Rethinking Point Cloud Registration as Masking and Reconstruction
2023 ICCV
*Guangyan Chen, Meiling Wang, Li Yuan, Yi Yang, Yufeng Yue*; Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2023, pp. 17717-17727
- paper: Rethinking Point Cloud Registration as Masking and Reconstruction (thecvf.com)
- code: CGuangyan-BIT/MRA (github.com)

这论文标题就很吸引人,但是研读下来作者只是想用MAE的结构,想要预测出对齐后点云,然后提高跨点云间配准点的特征描述一致性,辅助特征提取网络训练
Abstract
文章核心立题: the invisible parts of each point cloud can serve as inherent masks, whereas the aligned point cloud pair can be treated as the reconstruction objective .
- 将点云配准视为masking and Reconstruction过程,以Point-MAE为基本思想,提出MRA(the Masked Reconstrction Auxiliary Network)。
- MRA可以很容易的嵌入到其他方法中further improve registration accuracy
- 基于MRA,提出一个novel、基于standard transformer-baesed method,MRT(the Masked Reconstruction Transformer)。
encode feauters -> inference the contextual features and overall structures of point cloud pairs -> the deviation correction modul to correct the spatial deviations in the putative corresponding point pairs
Description
- input:
- source point cloud \(X = \{x_1, x_2, …,x_M\} \subseteq \mathbb{R}^3\)
- target point cloud \(Y = \{y_1, y_2, …, y_N\} \subseteq \mathbb{R}^3\)
- output: the rigid transformation \(\{\hat{R} \in SO(3), \hat{t} \in \mathbb{R}^3\}\) that align the source point cloud with the target point cloud.
(MRT是用来提特征的,应该也是dense description,MRA是用来辅助训练MRT的。)

- MRT step: input point cloud pair \(X\) , \(Y\) 利用KPConv进行dense description,得到superpoints \([\widetilde{X}:F^{\widetilde{X}}]\) , \([\widetilde{Y}:F^{\widetilde{Y}}]\) 。然后其中的特征描述 \(F\) 经过Transformer Encoder Module提取contextual information and overall structure 重构每个特征描述 \(F^{\widetilde{X}}\) , \(F^{\widetilde{Y}}\) 。
- auxiliary network step:two module is parallel used to training MRT
- MRA: the MRA separately receives the encoded features of each point cloud and predicts the other aligned point cloud, reconstructing the complete point cloud.
- Registration network: predict point corrrespondences \(\hat{y},\ \hat{x}\) and overlap scores \(\hat{o}^{\widetilde{X}},\ \hat{o}^{\widetilde{Y}}\) in the Deviation Correction module, then use Wighted Procrustes module to regress the transformaion.
MRT Step
- KPConv network:
- input downsampled point clouds: \(X \in \mathbb{M \times 3}\), \(Y \in \mathbb{N \times 3}\)
- obtain superpoints and features: \([\widetilde{X} \in \mathbb{M^{'} \times 3}:F^{\widetilde{X}}\in \mathbb{R}^{M^{'} \times D}]\) , \([\widetilde{Y} \in \mathbb{M^{'} \times 3}:F^{\widetilde{Y}}\in \mathbb{R}^{N^{'} \times D}]\)
- Transformer Encoder:
- input superpoints and features into \(L_e\) - layer transformer encoder( cross-attention and sinusoidal positional encodings )
- output the encoded features \(\mathcal{F}^{\widetilde{X}}\) , \(\mathcal{F}^{\widetilde{Y}}\) .
cross-attention有助于两个point cloud提取一致性特征。
MRA Step

一个纯MAE style的网络结构, mask token 代表对齐后相应的point cloud patch表示。输入对齐前的point cloud patch,相应的token,根据GT rigid transformation信息生成的position embedding,和mask token,输出预测的对齐后point cloud patch,再与GT 生成的对齐结果做chamfer Loss。
虽然表面上这里有很多与变换相关的操作,但是细细思考会发现这里所有的变换信息都建立在GT上,所以我倾向于这里与MRT里的cross-attention一起提高了配准点对在特征上的表示一致性,当然肯定对特征表示的语义完整性有提高。
- input -> MRT outputs: super points pair and corresponding features: \([\widetilde{X} \in \mathbb{M^{'} \times 3}:\mathcal{F}^{\widetilde{X}}\in \mathbb{R}^{M^{'} \times D}]\) , \([\widetilde{Y} \in \mathbb{M^{'} \times 3}:\mathcal{F}^{\widetilde{Y}}\in \mathbb{R}^{N^{'} \times D}]\) 。
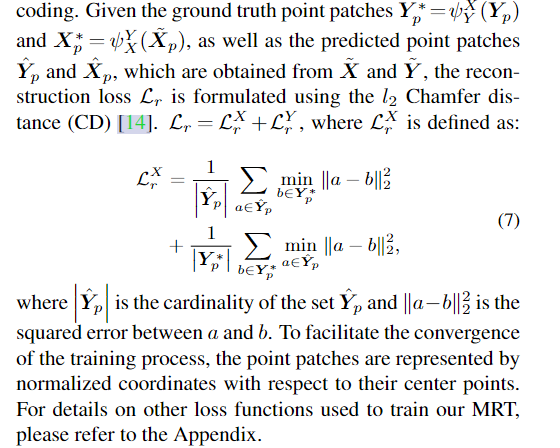
- output: chamfer L2 loss between predicted aligned point cloud patch and ground truth aligned point cloud.
步骤:
- use FPS to extract center points \(\widetilde{X}_c\) , \(\widetilde{Y}_c\) in super points. use KNN to generate point cloud patch; get the tokens \(T^{\widetilde{X}}\) , \(T^{\widetilde{Y}}\) by composing the encoded features \(\mathcal{F}^{\widetilde{X}}\) , \(\mathcal{F}^{\widetilde{Y}}\) .use mask token \(T^{\widetilde{X}}_m ∈ \mathbb{R}^{g×D}\), \(T^{\widetilde{Y}}_m ∈ \mathbb{R}^{g×D}\) to correspond the aligned point cloud patch in the output of decoder.
- use groud truth transformation from \(Y\) to \(X\), and from \(X\) to \(Y\) to generate the position embedding for each layer in decoder.
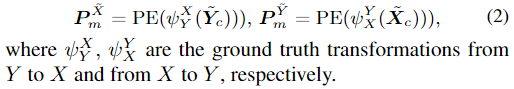
- self-attention and two-layer-FC transfromer decoder to reconstruct the mask token to represent the token of aligned point cloud patch.
- use two-layer MLP with two FC and ReLu to predict the aligned point cloud patch responding to the decoded mask tokens.
- chamfer loss: the ground truch aligned point cloud patch and the predicted one.
coarse registration step
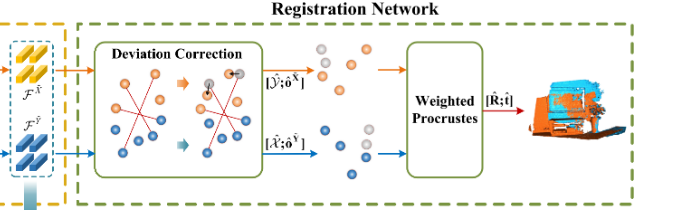
由于MRT提取的特征强聚合(cross-attention的缘故)了跨点云间的语义信息,根据余弦相似性计算soft corresponding wighted,加权求和得到correspodence point pair,在拼接特征以及对应点对的坐标用MLP拟合加权求和得到的点对坐标与真实位置的偏差。构筑更鲁棒的匹配结果。(这种预测bias的方式经常见)。之后使用weighted procustes模块预测rigid transformaion。
我更想倾向于这样描述:单纯加权求和得到的坐标结果大概率与真实坐标有所偏差,引入另一个可变分量来对加权后的预测结果做调控,能够使得预测结果更加鲁棒,更加稳定,甚至能更加精确,从而在现象上,显示为偏差值。并且这里的余弦相似性从一定程度上可以提高非配准点之前的差异性。
- input: the feature \(\mathcal{F}^{\widetilde{X}}\) , \(\mathcal{F}^{\widetilde{Y}}\) extracted by MRT
- output: predicted rigid transformation: \([\hat{R}; \hat{t}]\)
步骤:
- predicted the corresponding points \(\mathcal{Y}\) for each super point \(\widetilde{X}\) :

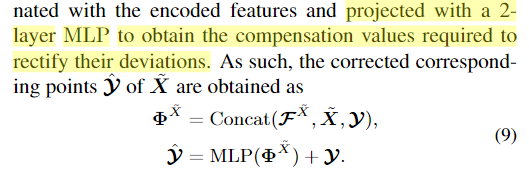
- use features and MLP predict the deviations which needs to add to the predicted corresponding points:
- predict the overlap scores for each point. which indicatee probabilities of ponts lying in the overlap regions:

- use the wighted procrustes to predict the rigid transformation and compute the loss with GT.
Experiment
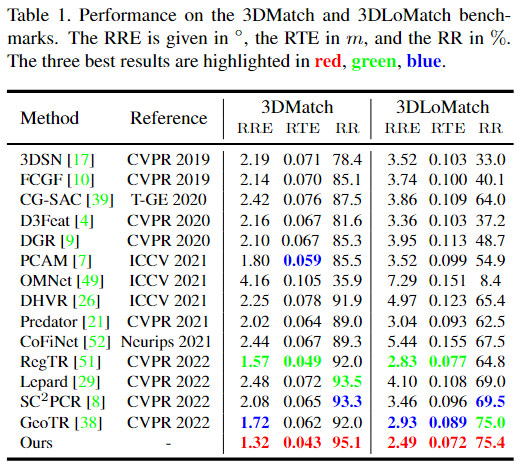
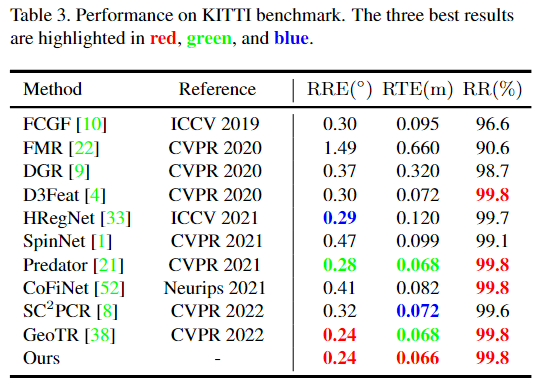
MRA的plug-and play,确实可以:
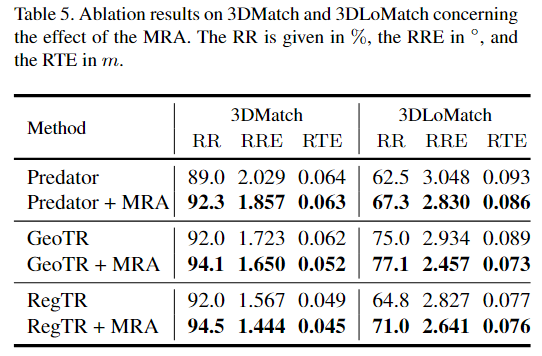
- Reconstruction Registration Rethinking Masking 论文reconstruction registration rethinking masking masking rethinking diffusion masking stable convolutional segmentation rethinking attention transformer rethinking improving encoding reconstruction registration rethinking inference retrieval faithful reconstruction comparison algorithms evaluation