;
device_destroy(gpio_key_class, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_destroy(gpio_key_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, "100ask_gpio_key");
count = of_gpio_count(node);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
free_irq(gpio_keys_100ask[i].irq, &gpio_keys_100ask[i]);
del_timer(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].key_timer);
tasklet_kill(&gpio_keys_100ask[i].tasklet);
}
kfree(gpio_keys_100ask);
return 0;
}
static const struct of_device_id ask100_keys[] = {
{ .compatible = "100ask,gpio_key" },
{ },
};
static struct platform_driver gpio_keys_driver = {
.probe = gpio_key_probe,
.remove = gpio_key_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "100ask_gpio_key",
.of_match_table = ask100_keys,
},
};
static int __init gpio_key_init(void)
{
int err;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
err = platform_driver_register(&gpio_keys_driver);
return err;
}
static void __exit gpio_key_exit(void)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
platform_driver_unregister(&gpio_keys_driver);
}
module_init(gpio_key_init);
module_exit(gpio_key_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
app代码
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <poll.h>
#include <signal.h>
static int fd;
/*
* ./button_test /dev/100ask_button0
*
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int val;
struct pollfd fds[1];
int timeout_ms = 5000;
int ret;
int flags;
int i;
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("Usage: %s <dev>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);
if (fd == -1)
{
printf("can not open file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
if (read(fd, &val, 4) == 4)
printf("get button: 0x%x\n", val);
else
printf("get button: -1\n");
}
flags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL);
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flags & ~O_NONBLOCK);
while (1)
{
if (read(fd, &val, 4) == 4)
printf("get button: 0x%x\n", val);
else
printf("while get button: -1\n");
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
驱动代码解析:

为每个按键注册中断服务
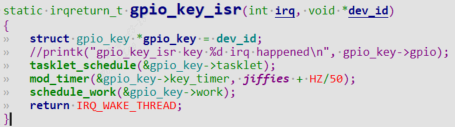
硬件中断上半部irq中做完重要事情如:清中断,然后返回IRQ_WAKE_THREAD
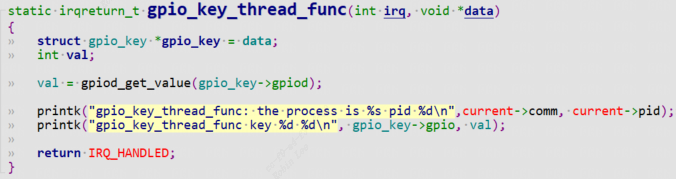
返回后,内核线程开始调度gpio_key_thread_func,中断线程化的处理函数gpio_key_thread_func做完后返回IRQ_HANDLED;
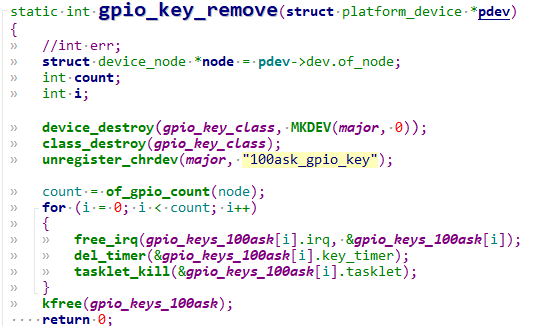
最后卸载驱动时取消irq注册
3. threaded_irq内核机制
前面中断相关结构体讲过struct irq_desc结构:
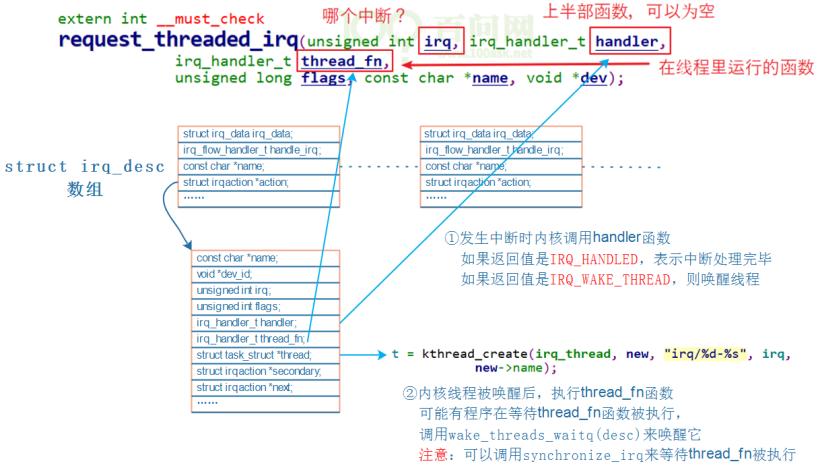
1. 当发生中断时,handler函数被调用,如果返回IRQ_HANDLED,表示中断处理完毕,如果返回IRQ_WAKE_THREAD表示要唤醒thread_fn.
2. 内核线程唤醒后,执行thread_fn
- request_threaded_irq过程:
点击查看代码
/**
* request_threaded_irq - allocate an interrupt line
* @irq: Interrupt line to allocate
* @handler: Function to be called when the IRQ occurs.
* Primary handler for threaded interrupts
* If NULL and thread_fn != NULL the default
* primary handler is installed
* @thread_fn: Function called from the irq handler thread
* If NULL, no irq thread is created
* @irqflags: Interrupt type flags
* @devname: An ascii name for the claiming device
* @dev_id: A cookie passed back to the handler function
*
* This call allocates interrupt resources and enables the
* interrupt line and IRQ handling. From the point this
* call is made your handler function may be invoked. Since
* your handler function must clear any interrupt the board
* raises, you must take care both to initialise your hardware
* and to set up the interrupt handler in the right order.
*
* If you want to set up a threaded irq handler for your device
* then you need to supply @handler and @thread_fn. @handler is
* still called in hard interrupt context and has to check
* whether the interrupt originates from the device. If yes it
* needs to disable the interrupt on the device and return
* IRQ_WAKE_THREAD which will wake up the handler thread and run
* @thread_fn. This split handler design is necessary to support
* shared interrupts.
*
* Dev_id must be globally unique. Normally the address of the
* device data structure is used as the cookie. Since the handler
* receives this value it makes sense to use it.
*
* If your interrupt is shared you must pass a non NULL dev_id
* as this is required when freeing the interrupt.
*
* Flags:
*
* IRQF_SHARED Interrupt is shared
* IRQF_TRIGGER_* Specify active edge(s) or level
*
*/
int request_threaded_irq(unsigned int irq, irq_handler_t handler,
irq_handler_t thread_fn, unsigned long irqflags,
const char *devname, void *dev_id)
{
struct irqaction *action;
struct irq_desc *desc;
int retval;
if (irq == IRQ_NOTCONNECTED)
return -ENOTCONN;
/*
* Sanity-check: shared interrupts must pass in a real dev-ID,
* otherwise we'll have trouble later trying to figure out
* which interrupt is which (messes up the interrupt freeing
* logic etc).
*
* Also IRQF_COND_SUSPEND only makes sense for shared interrupts and
* it cannot be set along with IRQF_NO_SUSPEND.
*/
if (((irqflags & IRQF_SHARED) && !dev_id) ||
(!(irqflags & IRQF_SHARED) && (irqflags & IRQF_COND_SUSPEND)) ||
((irqflags & IRQF_NO_SUSPEND) && (irqflags & IRQF_COND_SUSPEND)))
return -EINVAL;
desc = irq_to_desc(irq);
if (!desc)
return -EINVAL;
if (!irq_settings_can_request(desc) ||
WARN_ON(irq_settings_is_per_cpu_devid(desc)))
return -EINVAL;
if (!handler) {
if (!thread_fn)
return -EINVAL;
handler = irq_default_primary_handler;
}
action = kzalloc(sizeof(struct irqaction), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!action)
return -ENOMEM;
action->handler = handler;
action->thread_fn = thread_fn;
action->flags = irqflags;
action->name = devname;
action->dev_id = dev_id;
retval = irq_chip_pm_get(&desc->irq_data);
if (retval < 0) {
kfree(action);
return retval;
}
chip_bus_lock(desc);
retval = __setup_irq(irq, desc, action);
chip_bus_sync_unlock(desc);
if (retval) {
irq_chip_pm_put(&desc->irq_data);
kfree(action->secondary);
kfree(action);
}
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_SHIRQ_FIXME
if (!retval && (irqflags & IRQF_SHARED)) {
/*
* It's a shared IRQ -- the driver ought to be prepared for it
* to happen immediately, so let's make sure....
* We disable the irq to make sure that a 'real' IRQ doesn't
* run in parallel with our fake.
*/
unsigned long flags;
disable_irq(irq);
local_irq_save(flags);
handler(irq, dev_id);
local_irq_restore(flags);
enable_irq(irq);
}
#endif
return retval;
}

首先根据irq num获取到struct irq_desc信息。
然后分配、设置一个 irqaction 结构体。设置中断相关参数
然后进入__setup_irq,__setup_irq 函数核心代码如下:
if (new->thread_fn && !nested) {
ret = setup_irq_thread(new, irq, false);
setup_irq_thread函数核心代码如下:
if (!secondary) {
t = kthread_create(irq_thread, new, "irq/%d-%s", irq,
new->name);
} else {
t = kthread_create(irq_thread, new, "irq/%d-s-%s", irq,
new->name);
param.sched_priority -= 1;
}
new->thread = t;
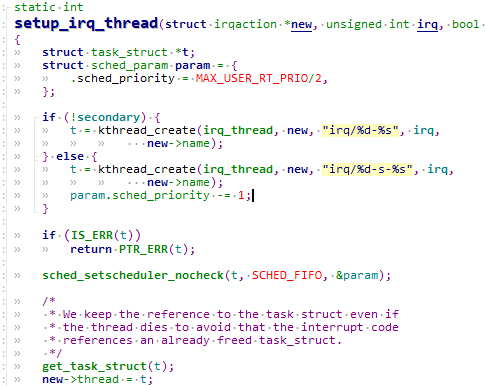
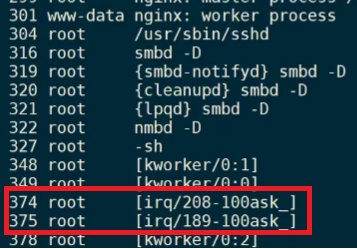
可以看到创建了irq_thread这个内核线程。线程名字为“irq/pid-中断名字”。kthread_create()只是创建一个内核线程,但并没有启动,需要调用wake_up_process()来启动线程,所以内核又帮我们定义了一个宏kthread_run来帮我们搞定. 然后将返回的task_strcut给到irqaction.
我们知道irqaction就包含了thread_fn和handler。
那么thread_fn是怎么被执行到的呢?
当中断产生时,gic驱动框架调用关系如下:
Breakpoint 1, gpio_keys_gpio_isr (irq=200, dev_id=0x863e6930) at drivers/input/keybo
ard/gpio_keys.c:393
393 {
(gdb) bt
#0 gpio_keys_gpio_isr (irq=200, dev_id=0x863e6930) at drivers/input/keyboard/gpio_k
eys.c:393
#1 0x80270528 in __handle_irq_event_percpu (desc=0x8616e300, flags=0x86517edc) at ke
rnel/irq/handle.c:145
#2 0x802705cc in handle_irq_event_percpu (desc=0x8616e300) at kernel/irq/handle.c:18
5
#3 0x80270640 in handle_irq_event (desc=0x8616e300) at kernel/irq/handle.c:202
#4 0x802738e8 in handle_level_irq (desc=0x8616e300) at kernel/irq/chip.c:518
#5 0x8026f7f8 in generic_handle_irq_desc (desc=<optimized out>) at ./include/linux/i
rqdesc.h:150
#6 generic_handle_irq (irq=<optimized out>) at kernel/irq/irqdesc.c:590
#7 0x805005e0 in mxc_gpio_irq_handler (port=0xc8, irq_stat=2252237104) at drivers/gp
io/gpio-mxc.c:274
#8 0x805006fc in mx3_gpio_irq_handler (desc=<optimized out>) at drivers/gpio/gpio-mx
c.c:291
#9 0x8026f7f8 in generic_handle_irq_desc (desc=<optimized out>) at ./include/linux/i
rqdesc.h:150
#10 generic_handle_irq (irq=<optimized out>) at kernel/irq/irqdesc.c:590
#11 0x8026fd0c in __handle_domain_irq (domain=0x86006000, hwirq=32, lookup=true, regs
=0x86517fb0) at kernel/irq/irqdesc.c:627
#12 0x80201484 in handle_domain_irq (regs=<optimized out>, hwirq=<optimized out>, dom
ain=<optimized out>) at ./include/linux/irqdesc.h:168
#13 gic_handle_irq (regs=0xc8) at drivers/irqchip/irq-gic.c:364
#14 0x8020b704 in __irq_usr () at arch/arm/kernel/entry-armv.S:464
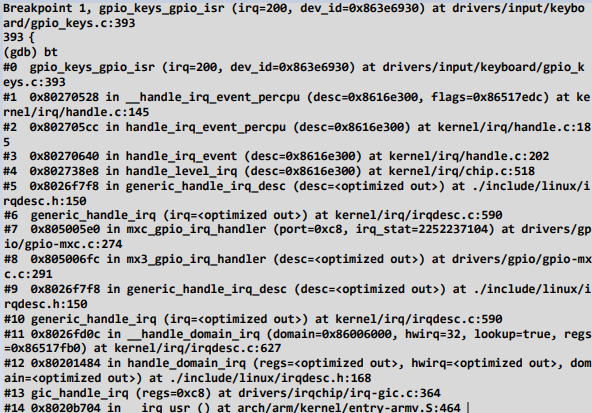
来看gpio_keys_gpio_isr是如何一层层调用上来的。从__handle_irq_event_percpu开始分析:(它在kernel\irq\handle.c中)
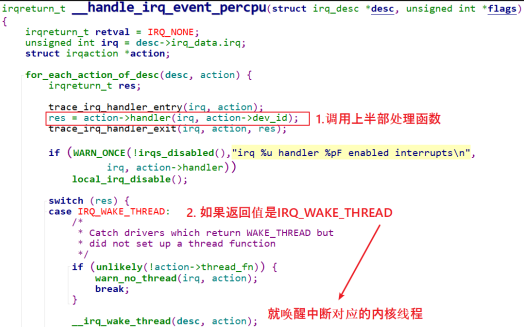
执行上半部提供的的handler函数。判断上半部返回值如果是IRQ_WAKE_THREAD,就唤醒中断线程处理函数。如果上半部返回值是IRQ_HANDLED,表示该中断无需线程化处理,直接退出。
__irq_wake_thread分析:(它在kernel\irq\handle.c中)
void __irq_wake_thread(struct irq_desc *desc, struct irqaction *action)
{
......
atomic_inc(&desc->threads_active);
wake_up_process(action->thread);
}
唤醒的是谁,就是action->thread,也就是对应前面kthread_create出来的irq_thread。
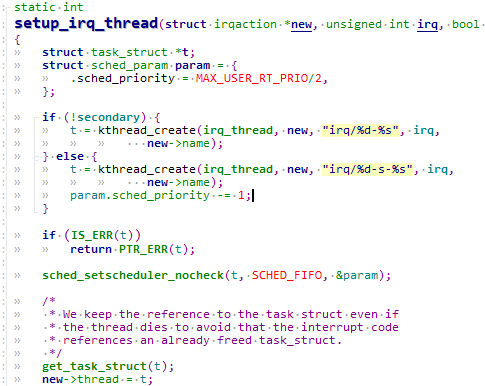
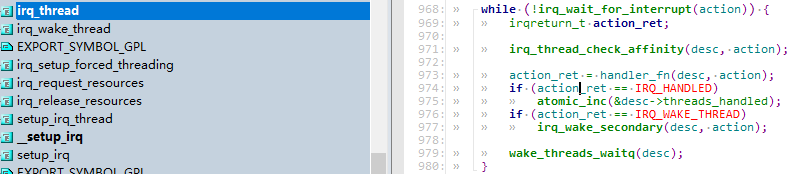
irq_thread函数分析:(kernel\irq\manage.c)平时irq_thread是处于休眠状态,不占用cpu资源。当被唤醒后,irq_thread进入唤醒状态调用handler_fn,也就是最终使用者预先设定的action->thread_fn。
/*
* Interrupt handler thread
*/
static int irq_thread(void *data)
{
struct callback_head on_exit_work;
struct irqaction *action = data;
struct irq_desc *desc = irq_to_desc(action->irq);
irqreturn_t (*handler_fn)(struct irq_desc *desc,
struct irqaction *action);
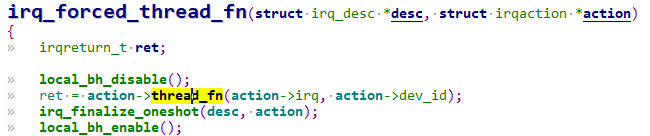
if (force_irqthreads && test_bit(IRQTF_FORCED_THREAD,
&action->thread_flags))
handler_fn = irq_forced_thread_fn;
else
handler_fn = irq_thread_fn;
init_task_work(&on_exit_work, irq_thread_dtor);
task_work_add(current, &on_exit_work, false);
irq_thread_check_affinity(desc, action);
while (!irq_wait_for_interrupt(action)) {
irqreturn_t action_ret;
irq_thread_check_affinity(desc, action);
action_ret = handler_fn(desc, action);
if (action_ret == IRQ_HANDLED)
atomic_inc(&desc->threads_handled);
if (action_ret == IRQ_WAKE_THREAD)
irq_wake_secondary(desc, action);
wake_threads_waitq(desc);
}
/*
* Interrupts explicitly requested as threaded interrupts want to be
* preemtible - many of them need to sleep and wait for slow busses to
* complete.
*/
static irqreturn_t irq_thread_fn(struct irq_desc *desc,
struct irqaction *action)
{
irqreturn_t ret;
ret = action->thread_fn(action->irq, action->dev_id);
irq_finalize_oneshot(desc, action);
return ret;
}