原理理解
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ie4y1f7XG/?spm_id_from=333.788&vd_source=f88ed35500cb30c7be9bbe418a5998ca
具体计算计算
https://blog.csdn.net/KYJL888/article/details/107222533
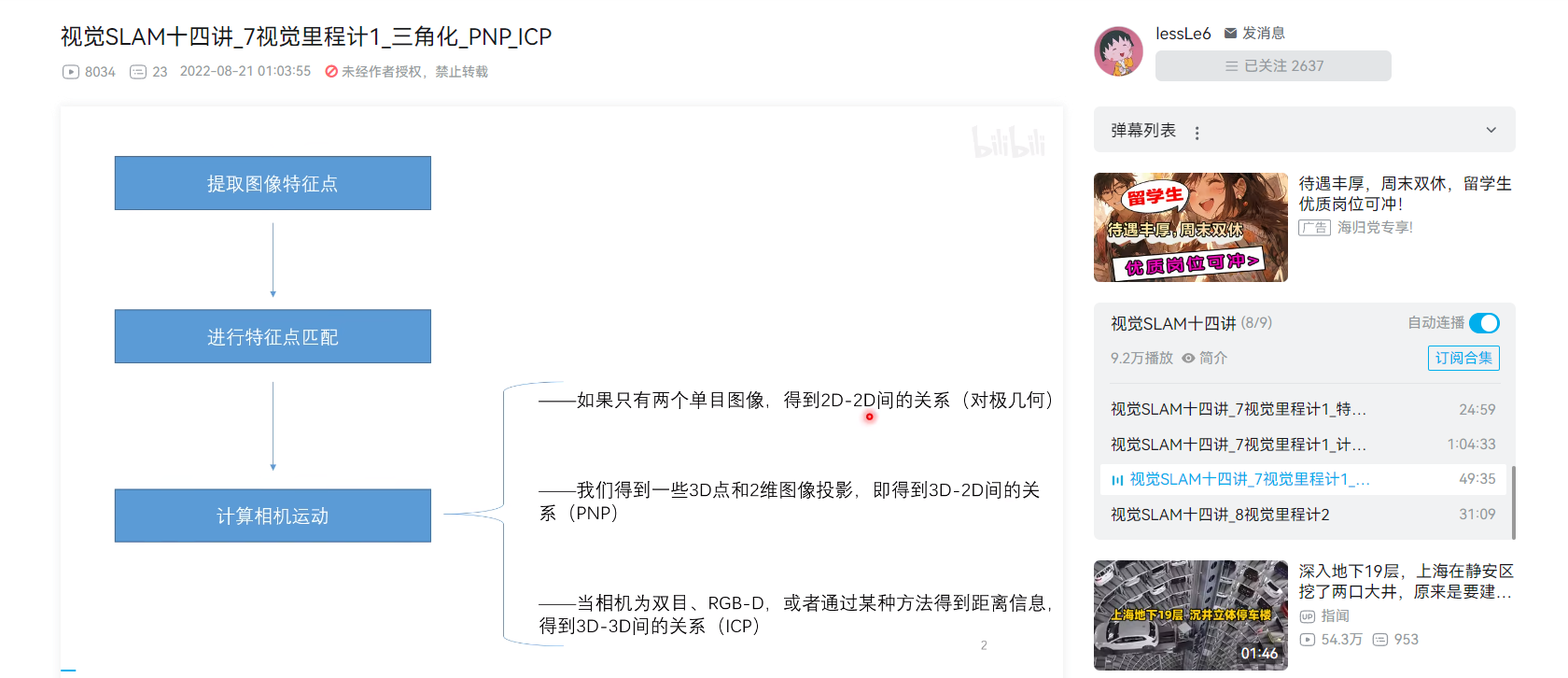
三角测量的目的是用来确定图片中某一个点的深度。为什么会有这样的需求呢?我们在前面的博客中提到了对极几何与单应变换。
在前面其实已经提到过了,在单目VO中,虽然我们可以通过本质矩阵与单应矩阵恢复出相机变换的位姿,但是这两种方法确定的位姿变换是具有尺度不确定性的。在双目vo中,我们会首先使用三角测量恢复出深度信息,再进行位姿估计。
1原理
其他测距方法
- 主动方法
- 结构光: 光已知空间方向的投影光线的集合称为结构光,结构光激光散斑通过投射具有高度伪随机性的激光散斑,会随着不同距离变换不同的图案,对三维空间直接标记,通过观察物体表面的散斑图案就可以判断其深度。
- ToF: 飞行时间法,通过连续发射光脉冲(一般是不可见光),到被观测物体上,然后接收从物体反射回去的光脉冲,通过探测光脉冲的往返飞行时间来计算被测物体距离。
- LIDAR: 激光雷达
- 使用深度学习构建神经网络对图像深度进行预测
单目测距
第一种思路

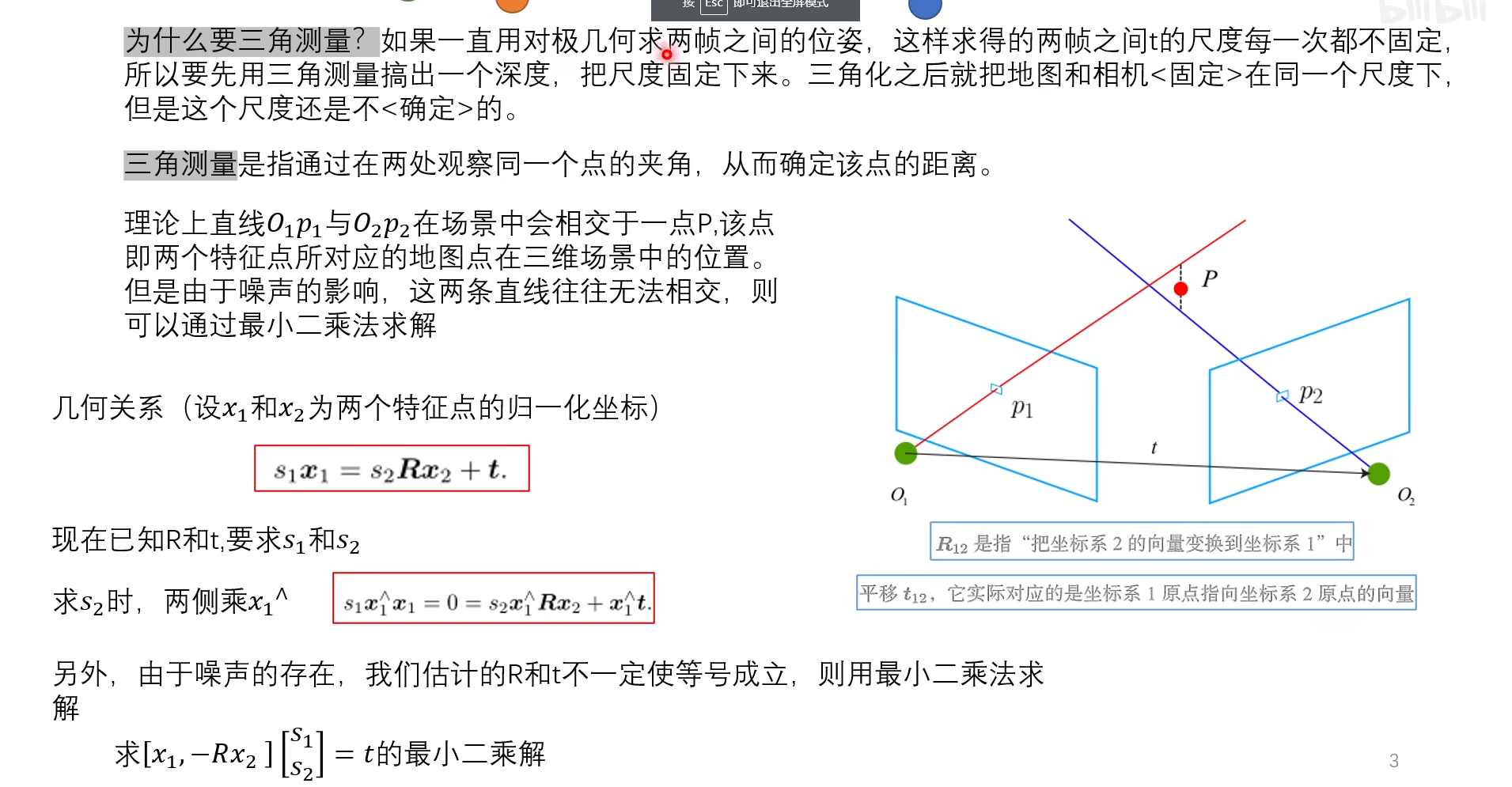
通过对极约束知道了 ,想要求解的是两个特征点的深度
。当然这两个深度是可以分开求的,如,先求
,那么对上式左乘一个
,得:
该式左侧为零,右侧可看成 的一个方程,可以根据它直接求得
。有了
,
也非常容易求出。于是,得到了两帧下的点的深度,确定了它们的空间坐标。由于噪声的存在,估得的
不一定精确使上式为零,所以常见的做法是求最小二乘解而不是零解。

代码实现(自己实现)
首先是上述思路的解法
bool depthFromTriangulation(
const SE3& T_search_ref,
const Vector3d& f_ref,
const Vector3d& f_cur,
double& depth)
{
Matrix<double,3,2> A;
A << T_search_ref.rotation_matrix()*f_ref, f_cur;
const Matrix2d AtA = A.transpose()*A;
if(AtA.determinant() < 0.000001)
return false;
const Vector2d depth2 = - AtA.inverse()*A.transpose()*T_search_ref.translation();
depth = fabs(depth2[0]);
return true;
}
第二种思路

自己实现的代码
// 用三角化计算深度
SE3 T_R_C = T_C_R.inverse();//T_C_R reference to current transformation matrix
Vector3d f_ref = px2cam( pt_ref );//参考帧的像素坐标转换到相机坐标系的坐标
f_ref.normalize();//参考帧上的点在相机坐标系下的归一化的坐标x_1
Vector3d f_curr = px2cam( pt_curr );//当前帧的像素坐标转换到相机坐标系的坐标
f_curr.normalize();//当前帧上的点在相机坐标系下的归一化的坐标x_2
// 方程
// d_ref * f_ref = d_cur * ( R_RC * f_cur ) + t_RC//d_ref=x_1,对应s_1x_1=s_2(R*x_2)+t
// => [ f_ref^T f_ref, -f_ref^T f_cur ] [d_ref] = [f_ref^T t]//s_1x_1^Tx_1=s_2x_1^Tx_2+x_1^Tt
// [ f_cur^T f_ref, -f_cur^T f_cur ] [d_cur] = [f_cur^T t]//s_2x_2^Tx_1=s_2x_2^Tx_2+x_2^Tt
// 二阶方程用克莱默法则求解并解之
Vector3d t = T_R_C.translation();//平移向量t
Vector3d f2 = T_R_C.rotation_matrix() * f_curr; //Rx_2
Vector2d b = Vector2d ( t.dot ( f_ref ), t.dot ( f2 ) );//tx_1,tRx_2
double A[4];
A[0] = f_ref.dot ( f_ref );//x_1*x_1
A[2] = f_ref.dot ( f2 );//x_1Rx_2
A[1] = -A[2];//-x_1Rx_2
A[3] = - f2.dot ( f2 );//-x_1Rx_2*x_1Rx_2
double d = A[0]*A[3]-A[1]*A[2];//
Vector2d lambdavec =
Vector2d ( A[3] * b ( 0,0 ) - A[1] * b ( 1,0 ),
-A[2] * b ( 0,0 ) + A[0] * b ( 1,0 )) /d;
Vector3d xm = lambdavec ( 0,0 ) * f_ref;
Vector3d xn = t + lambdavec ( 1,0 ) * f2;
Vector3d d_esti = ( xm+xn ) / 2.0; // 三角化算得的深度向量
double depth_estimation = d_esti.norm(); // 深度值
运用克莱姆法则可以很有效地解决以下方程组。
代码实现(使用opencv提供的接口)
void triangulation (
const vector< KeyPoint >& keypoint_1,
const vector< KeyPoint >& keypoint_2,
const std::vector< DMatch >& matches,
const Mat& R, const Mat& t,
vector< Point3d >& points )
{
//相机第一个位置处的位姿
Mat T1 = (Mat_<float> (3,4) <<
1,0,0,0,
0,1,0,0,
0,0,1,0);
//相机第二个位置处的位姿
Mat T2 = (Mat_<float> (3,4) <<
R.at<double>(0,0), R.at<double>(0,1), R.at<double>(0,2), t.at<double>(0,0),
R.at<double>(1,0), R.at<double>(1,1), R.at<double>(1,2), t.at<double>(1,0),
R.at<double>(2,0), R.at<double>(2,1), R.at<double>(2,2), t.at<double>(2,0)
);
// 相机内参
Mat K = ( Mat_<double> ( 3,3 ) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1 );
vector<Point2f> pts_1, pts_2;
for ( DMatch m:matches )
{
// 将像素坐标转换至相机平面坐标,为什么要这一步,上面推导中有讲
pts_1.push_back ( pixel2cam( keypoint_1[m.queryIdx].pt, K) );
pts_2.push_back ( pixel2cam( keypoint_2[m.trainIdx].pt, K) );
}
Mat pts_4d;
//opencv提供的三角测量函数
cv::triangulatePoints( T1, T2, pts_1, pts_2, pts_4d );
// 转换成非齐次坐标
for ( int i=0; i<pts_4d.cols; i++ )
{
Mat x = pts_4d.col(i);
x /= x.at<float>(3,0); // 归一化
Point3d p (
x.at<float>(0,0),
x.at<float>(1,0),
x.at<float>(2,0)
);
points.push_back( p );
}
}
Point2f pixel2cam ( const Point2d& p, const Mat& K )
{
return Point2f
(
( p.x - K.at<double>(0,2) ) / K.at<double>(0,0),
( p.y - K.at<double>(1,2) ) / K.at<double>(1,1)
);
}
第三种思路(最小二乘法求解深度)
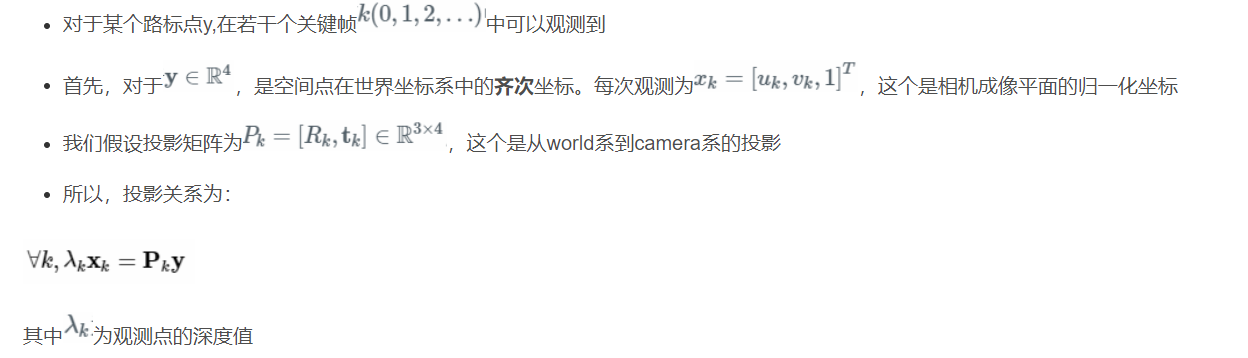


最小二乘求解

// vins中初始化sfm时根据一个三维点在两帧中的投影位置确定三维点位置
void GlobalSFM::triangulatePoint(Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 4> &Pose0, Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 4> &Pose1,
Vector2d &point0, Vector2d &point1, Vector3d &point_3d)
{
Matrix4d design_matrix = Matrix4d::Zero();
design_matrix.row(0) = point0[0] * Pose0.row(2) - Pose0.row(0);
design_matrix.row(1) = point0[1] * Pose0.row(2) - Pose0.row(1);
design_matrix.row(2) = point1[0] * Pose1.row(2) - Pose1.row(0);
design_matrix.row(3) = point1[1] * Pose1.row(2) - Pose1.row(1);
Vector4d triangulated_point;
triangulated_point =
design_matrix.jacobiSvd(Eigen::ComputeFullV).matrixV().rightCols<1>();
point_3d(0) = triangulated_point(0) / triangulated_point(3);
point_3d(1) = triangulated_point(1) / triangulated_point(3);
point_3d(2) = triangulated_point(2) / triangulated_point(3);
}
用概率方法更新矫正深度值
从上述讲述中,我们已经知道通过两帧图像的匹配点,可以得到一个等式,可以计算出这一点的深度值,所以,如果有n副图像进行匹配,那我们会得到n-1个等式。此时我们就可以计算出这一点的n-1个空间位置的测量值。
好的测量值是符合正态分布的,噪声符合均匀分布,此时我们可以通过一些概率的方法对多次测量结果进行融合,得到更鲁棒的结果。
-
在SVO中,使用贝叶斯方法(最大后验概率)进行更新
-
在LSD中,使用卡尔曼滤波进行深度测量值的滤波